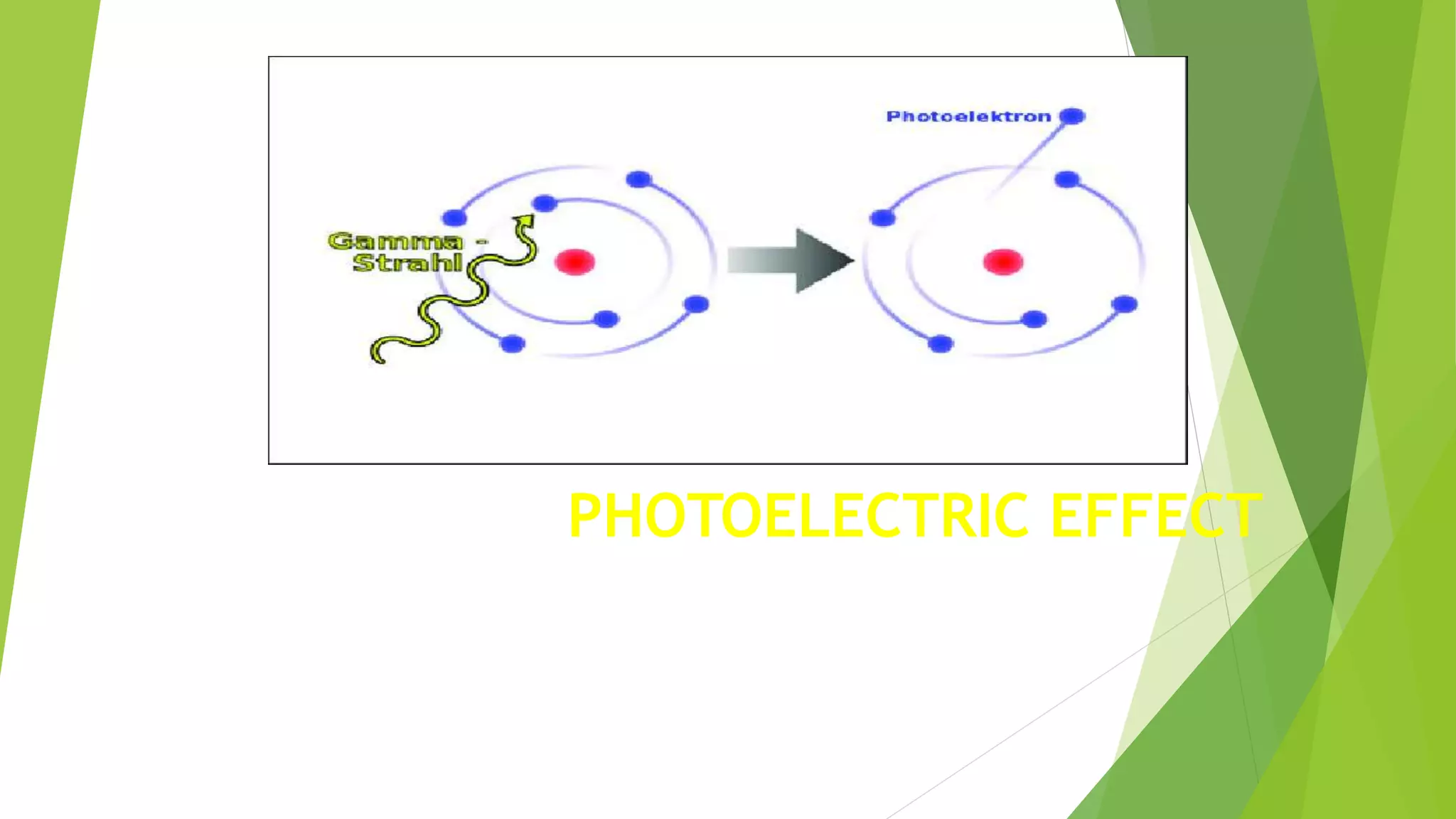
