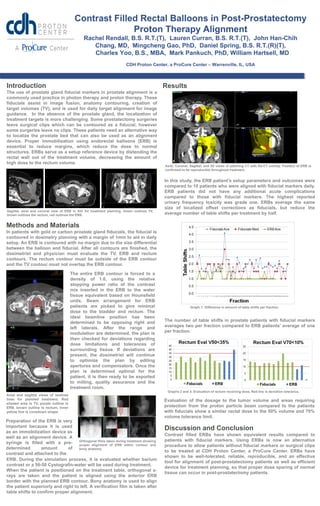
Poster ERB Final
- 1. 1 Contrast Filled Rectal Balloons in Post-Prostatectomy Proton Therapy Alignment Rachel Rendall, B.S. R.T.(T), Lauren Curran, B.S. R.T.(T), John Han-Chih Chang, MD, Mingcheng Gao, PhD, Daniel Spring, B.S. R.T.(R)(T), Charles Yoo, B.S., MBA, Mark Pankuch, PhD, William Hartsell, MD CDH Proton Center, a ProCure Center – Warrenville, IL, USA Sagittal, axial and coronal view of ERB in XIO for treatment planning. Green outlines TV, brown outlines the rectum, red outlines the ERB. Axial, Coronal, Sagittal, and 3D views of planning CT with Re-CT overlay. Position of ERB is confirmed to be reproducible throughout treatment. Orthogonal films taken during treatment showing proper alignment of ERB within contour and bony anatomy. Graph 1: Difference in amount of table shifts per fraction. Graphs 2 and 3: Evaluation of rectum receiving dose. Red line is deviation tolerance. Introduction The use of prostate gland fiducial markers in prostate alignment is a commonly used practice in photon therapy and proton therapy. These fiducials assist in image fusion, anatomy contouring, creation of target volumes (TV), and is used for daily target alignment for image guidance. In the absence of the prostate gland, the localization of treatment targets is more challenging. Some prostatectomy surgeries leave surgical clips which can be contoured as a fiducial, however some surgeries leave no clips. These patients need an alternative way to localize the prostate bed that can also be used as an alignment device. Proper immobilization using endorectal balloons (ERB) is essential to reduce margins, which reduce the dose to normal structures. ERBs serve as a setup reference device by distending the rectal wall out of the treatment volume, decreasing the amount of high dose to the rectum volume. Methods and Materials In patients with gold or carbon prostate gland fiducials, the fiducial is contoured in dosimetry planning with a margin of 1mm to aid in daily setup. An ERB is contoured with no margin due to the size differential between the balloon and fiducial. After all contours are finished, the dosimetrist and physician must evaluate the TV, ERB and rectum contours. The rectum contour must be outside of the ERB contour and the TV contour must not overlap the ERB contour. Results Discussion and Conclusion Contrast filled ERBs have shown equivalent results compared to patients with fiducial markers. Using ERBs is now an alternative procedure to allow patients without fiducial markers or surgical clips to be treated at CDH Proton Center, a ProCure Center. ERBs have shown to be well-tolerated, reliable, reproducible, and an effective tool for alignment of post-prostatectomy patients as well as efficient device for treatment planning, so that proper dose sparing of normal tissue can occur in post-prostatectomy patients. The entire ERB contour is forced to a density of 1.0, using the relative stopping power ratio of the contrast mix inserted in the ERB to the water tissue equivalent based on Hounsfield units. Beam arrangement for ERB patients are picked to give minimal dose to the bladder and rectum. The ideal beamline position has been determined to be opposing right and left laterals. After the range and modulation are determined, the plan is then checked for deviations regarding dose limitations and tolerances of surrounding tissue. If deviations are present, the dosimetrist will continue to optimize the plan by editing apertures and compensators. Once the plan is determined optimal for the patient, it is then ready to be exported to milling, quality assurance and the treatment room. Preparation of the ERB is very important because it is used as an immobilization device as well as an alignment device. A syringe is filled with a pre- determined amount of contrast and attached to the ERB. During the simulation process, it is evaluated whether barium contrast or a 50-50 Cystografin-water will be used during treatment. When the patient is positioned on the treatment table, orthogonal x- rays are taken and the patient is aligned using the anterior ERB border with the planned ERB contour. Bony anatomy is used to align the patient superiorly and right to left. A verification film is taken after table shifts to confirm proper alignment. Axial and sagittal views of isodose lines for planned treatment. Red shaded area is TV, purple outline is ERB, brown outline is rectum, inner yellow line is conedown shape. Evaluation of the dosage to the tumor volume and areas requiring protection from the proton particle beam compared to the patients with fiducials show a similar rectal dose to the 50% volume and 70% volume tolerance limit. The number of table shifts in prostate patients with fiducial markers averages two per fraction compared to ERB patients’ average of one per fraction. In this study, the ERB patient’s setup parameters and outcomes were compared to 10 patients who were aligned with fiducial markers daily. ERB patients did not have any additional acute complications compared to those with fiducial markers. The highest reported urinary frequency toxicity was grade one. ERBs average the same size of localized offset corrections as fiducials, but reduce the average number of table shifts per treatment by half.