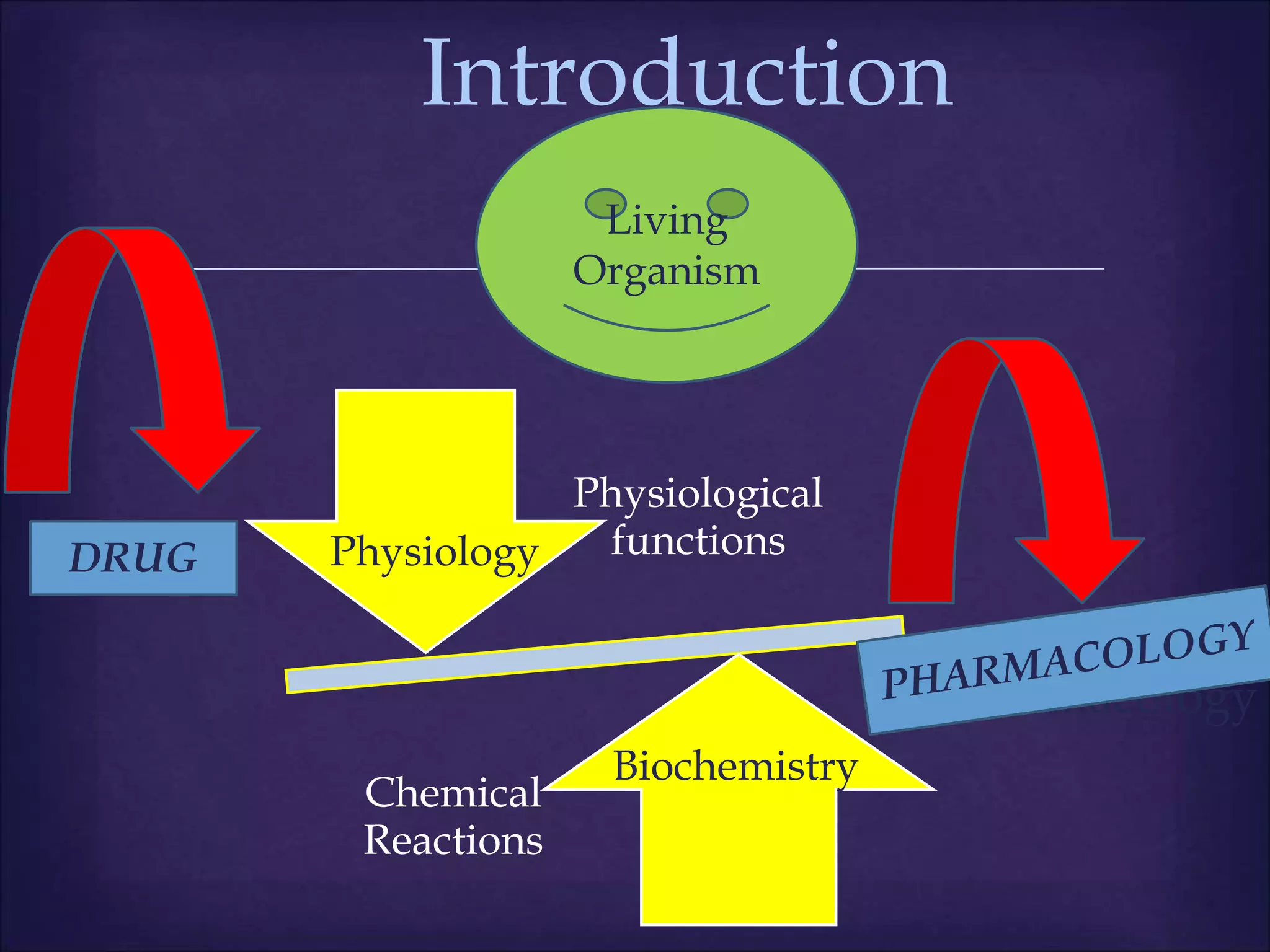
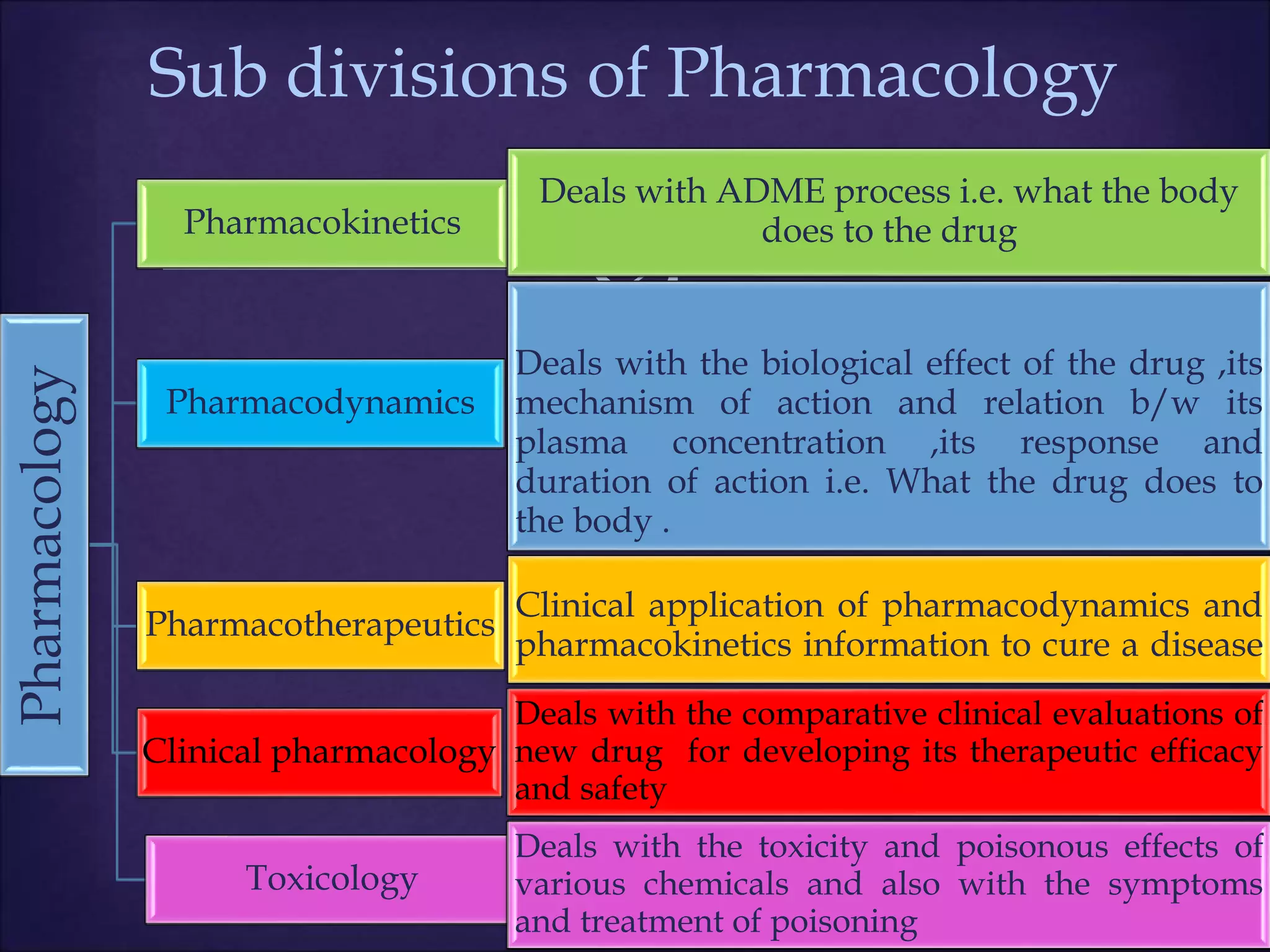
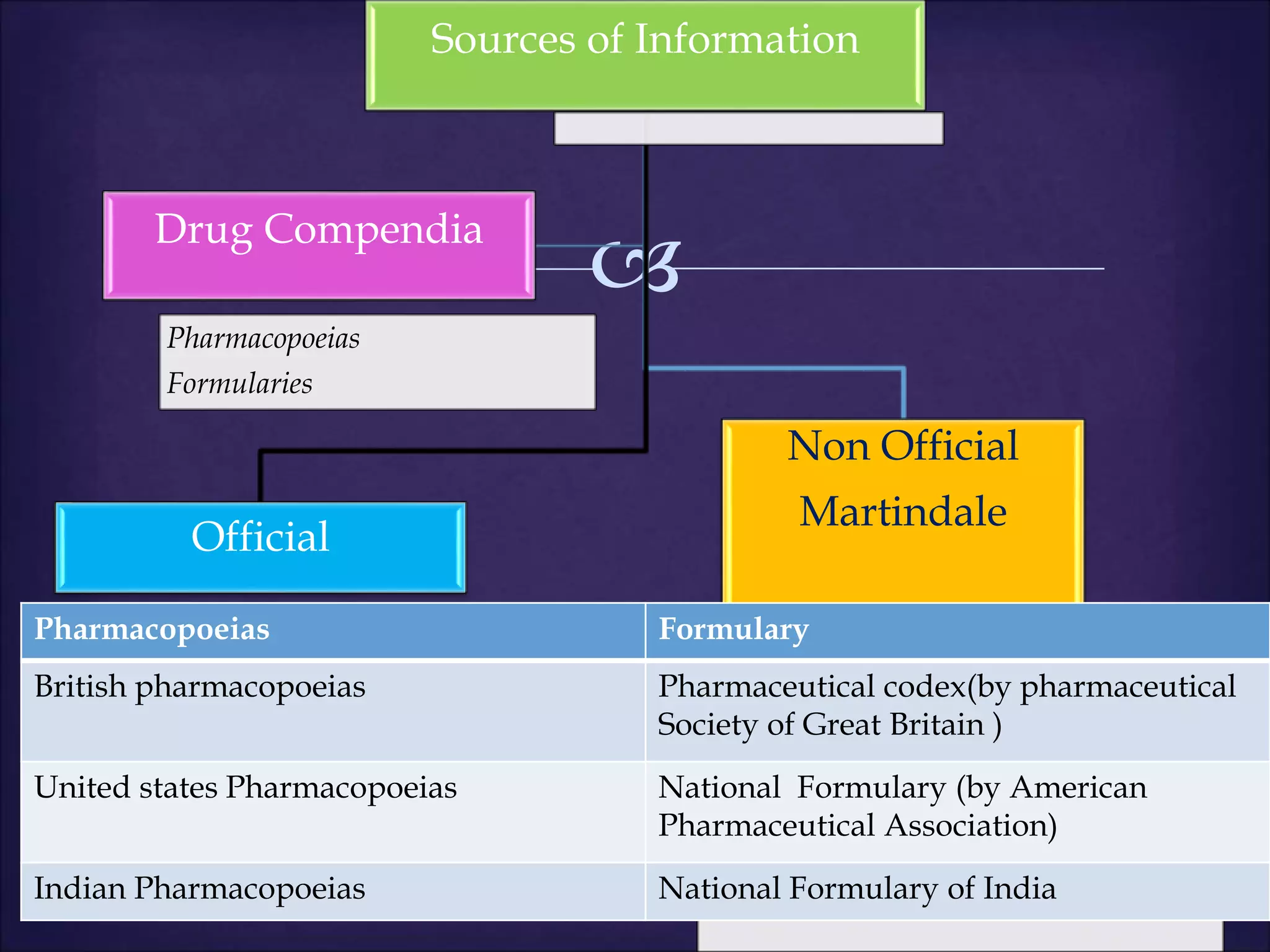