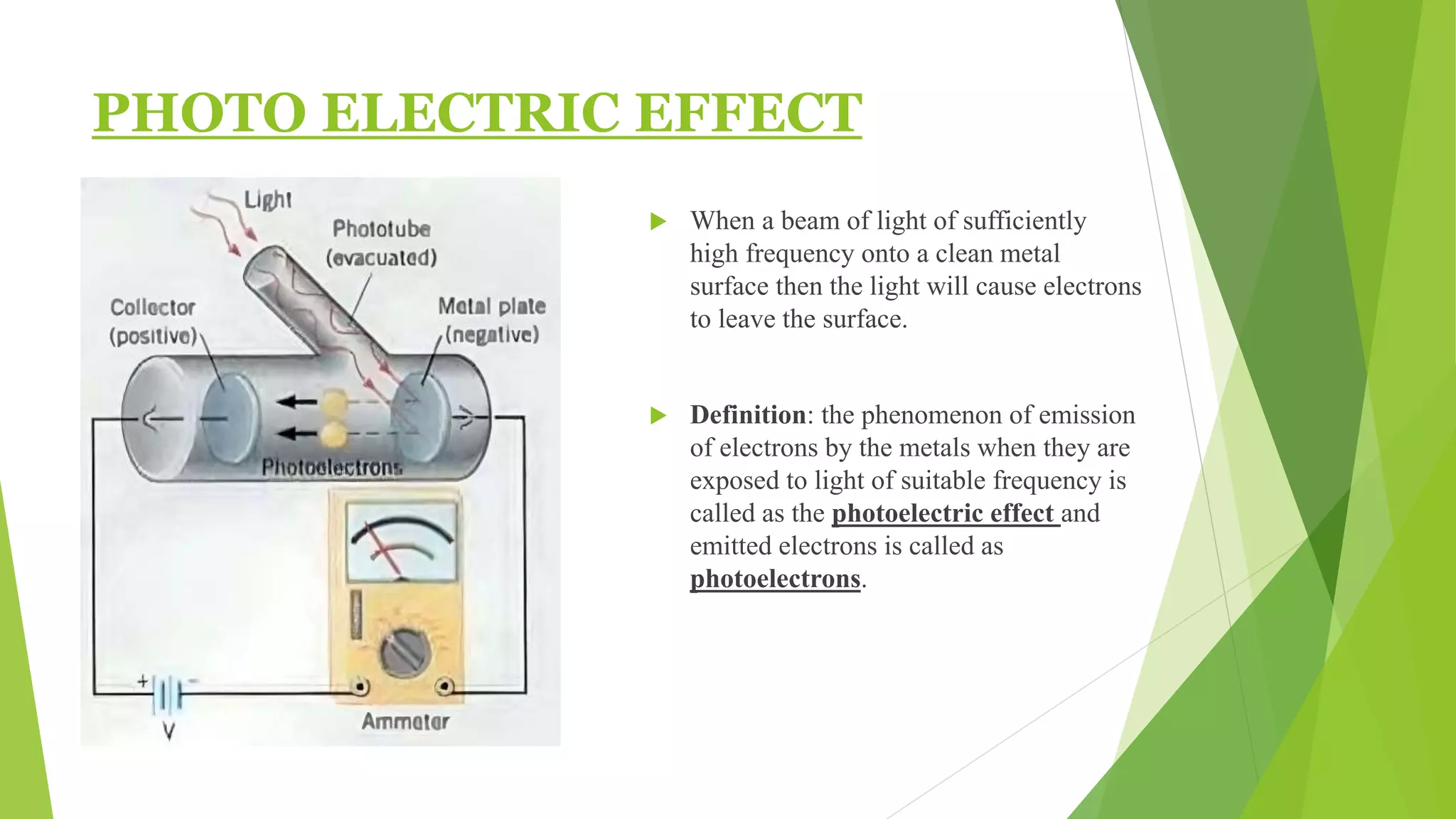
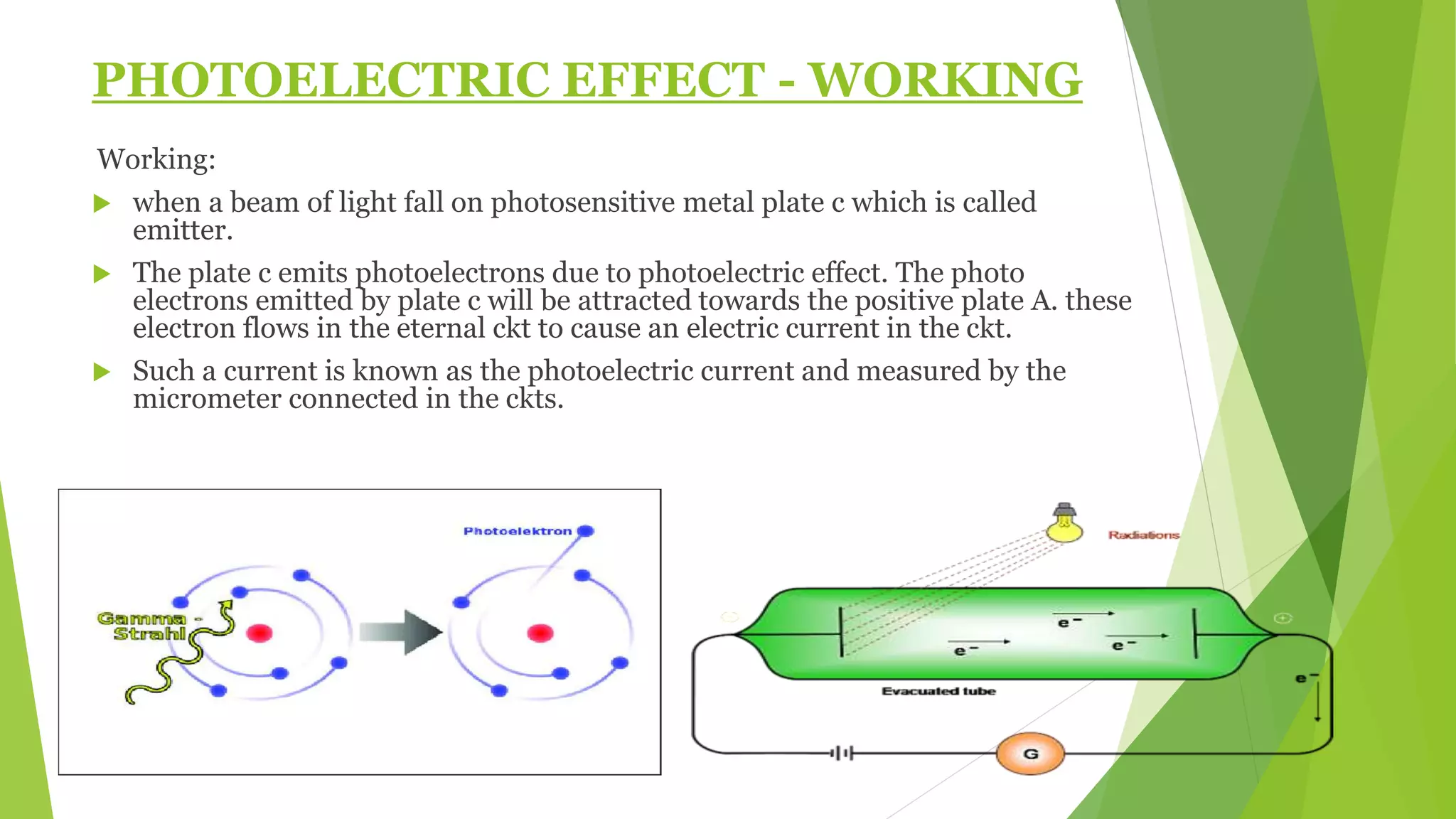
