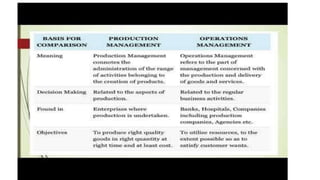
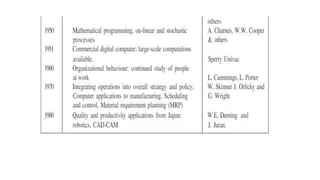
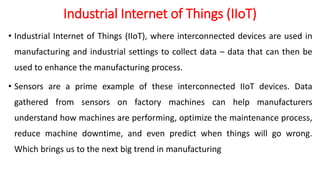
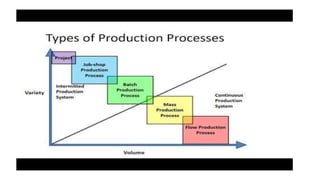
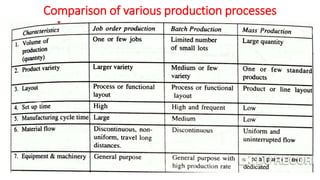
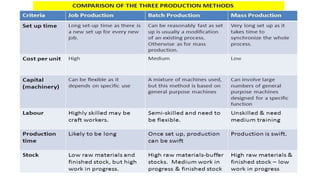
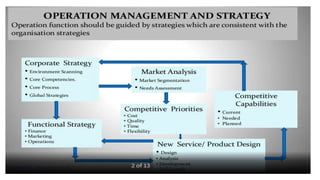
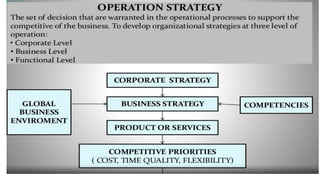
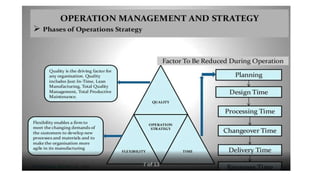
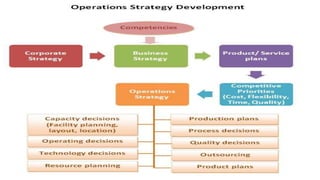
Production and operations management deals with managing the processes that transform inputs into finished goods and services. It aims to maximize efficiency and quality while minimizing costs. Key functions include production planning and control, scheduling, and quality control. Recent trends in manufacturing include increased automation through robotics, predictive maintenance using sensor data, digital twins for simulation, and smart, sustainable product design. The differences between production management and operations management relate mainly to their outputs - production focuses on goods, operations includes services. Both are important for meeting organizational objectives.