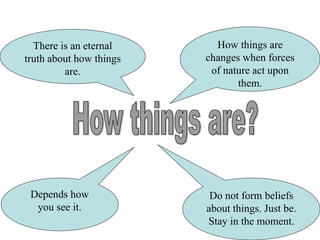
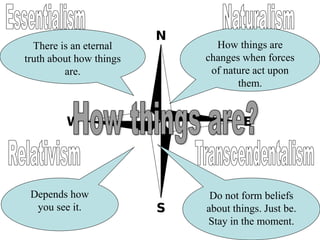
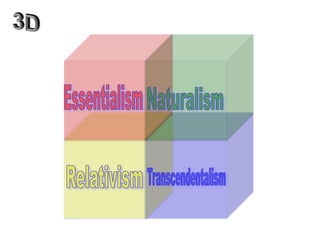
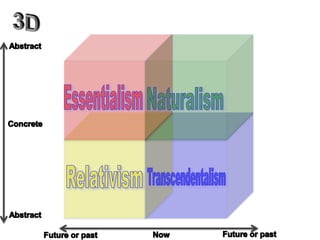
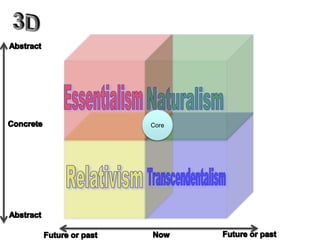
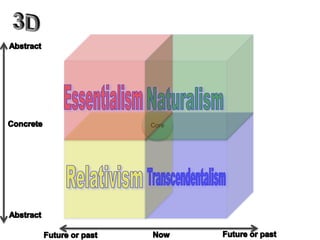
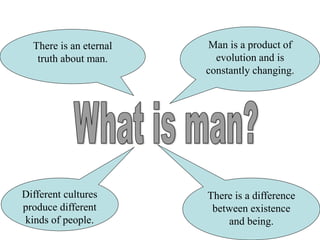
The document categorizes four main theories of human nature: essentialism, naturalism, relativism/culturalism, and existentialism/Buddhism. Essentialism views humans as having an unchanging essence or character. Naturalism sees humans as products of evolution and nature. Relativism/culturalism believes different cultures produce different kinds of people. Existentialism and Buddhism emphasize detachment from beliefs and living in the present moment.