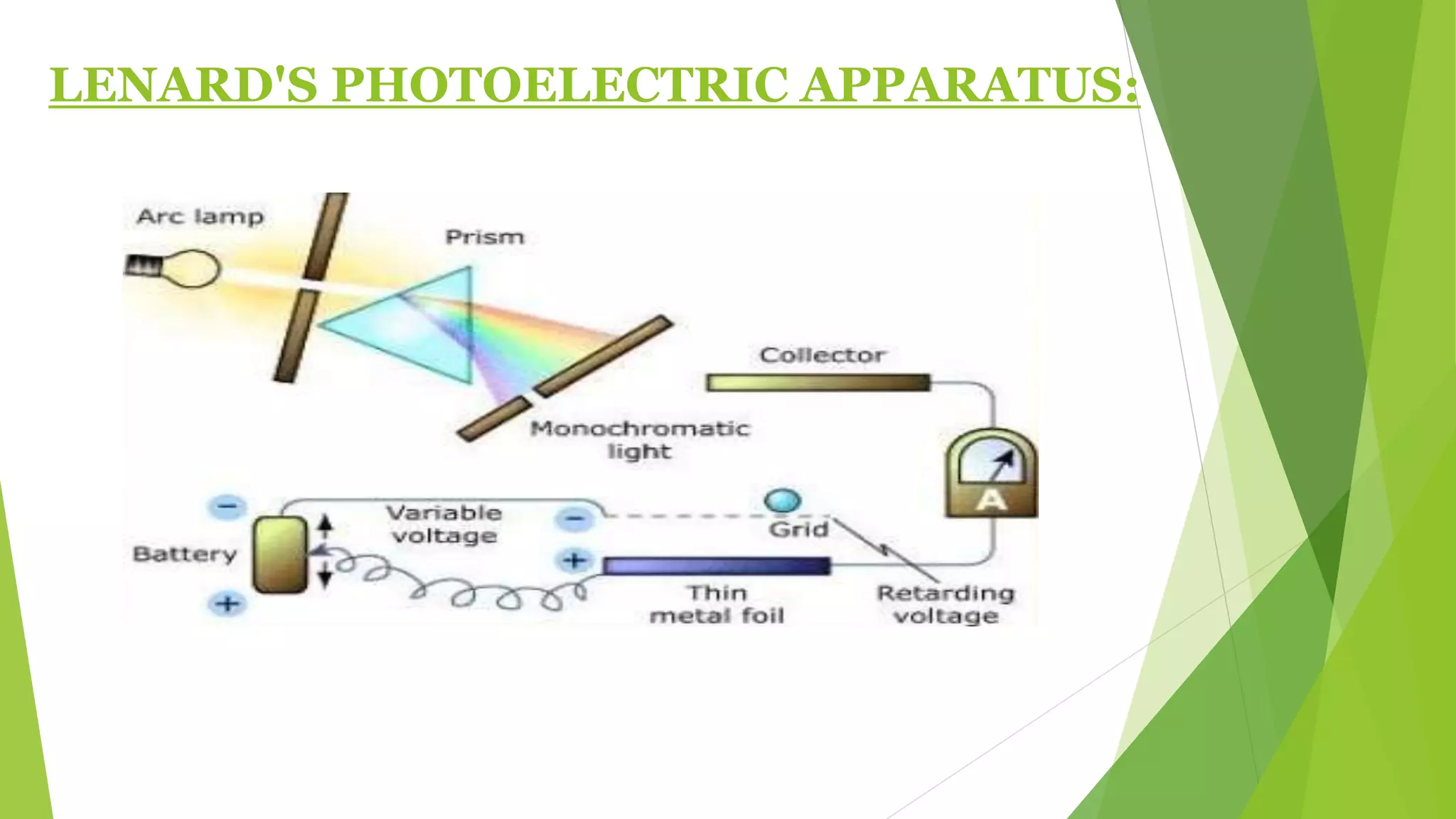
