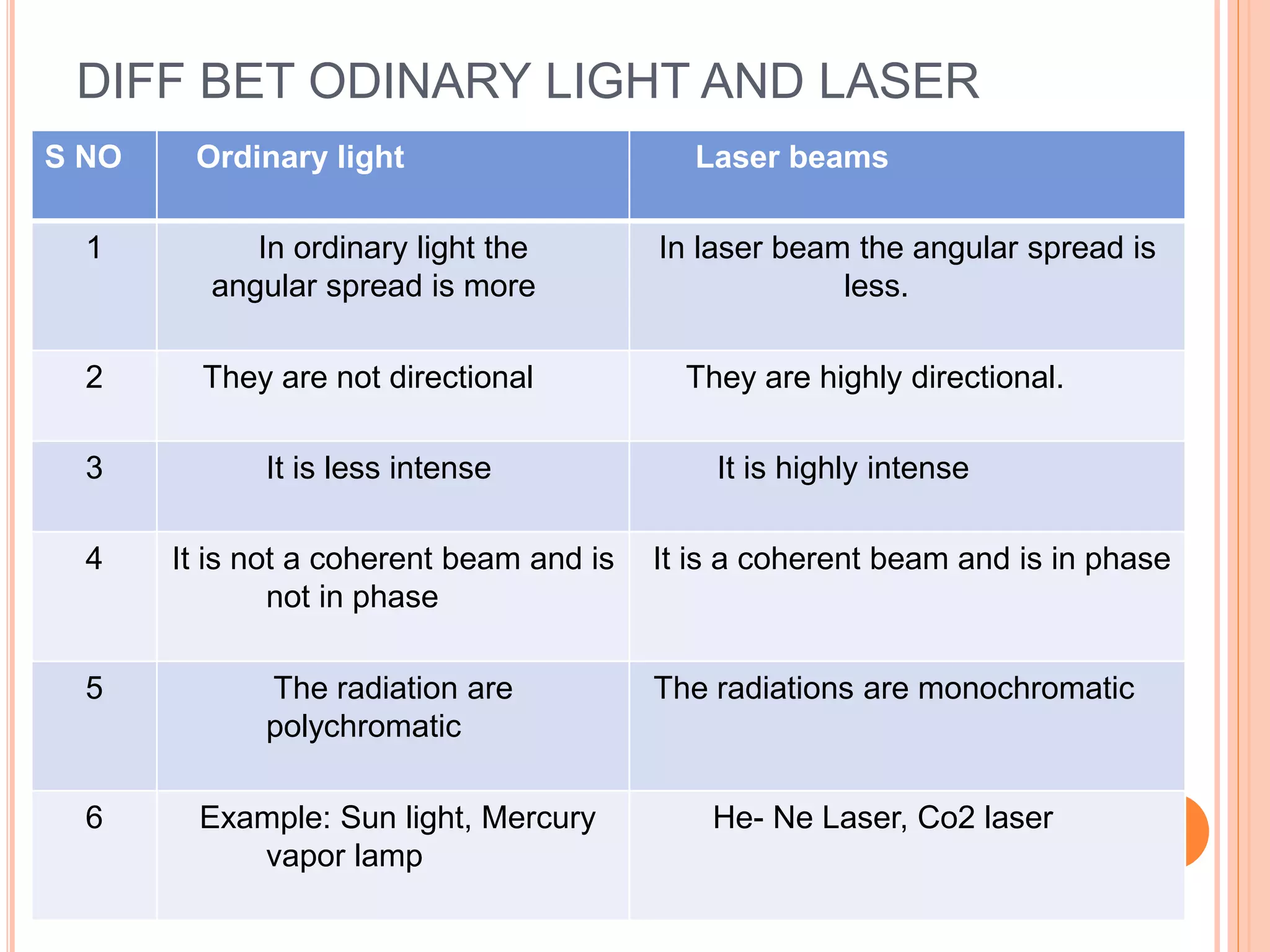
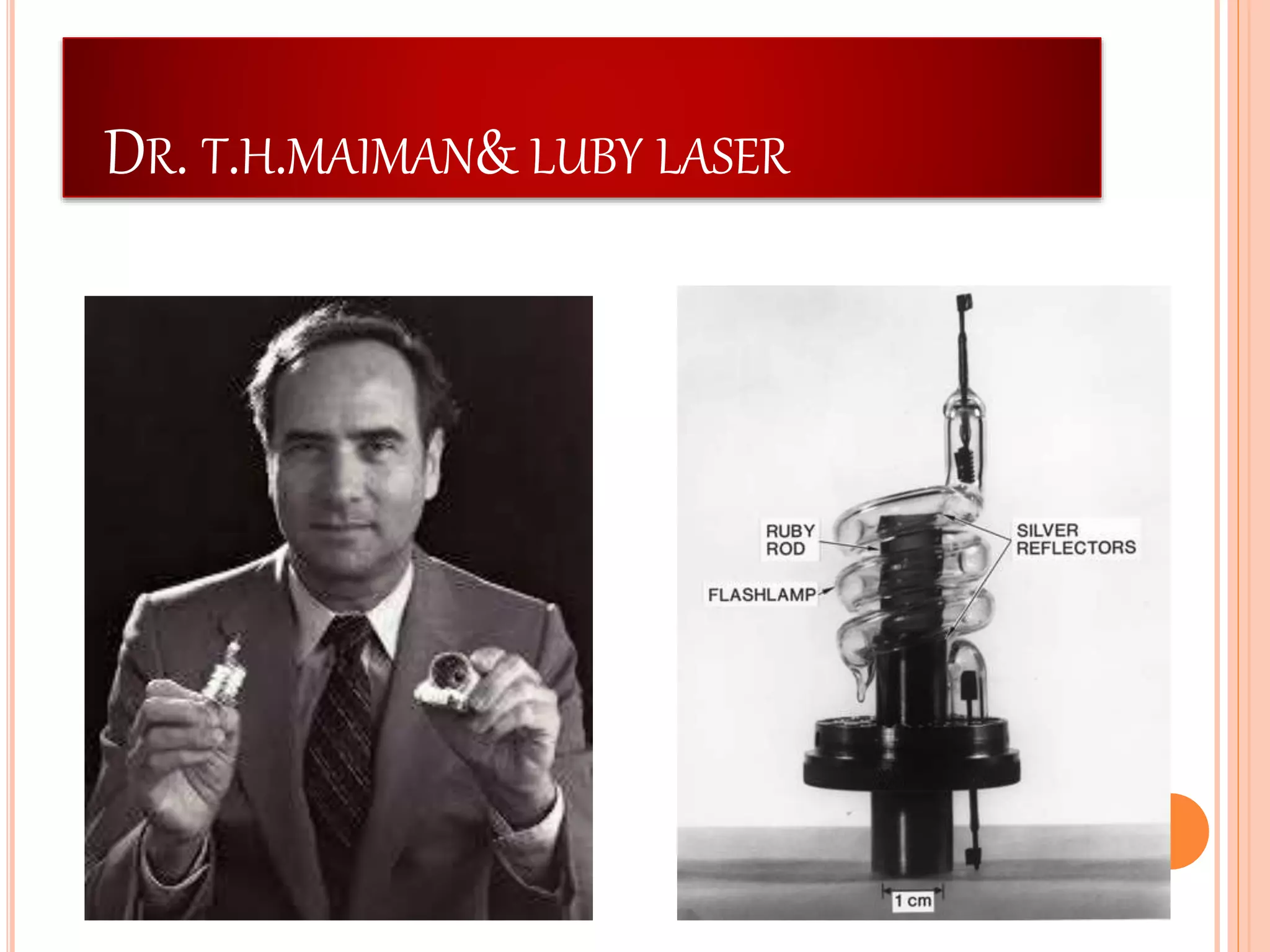
Laser stands for "Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation." Lasers emit a powerful, monochromatic, collimated beam of light that is coherent in nature. Lasers have several key characteristics that distinguish them from ordinary light sources: (1) They are highly directional with an angular spread of 1mm/m compared to 1m/m for ordinary light; (2) They have high intensity due to their directionality focusing the beam; and (3) They are highly monochromatic and coherent, with wave trains of the same frequency that are in phase. The first working laser was demonstrated in 1960 by Dr. Theodore Maiman using a ruby crystal.