This document discusses the role of chronic inflammation in cardiovascular diseases related to atherosclerosis. It notes that atherosclerosis is a chronic non-communicable disease involving the retention and deposition of lipids in artery walls. Chronic inflammation and autoimmune processes are involved in atherosclerosis. Diet and other lifestyle factors like smoking and physical inactivity can promote chronic inflammation and accelerate the development of atherosclerosis. Anti-inflammatory diets high in whole foods, omega-3 fatty acids, and spices are recommended to reduce inflammation and cardiovascular risk.






















![Alois Jungbauer , Svjetlana Medjakovic
Anti-inflammatory properties of culinary herbs and spices that ameliorate the effects of metabolic syndrome
Maturitas Volume 71, Issue 3 2012 227 - 239
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.12.009
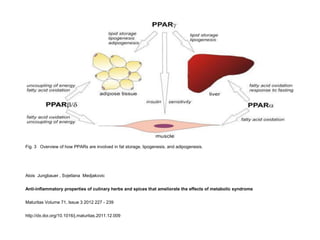
Fig. 1 Schematic overview of how metabolic syndrome develops from adipose tissue <ce:cross-ref refid="bib0035"> [7]</ce:cross-
ref> .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plemost2013nice-130416165919-phpapp02/85/Regime-anti-inflammatoire-et-atherome-26-320.jpg)