The document discusses various techniques for penetration testing and attacking web applications using Ruby tools and libraries. It provides examples of using tools like Anemone for crawling sites, Casper for observing browser requests, Enchant for directory brute forcing, and Ciphersurfer for evaluating SSL configurations. The document encourages attackers to change their mindset and look for vulnerabilities from the perspective of an attacker rather than a developer.







![Leverage your attack surface
$ gem install links
$ links -r http://www.yourtarget.com
# TESTING: SPIDERS, ROBOTS, AND CRAWLERS (OWASP-IG-001)
def self.robots(site, only_disallow=true)
if (! site.start_with? 'http://') and (! site.start_with? 'https://')
site = 'http://'+site
end
list = []
begin
res=Net::HTTP.get_response(URI(site+'/robots.txt'))
if (res.code != "200")
return []
end
“Just a bunch of ruby loc res.body.split("n").each do |line|
away...” if only_disallow
if (line.downcase.start_with?('disallow'))
list << line.split(":")[1].strip.chomp
end
else
if (line.downcase.start_with?('allow') or line.downcase.start_with?('disallow'))
list << line.split(":")[1].strip.chomp
end
end
end
rescue
return []
end
list
end RubyDay IT, Milan, 15 June
9
2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pickinggemrubyforpenetrationtesters-120627072257-phpapp02/85/Picking-gem-ruby-for-penetration-testers-9-320.jpg)



![Build a transparent
module Casper
class Proxy < WEBrick::HTTPProxyServer
attr_reader :req_count
attr_reader :hosts
Extending
def initialize(config={})
@req_count = 0
@hosts=[]
WEBRick config[:Port] ||= 8080
config[:AccessLog] = []
config[:ProxyContentHandler] = Proc.new do |req, res|
log_requests(req, res)
end
super(config)
end
private
def log_requests(req, res)
$stdout.puts "[#{Time.now}] #{req.request_line.chomp}n"
if @hosts.index(req.host).nil?
@hosts << req.host
end Make the
business
inc_req_count
end
def inc_req_count
@req_count += 1
end
RubyDay IT, Milan, 15 June
14
2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pickinggemrubyforpenetrationtesters-120627072257-phpapp02/85/Picking-gem-ruby-for-penetration-testers-14-320.jpg)







![Check for backup
Crawl the web site and
append file extension to
your GETs
require 'anemone'
require 'httpclient'
h=HTTPClient.new()
Anemone.crawl(ARGV[0]) do |anemone|
anemone.on_every_page do |page|
response = h.get(page.url)
puts "Original: #{page.url}: #{response.code}"
response = h.get(page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat(".bak"))
puts "BAK: #{page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat(".bak")}: #{response.code}"
response = h.get(page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat(".old"))
puts "OLD: #{page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat(".old")}: #{response.code}"
response = h.get(page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat("~"))
puts "~: #{page.url.to_s.split(";")[0].concat("~")}: #{response.code}"
end
end
RubyDay IT, Milan, 15 June
22
2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pickinggemrubyforpenetrationtesters-120627072257-phpapp02/85/Picking-gem-ruby-for-penetration-testers-22-320.jpg)


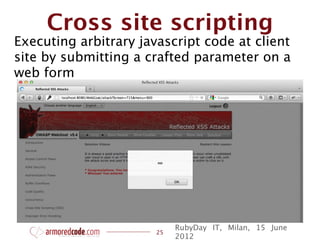
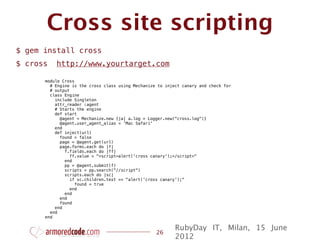
![Cross site scripting
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
$LOAD_PATH.unshift(File.expand_path(File.dirname(__FILE__) + '/../lib'))
require 'mechanize'
require 'ap'
require 'logger'
require 'cross'
host = Cross::Host.new(ARGV[0])
ap "cross " + Cross::Version.version[:string] + " (C) 2011 - thesp0nge"
ap "target: " + host.host
engine = Cross::Engine.instance
engine.start
if engine.inject(ARGV[0])
ap "Canary found in output page. Suspected XSS"
end
It doesn’t work with iframe
apps :-(
RubyDay IT, Milan, 15 June
27
2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pickinggemrubyforpenetrationtesters-120627072257-phpapp02/85/Picking-gem-ruby-for-penetration-testers-27-320.jpg)




