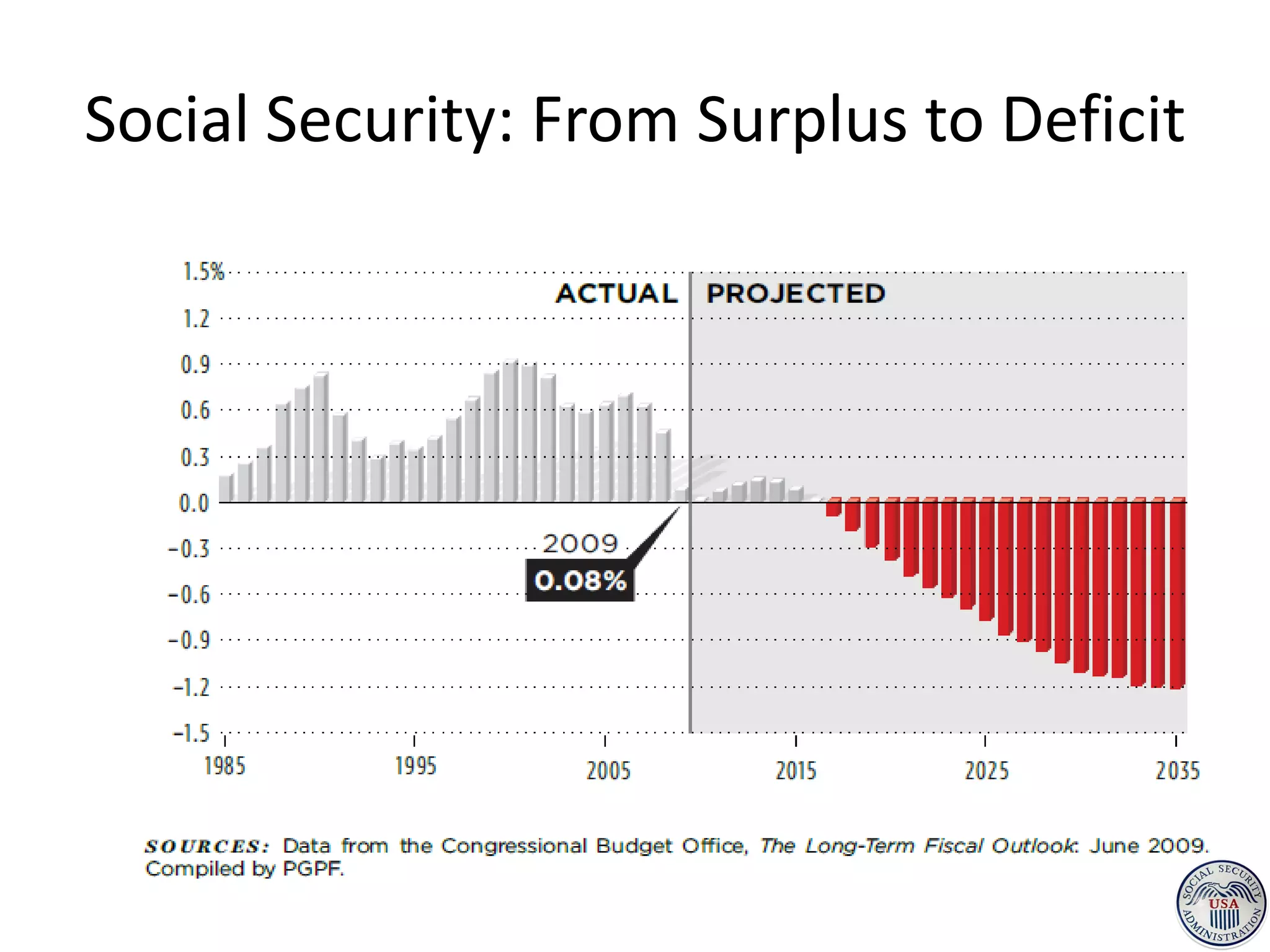
