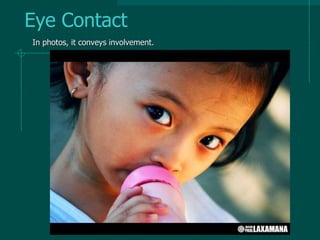
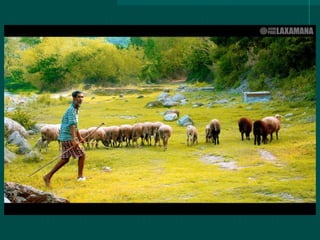
This document provides an overview of photojournalism, including its definition as using visual language to convey honest reports through photographs. It discusses the difference between photography and photojournalism, with photojournalists focusing on capturing verbs or actions. The rest of the document outlines important technical and compositional considerations for photojournalism, such as proper focus, balance, and capturing moments. It also discusses elements like lines, shapes, perspective, lighting, and framing that photojournalists should consider in their work.