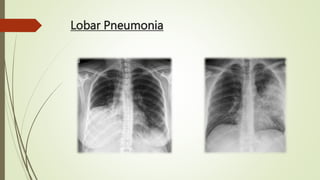
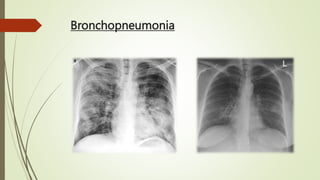
Pneumonia is an acute infectious respiratory disease characterized by pulmonary shadowing, with types including lobar and bronchopneumonia. It can be categorized as community-acquired or hospital-acquired pneumonia, identified by clinical features, risk factors, and specific pathogens. Diagnosis involves a variety of investigations, and management typically includes antibiotics and supportive care, with prognosis varying significantly based on severity.