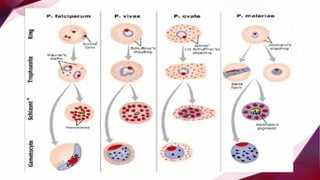
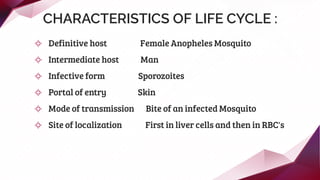
This document provides information about Plasmodium, the protozoan parasite that causes malaria. It discusses the key topics of the morphology, life cycle, transmission, pathogenesis and clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of malaria. Some important points covered are that Plasmodium has a life cycle that involves both humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes as hosts, being transmitted via the mosquito's bite. It causes disease by infecting and destroying red blood cells. The four main species that infect humans are P. vivax, P. falciparum, P. malariae, and P. ovale, with P. vivax and P. falciparum being most common in India.