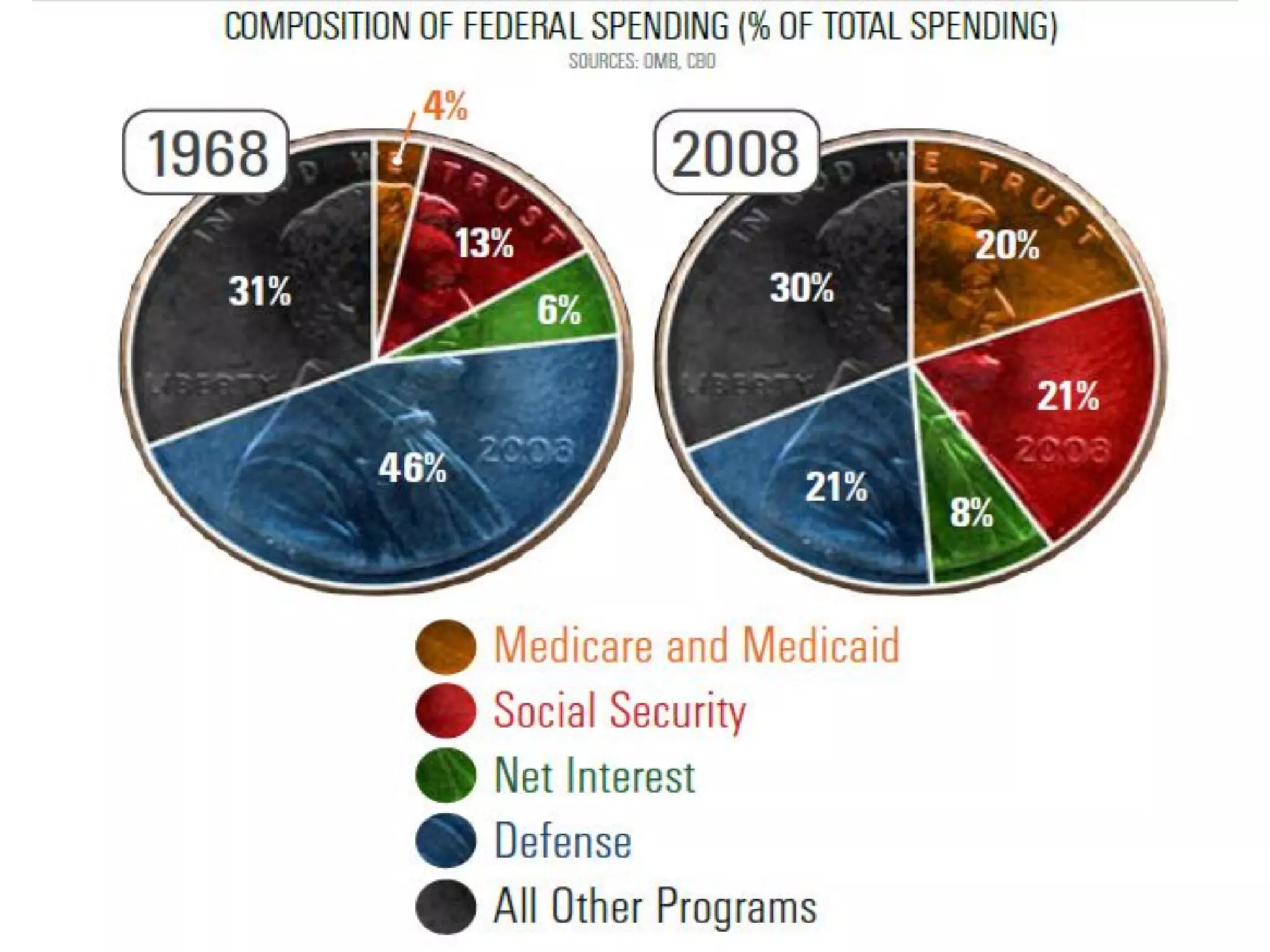
