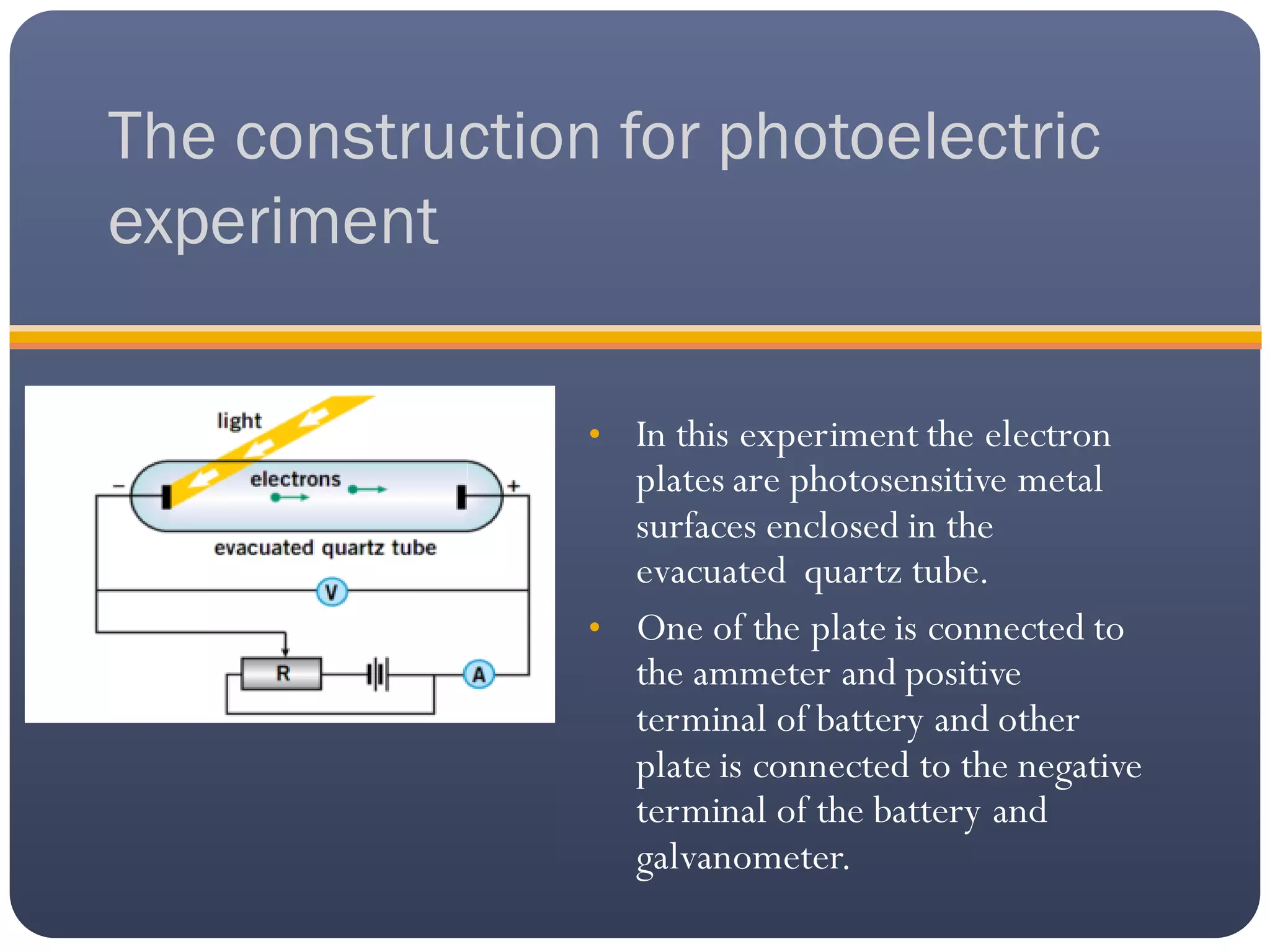
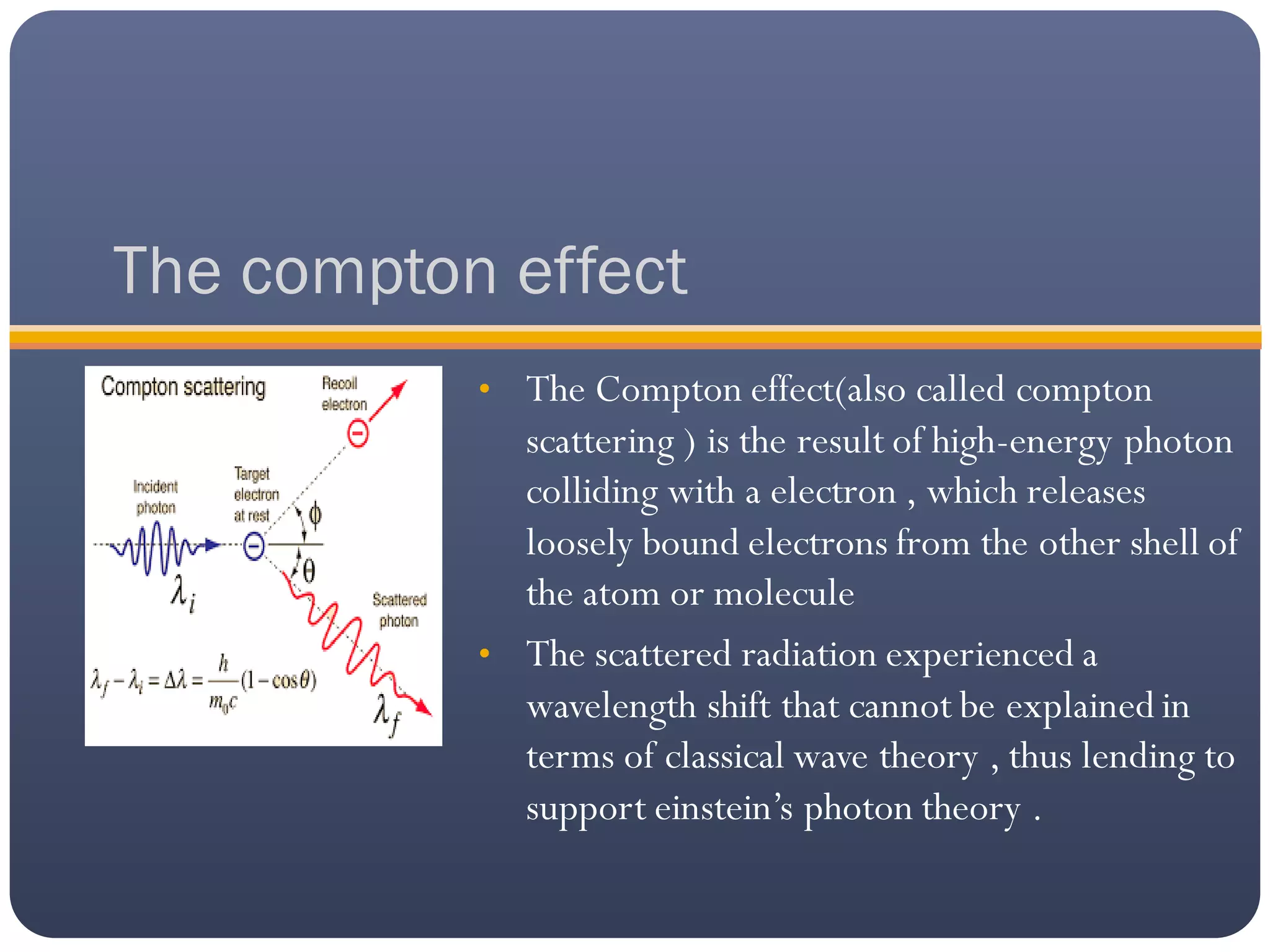
The photoelectric effect occurs when light of a suitable wavelength ejects electrons from a metallic surface. An experiment to study this effect involves using a quartz tube with two electron plates - one connected to a battery and ammeter, the other to a battery and galvanometer. When light hits the emitting plate, photoelectrons are ejected and travel to the positive plate, causing a current and galvanometer deflection. The number and kinetic energy of ejected electrons depends on factors like radiation intensity and frequency. The photoelectric effect is used in solar panels, cameras, and burglar alarms. The Compton effect describes high-energy photon scattering from electrons in atoms, which was evidence for Einstein's photon theory. It is important