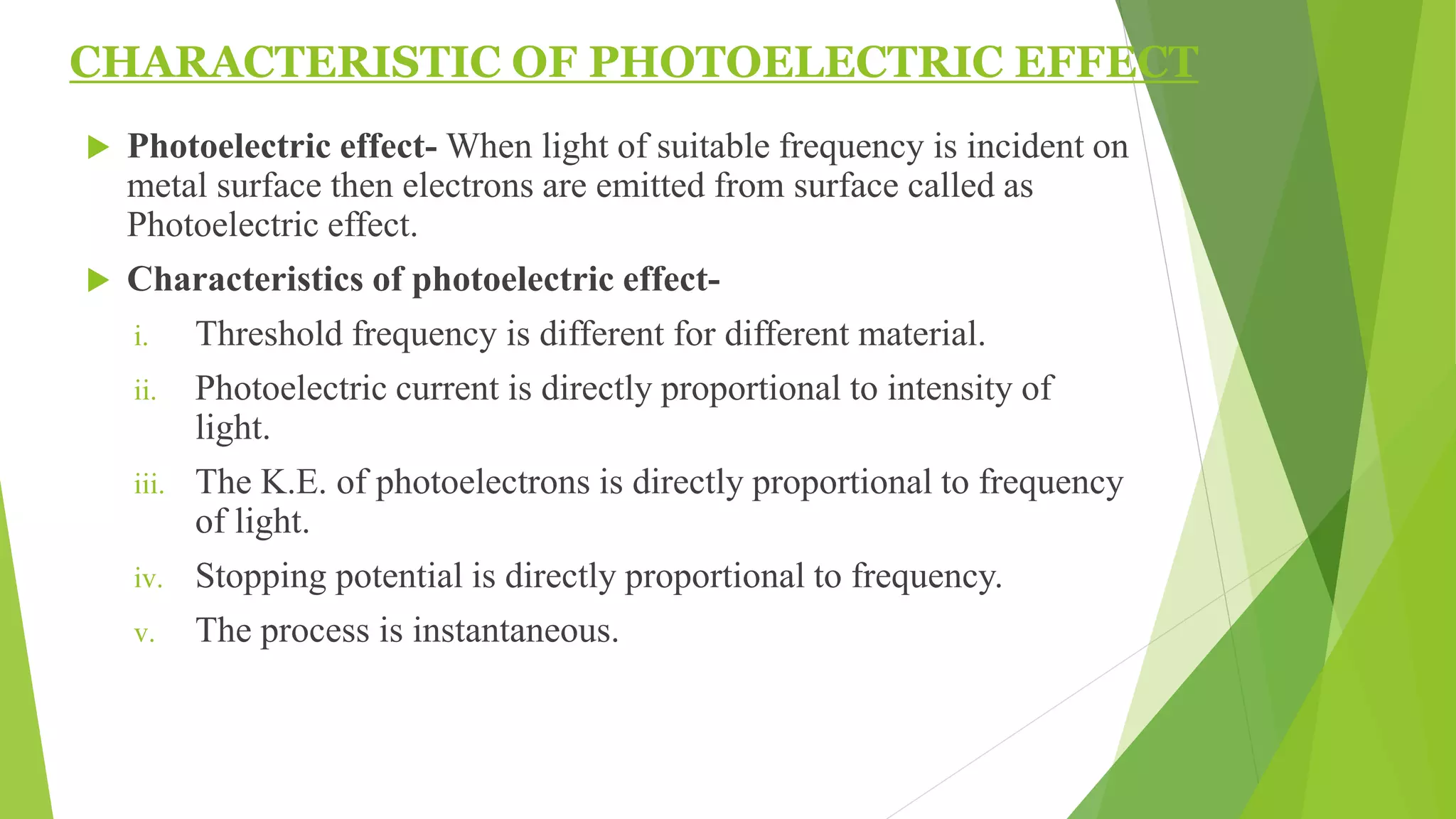
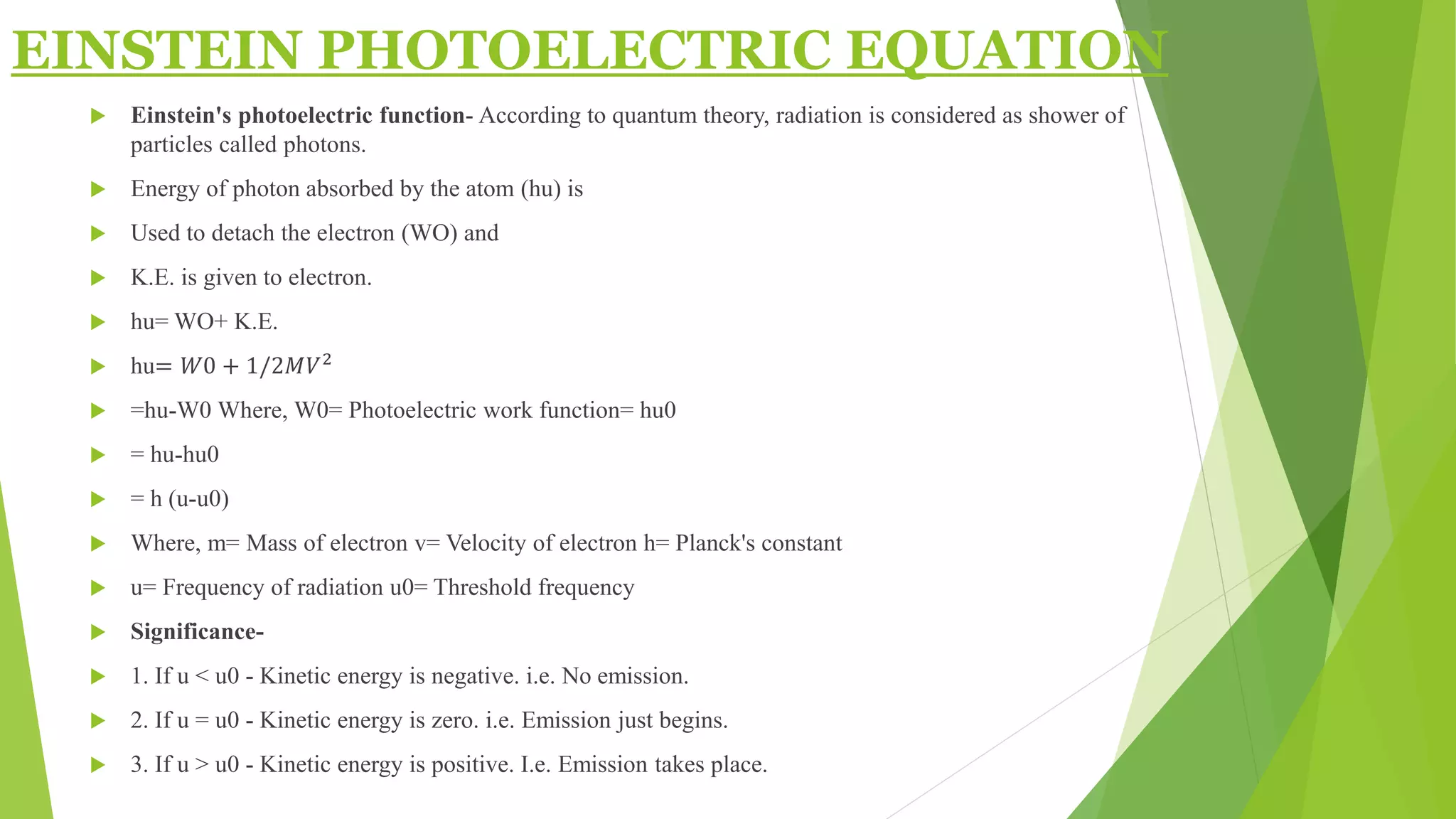