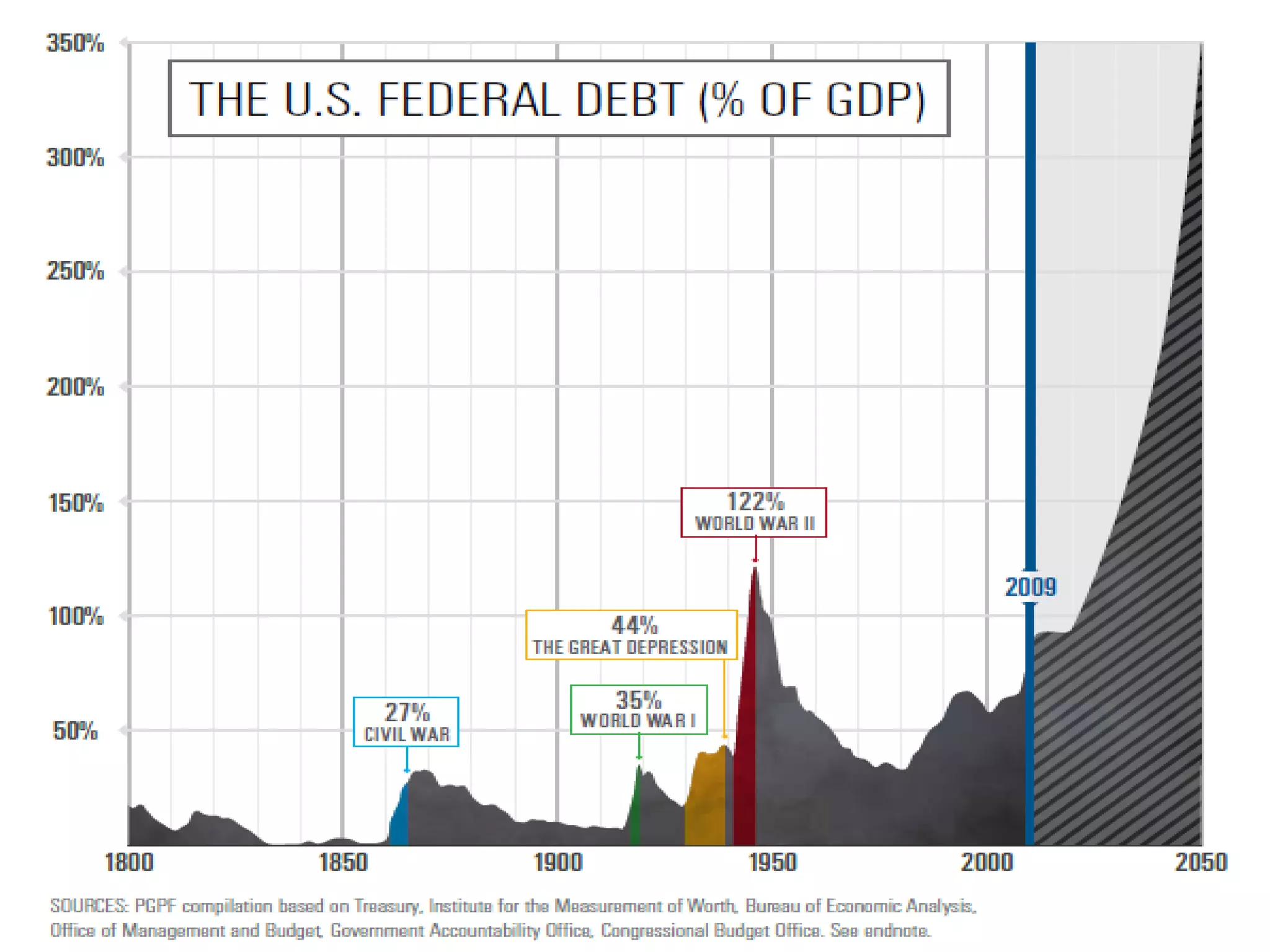
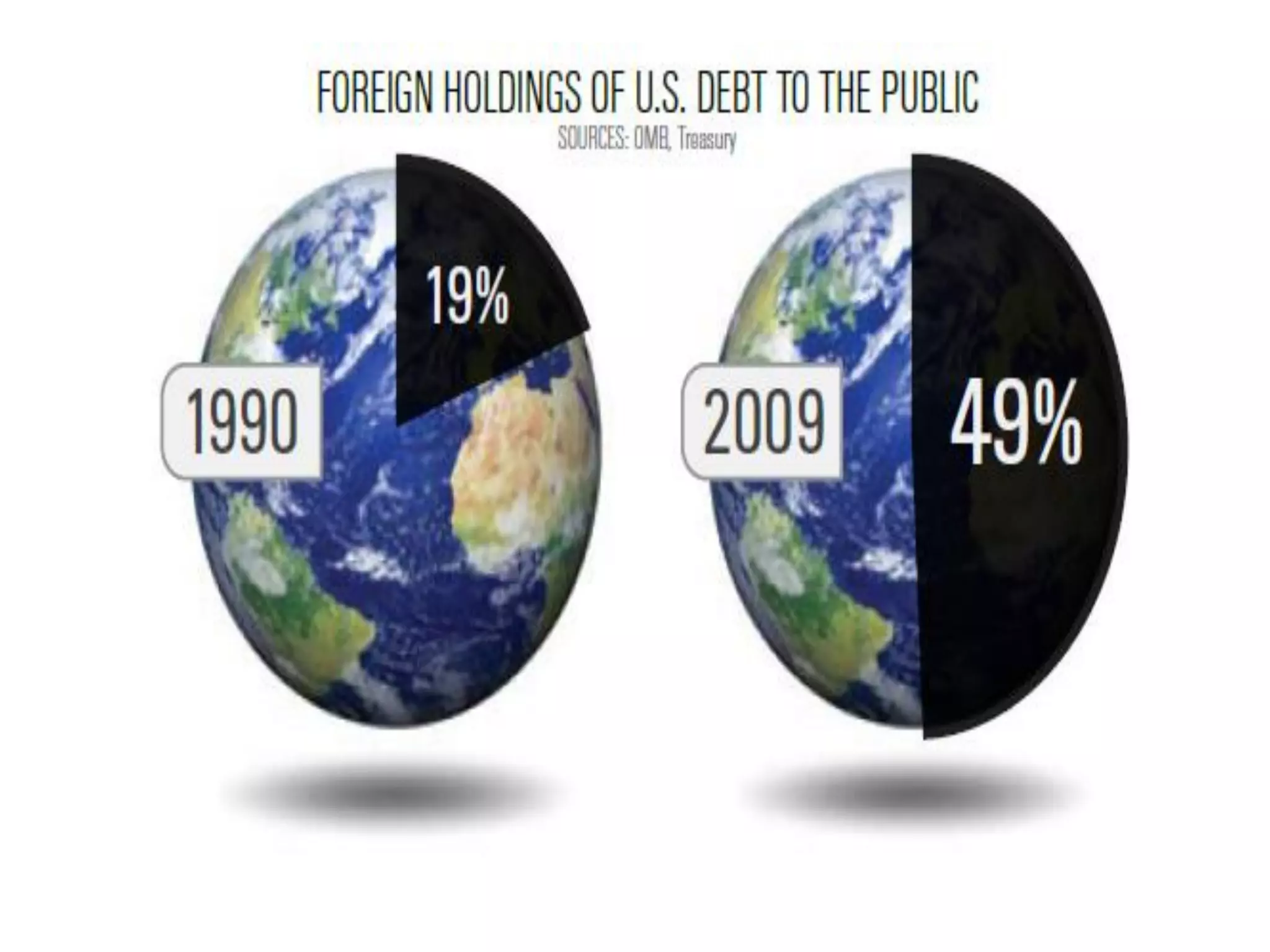
