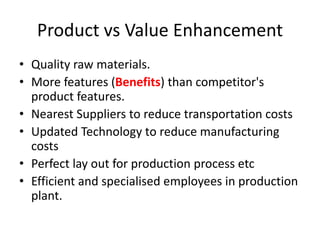
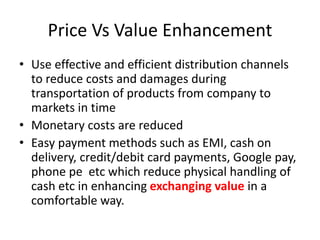
This document discusses marketing principles including the 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) and the value delivery process. It explains that the 4Ps fulfill customer needs but value is relative based on competitors. It then defines each P and how companies can enhance value at each step through approaches like using quality materials, efficient distribution channels, and widely available products. Communicating additional benefits beyond the product is key to promoting value. The marketing environment that affects strategy is also summarized, including micro factors like suppliers, customers and competitors, and macro external forces.