PHP is a widely-used open source scripting language for web development that was originally created in 1995. PHP code is embedded within HTML code and executed server-side to produce dynamic web pages. Some key features of PHP include that it is free, cross-platform, and can connect to databases like MySQL. PHP code is delimited within tags and can include conditional logic, loops, functions, and object-oriented programming.














![Session Variables
● Not automatically created
● Script needs to start session using session_start()
● Data stored/accessed via superglobal array $_SESSION
● Data can be accessed from any PHP script during the session
● session_start(); $_SESSION['yourName'] = "Paul";
● print("Hello $_SESSION['yourName']");
● Destroying a Session: unset($_SESSION['views']) And session_destroy()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-17-320.jpg)


![How Create a Connection
● mysql_connect
● mysql_connect -- Open a connection to a MySQL Server
● resource mysql_connect ( [string server [, string username [, string password
[, bool new_link [, int client_flags]]]]])
● mysql_connect() establishes a connection to a MySQL server. The following
defaults are assumed for missing optional parameters: server =
'localhost:3306', username = name of the user that owns the server process
and password = empty password.
● The server parameter can also include a port number. e.g. "hostname:port"
or a path to a local socket e.g. ":/path/to/socket" for the localhost.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-20-320.jpg)
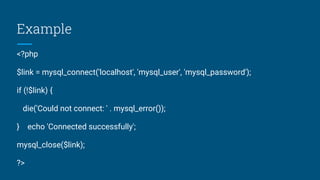
![How to close connection
● Mysql_close: mysql_close -- Close MySQL connection
● Description:
● bool mysql_close ( [resource link_identifier])
● Returns TRUE on success or FALSE on failure.
● mysql_close() closes the connection to the MySQL server that's associated
with the specified link identifier. If link_identifier isn't specified, the last
opened link is used.
● Using mysql_close() isn't usually necessary, as non-persistent open links are
automatically closed at the end of the script's execution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-22-320.jpg)
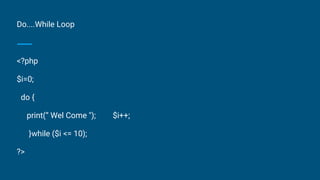
![How to execute query in php
● Mysql_query (PHP 3, PHP 4 )
● mysql_query -- Send a MySQL query
● Description: resource mysql_query ( string query [, resource link_identifier])
● Query Types: Select, Insert, Update, Delete
● mysql_query() sends a query to the currently active database on the server
that's associated with the specified link identifier. If link_identifier isn't
specified, the last opened link is assumed. If no link is open, the function tries
to establish a link as if mysql_connect() was called with no arguments, and
use it. The result of the query is buffered.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-23-320.jpg)



![Mysql_fetch_array
● Mysql_fetch_array (PHP 3, PHP 4 )
● mysql_fetch_array -- Fetch a result row as an associative array, a numeric
array, or both.
● Syntax: array mysql_fetch_array ( resource result [, int result_type])
Returns an array that corresponds to the fetched row, or FALSE if there are
no more rows.
● mysql_fetch_array() is an extended version of mysql_fetch_row(). In addition
to storing the data in the numeric indices of the result array, it also stores
the data in associative indices, using the field names as keys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-27-320.jpg)



![Defining PHP Classes
<?php
class phpClass {
var $var1;
var $var2 = "constant string";
function myfunc ($arg1, $arg2) { [..]
} [..] }
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200117164903/85/Php-31-320.jpg)