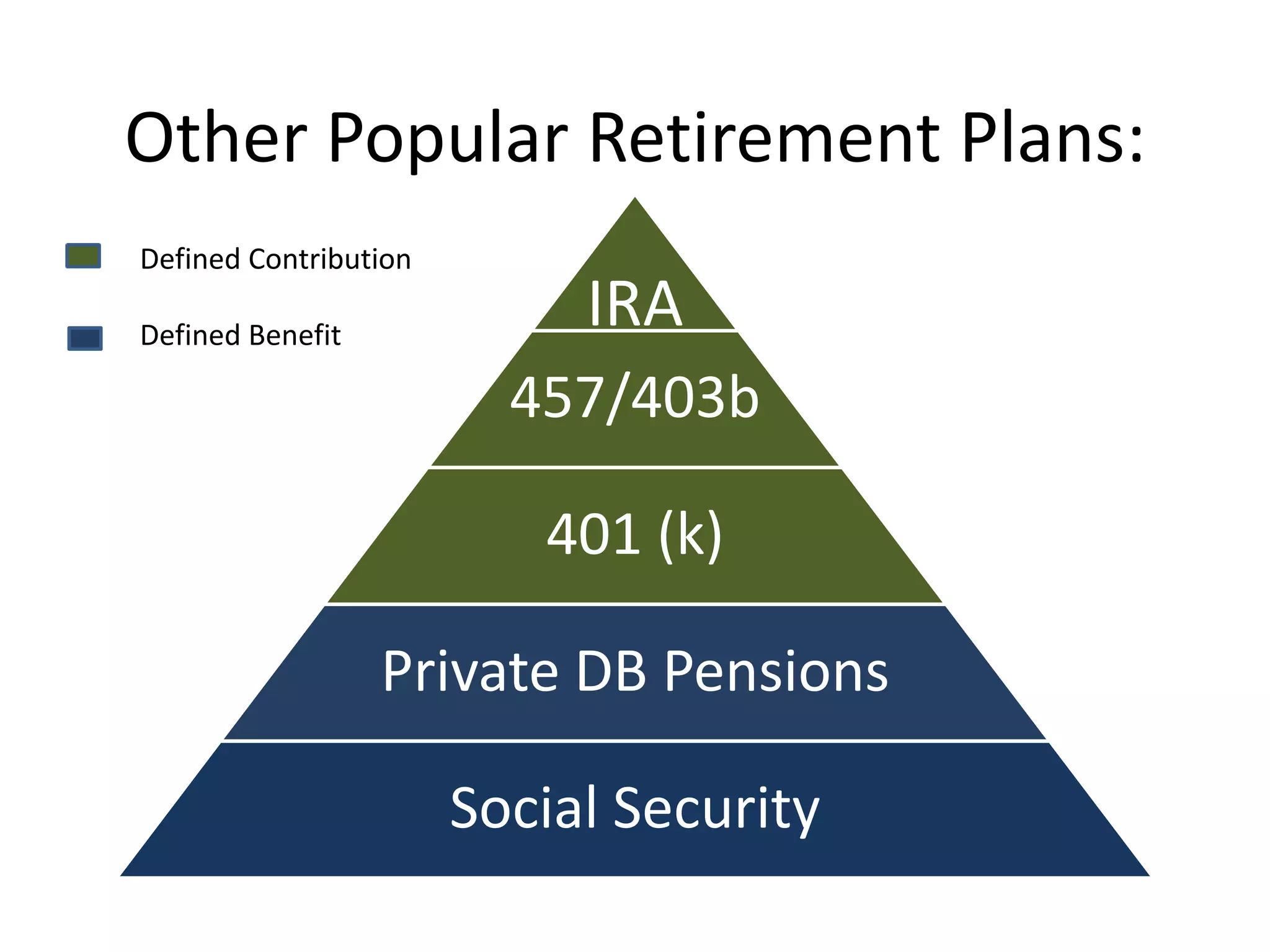