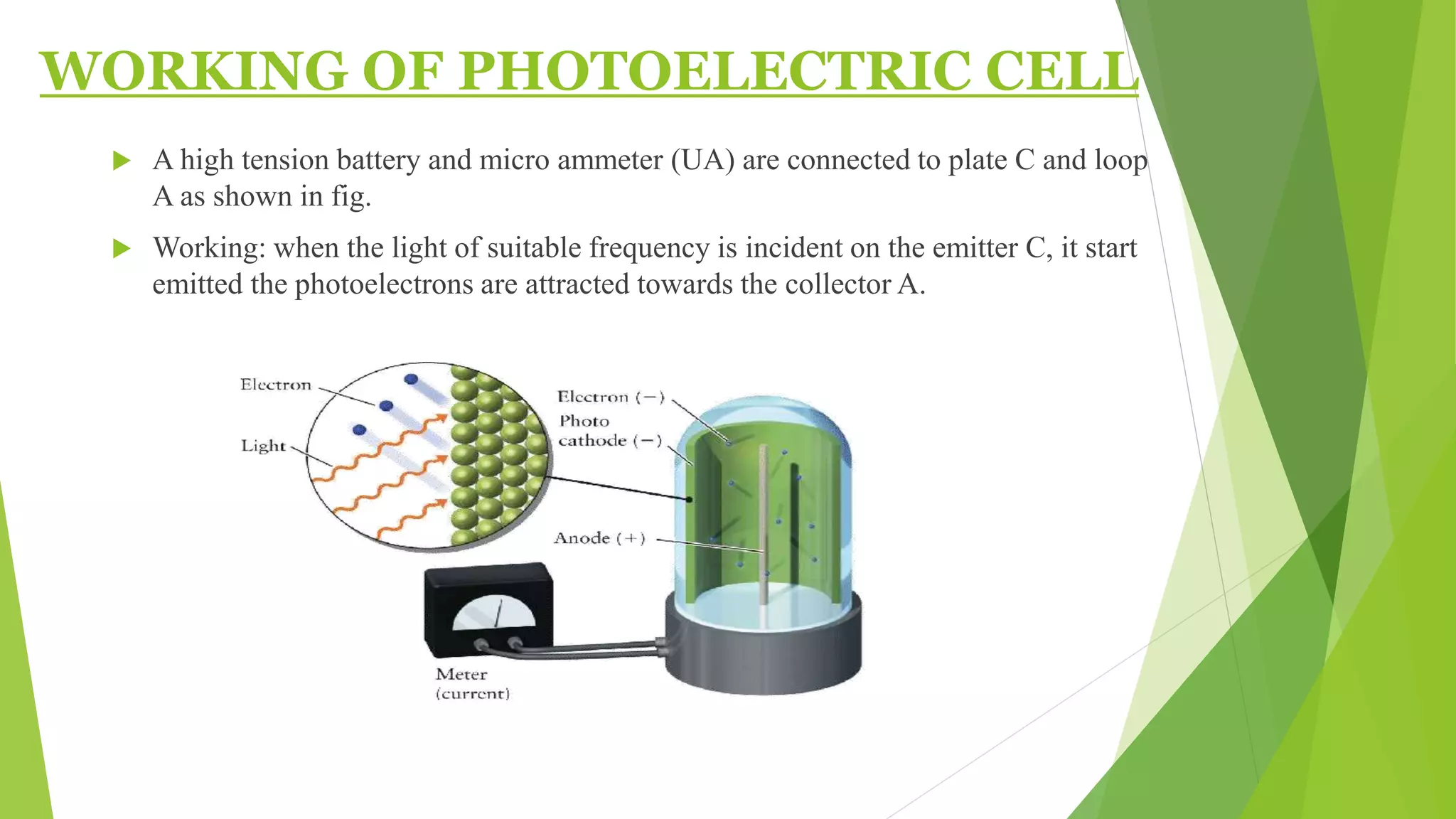
1. The photoelectric effect occurs when light of sufficient frequency shines on a metal surface, causing electrons to be emitted.