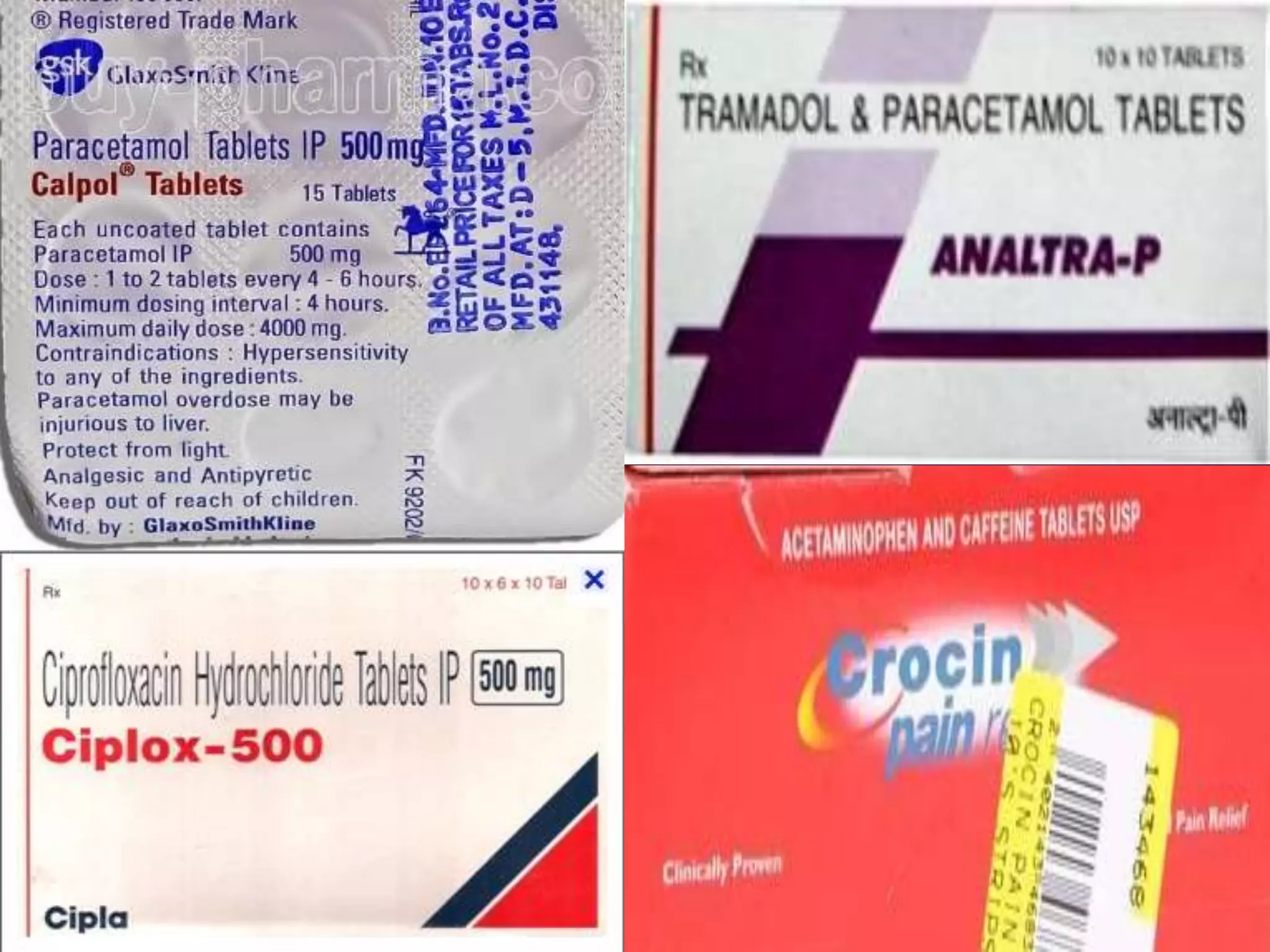
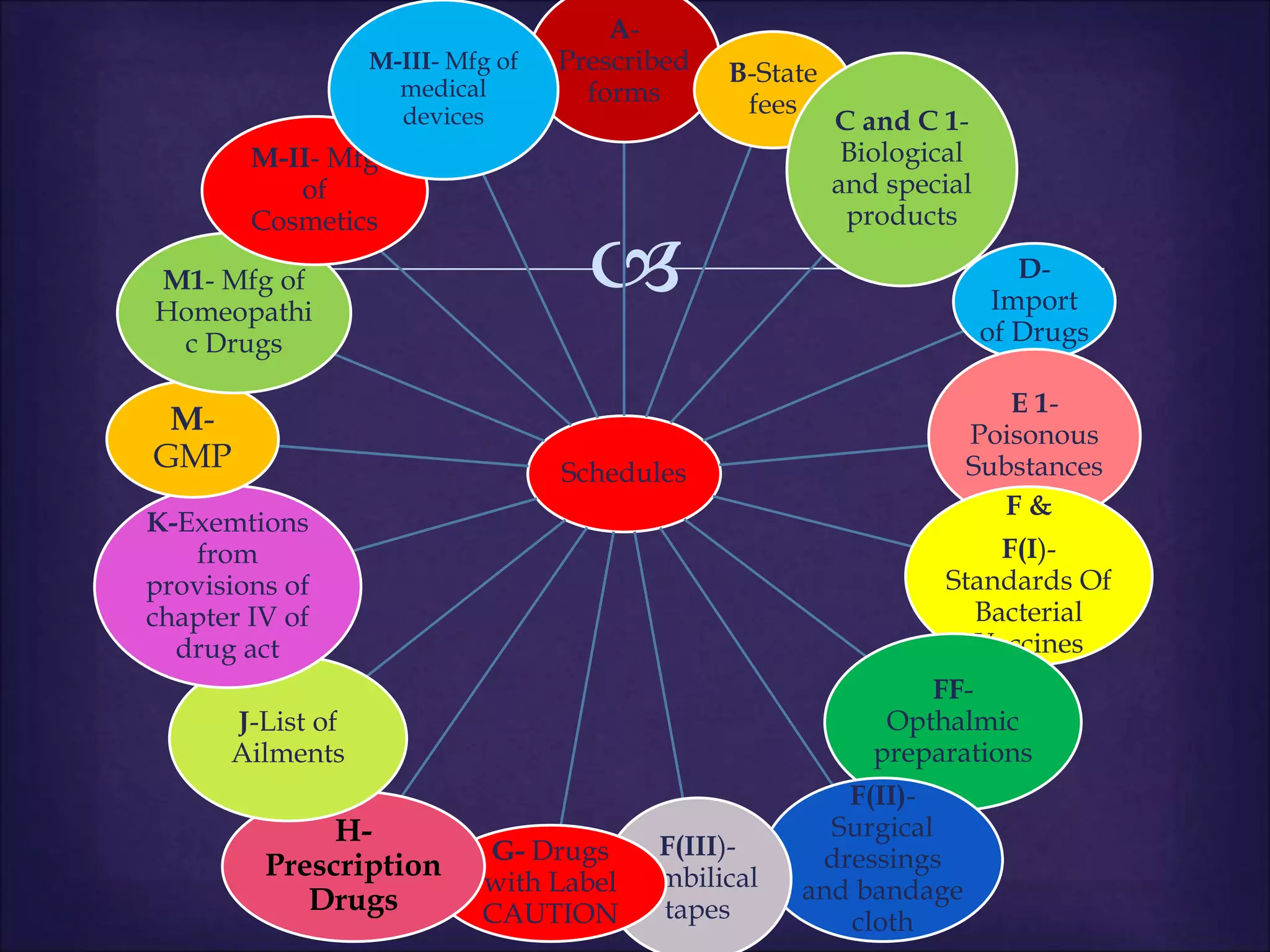
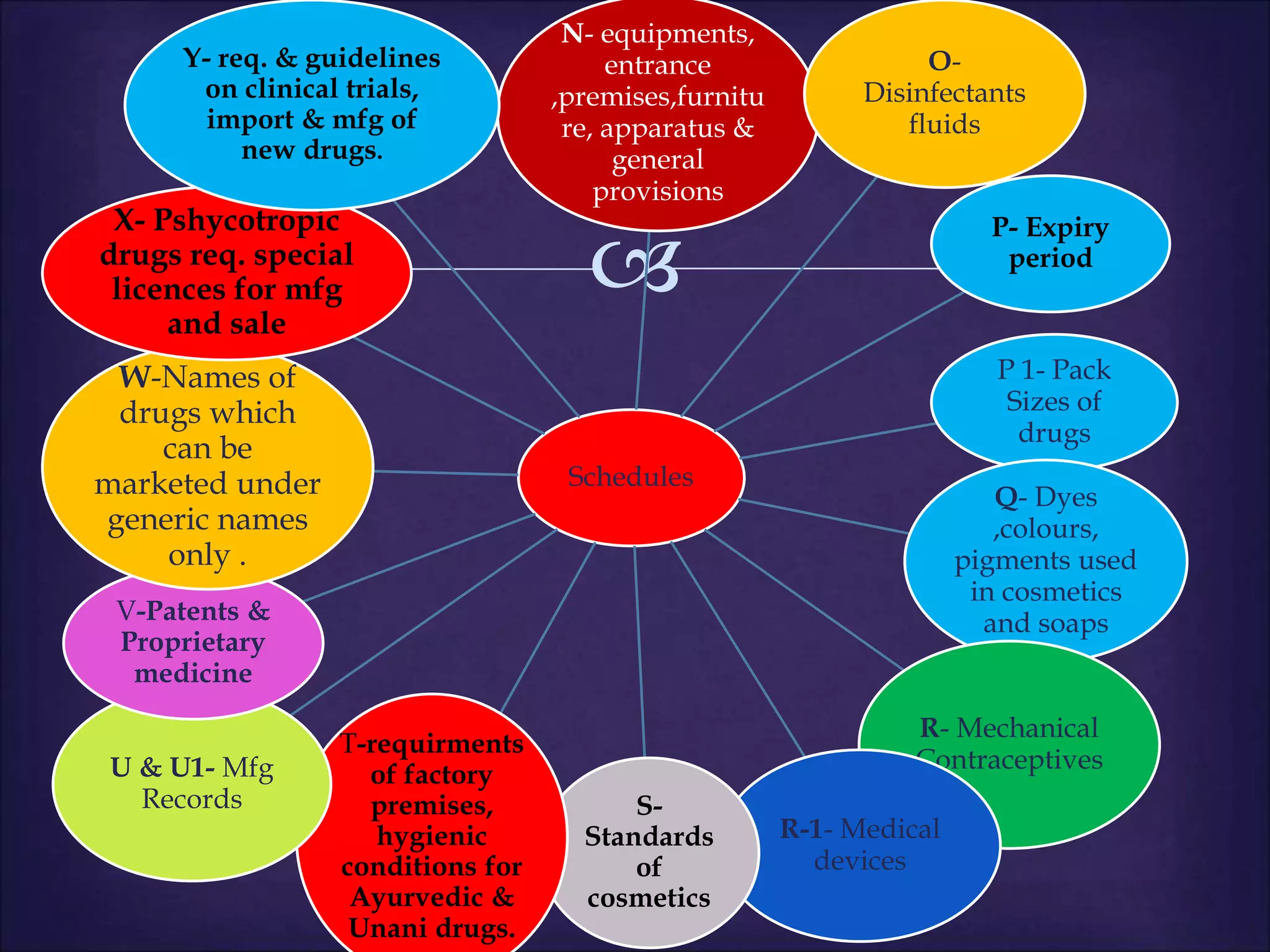
This document discusses various topics related to pharmacology including definitions of drugs, classifications of drugs, subdivisions of pharmacology, sources of drug information, essential medicines, orphan drugs, drug schedules, and drug nomenclature. It provides classifications of prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs. It also summarizes key concepts in pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, pharmacotherapeutics, and toxicology.