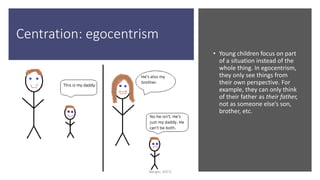
Piaget's theory outlines four obstacles to logical thinking in the preoperational stage of development from ages 2 to 6: centration, where children focus on parts rather than wholes from their own perspective; focus on appearance, judging based on outward characteristics alone; static reasoning, believing things cannot change from their current state; and irreversibility, thinking changes cannot be undone once made. Examples are provided for each obstacle.