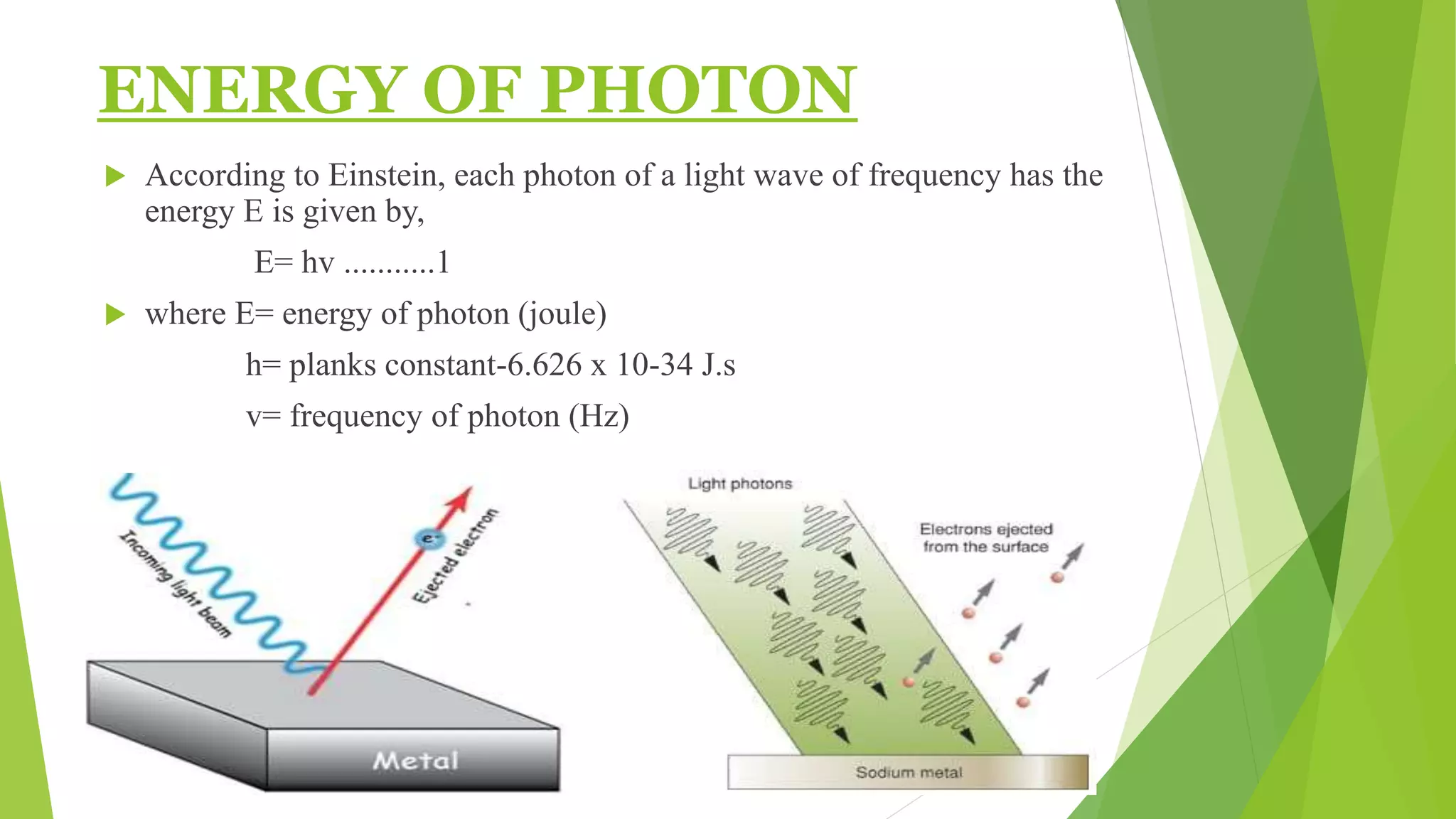
2. Einstein explained the photoelectric effect using the photon model of light, where light consists of discrete packets of energy called photons.
3. The kinetic energy of emitted electrons depends on the frequency of light, not its intensity, supporting the photon model over classical wave theory.