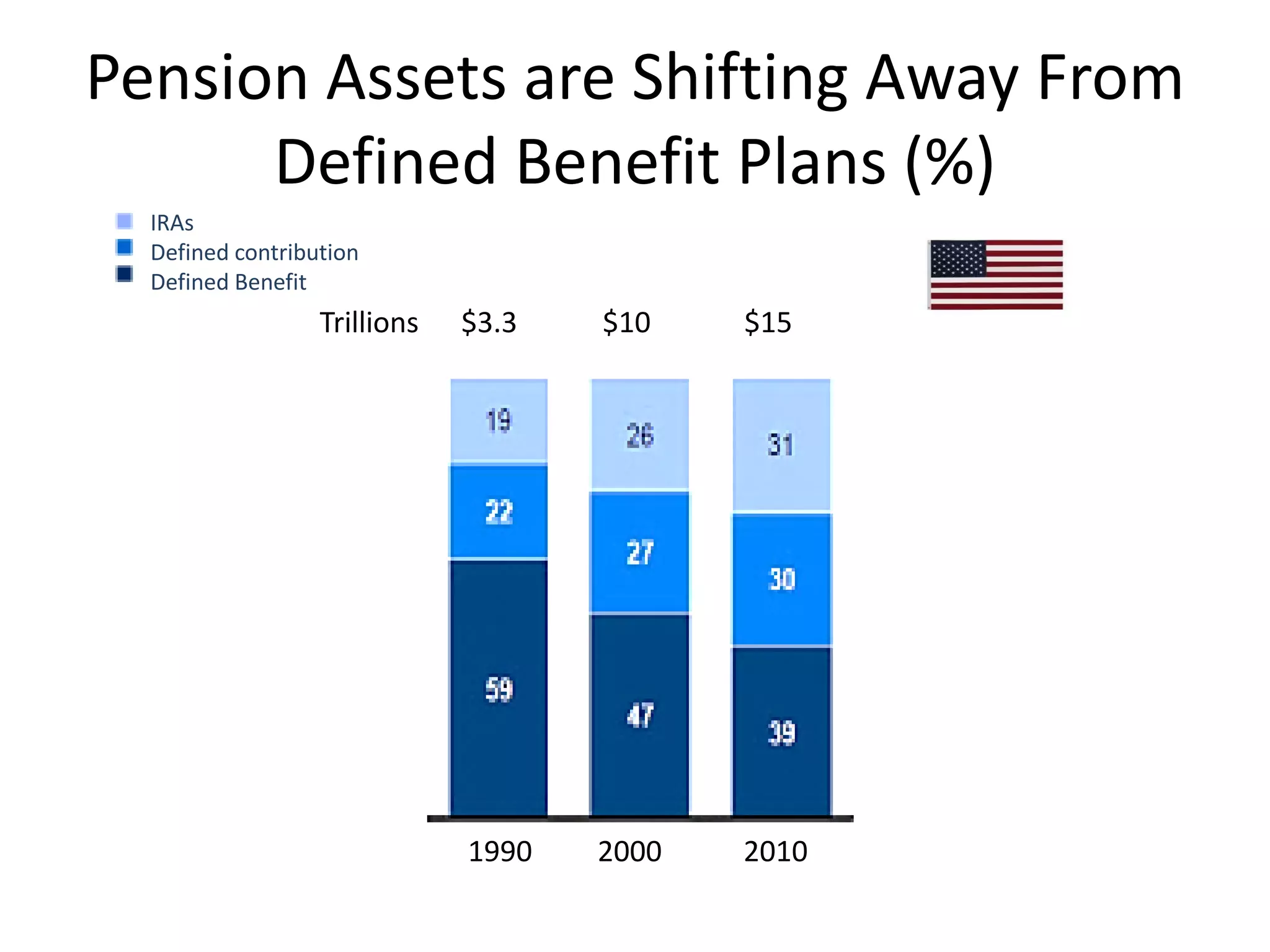
