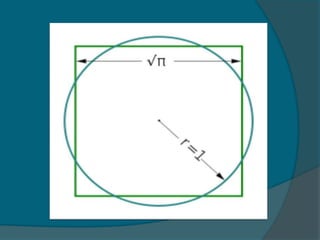
This document defines pi and provides a brief history of approximations of pi in ancient civilizations. It discusses pi's definition as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. Approximations of pi are given, including decimal, binary, hexadecimal, and sexagesimal representations. Ancient Egyptians and Babylonians approximated pi around 1900 BC. In India around 600 BC, pi was approximated to (9785/5568)2. The document also notes that the dimensions of structures like the Great Pyramid of Giza and King Solomon's temple suggest approximations of pi in ancient times.