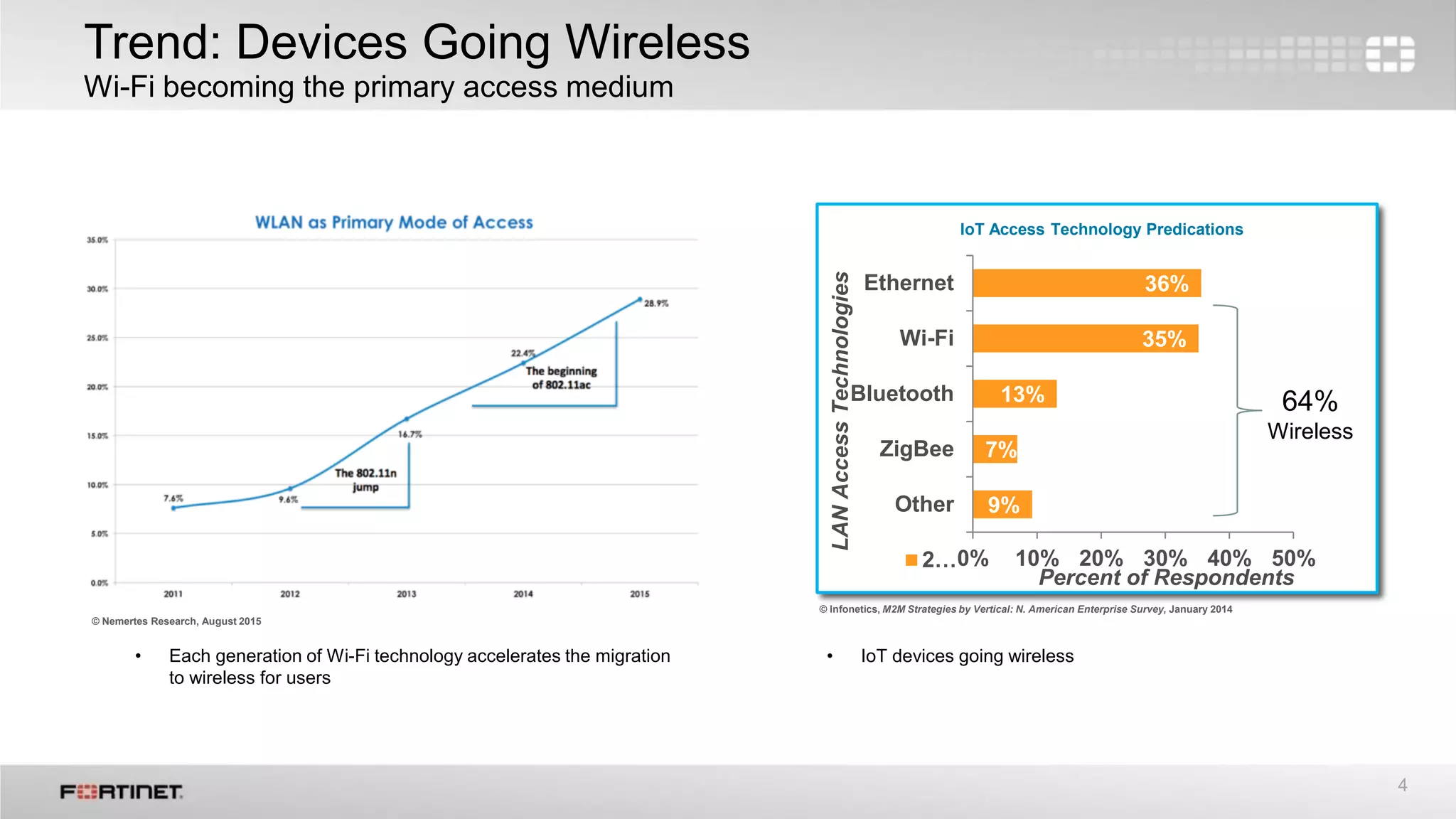
Fortinet provides secure wireless infrastructure solutions that are flexible and scalable for mobile environments. Their wireless offerings include access points and management capabilities. Fortinet wireless infrastructure allows for channel planning flexibility, low latency roaming, and separation of wireless access and security purchases. Key features include virtual cell technology, zero-handoff roaming, airtime fairness, and options for single channel, channel layering or striping to optimize performance.