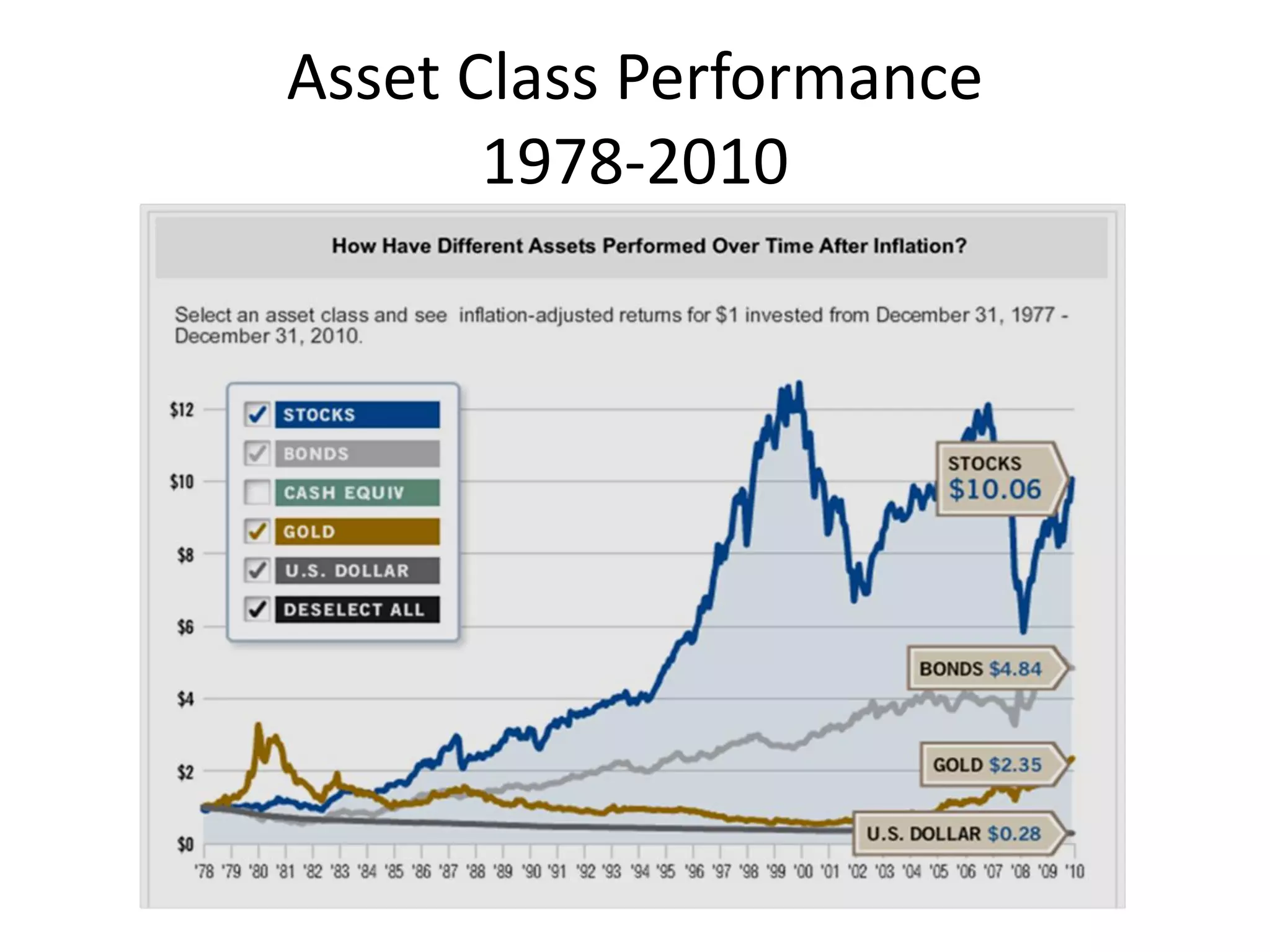
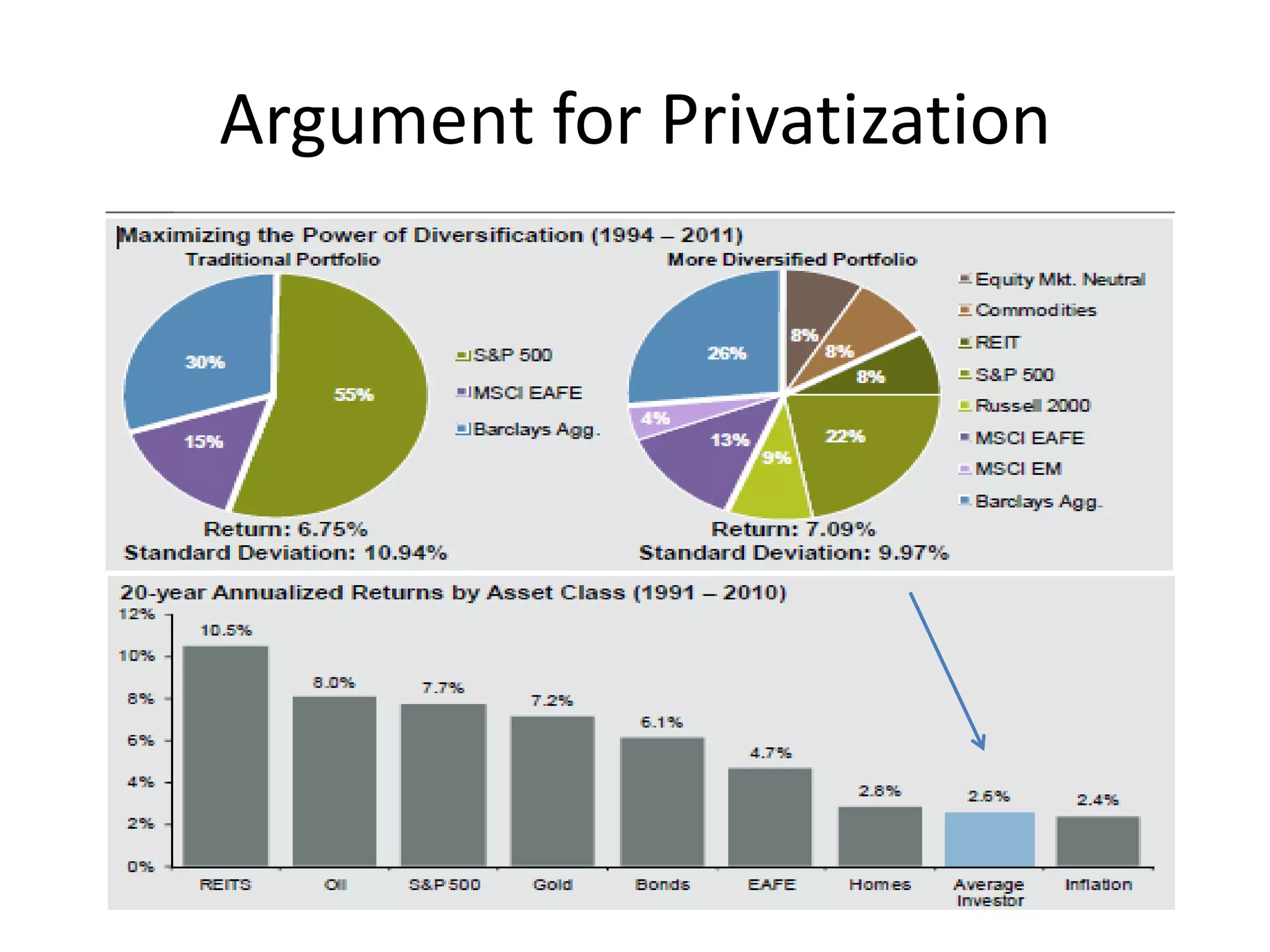
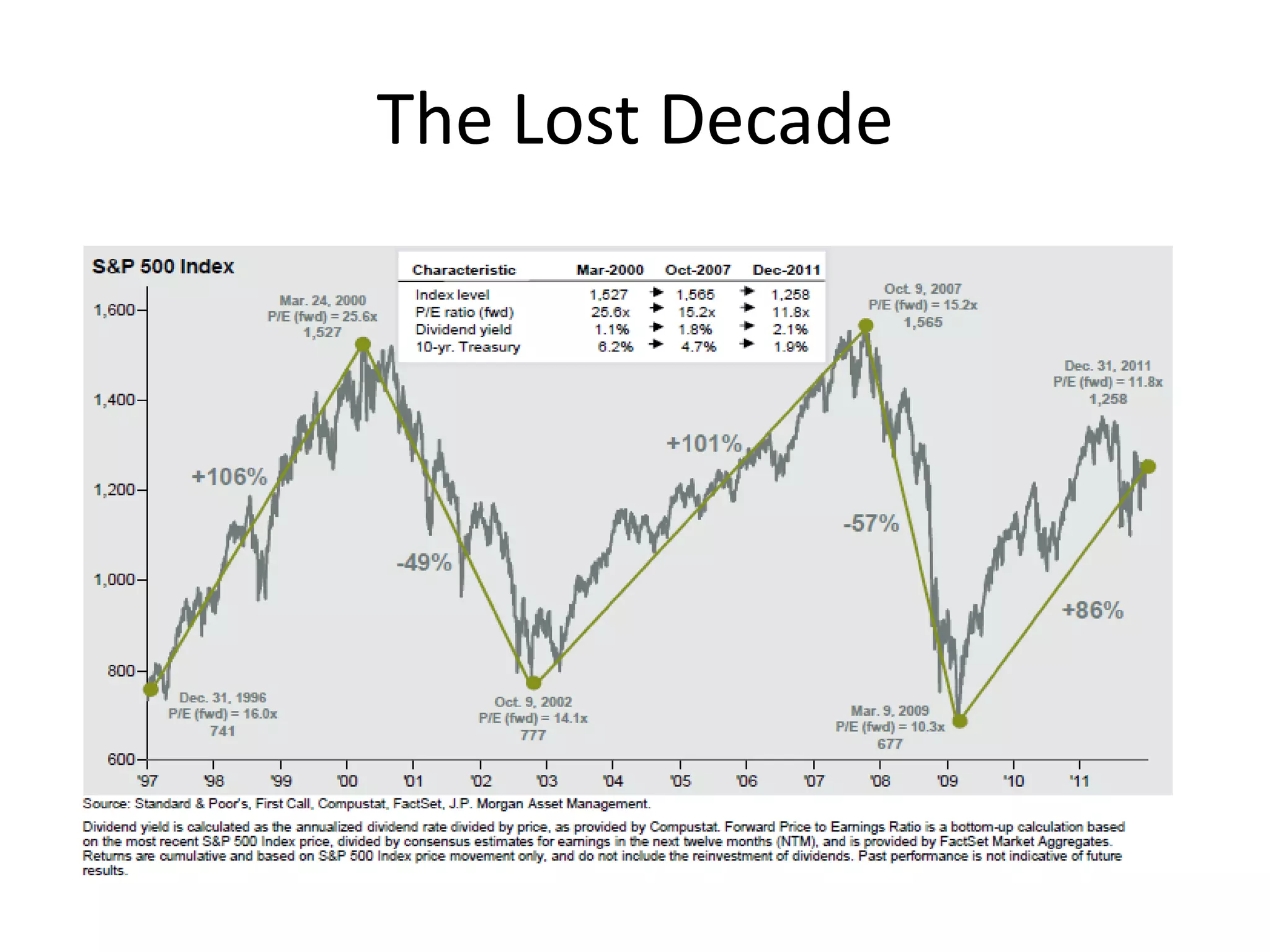
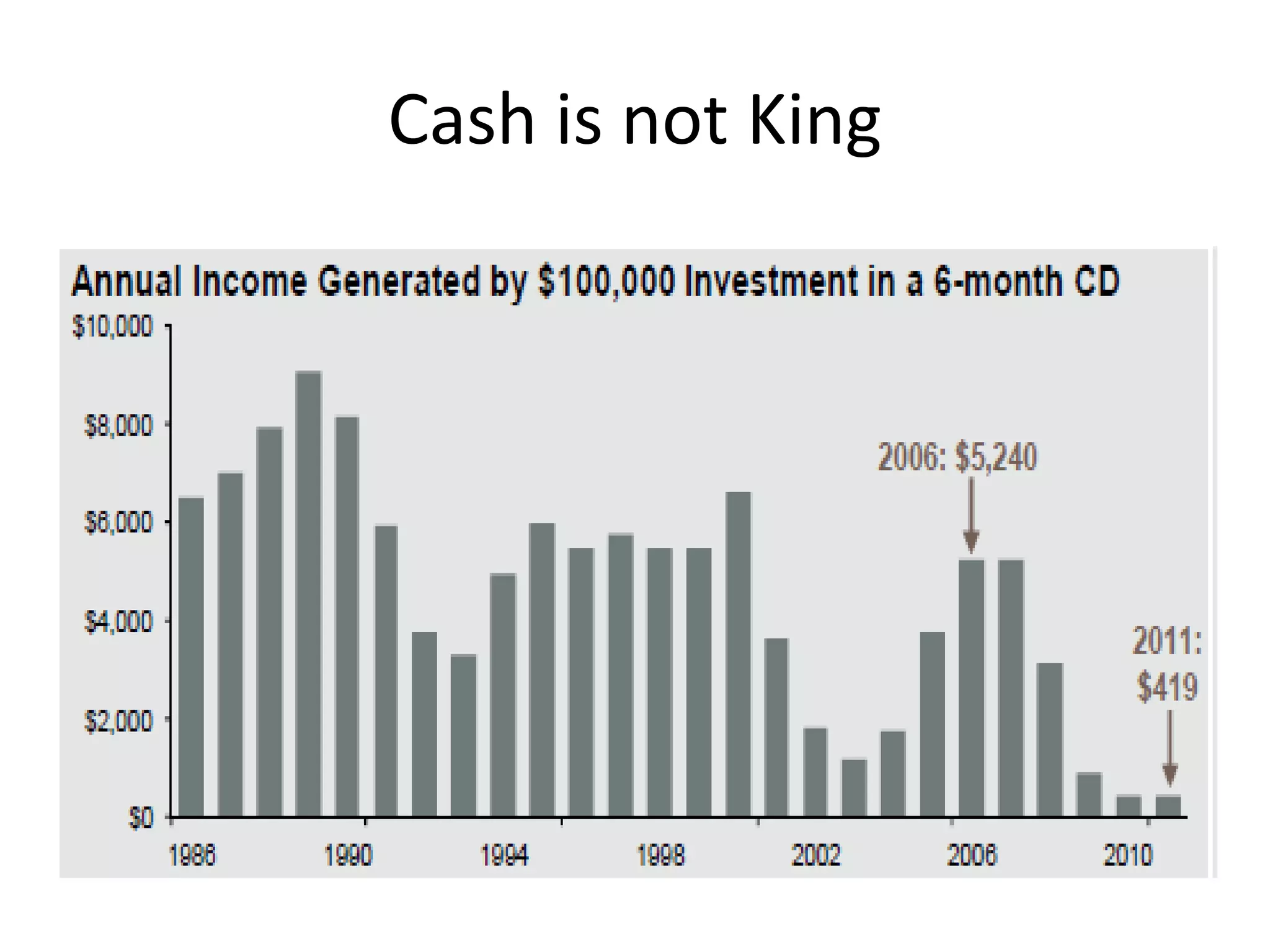
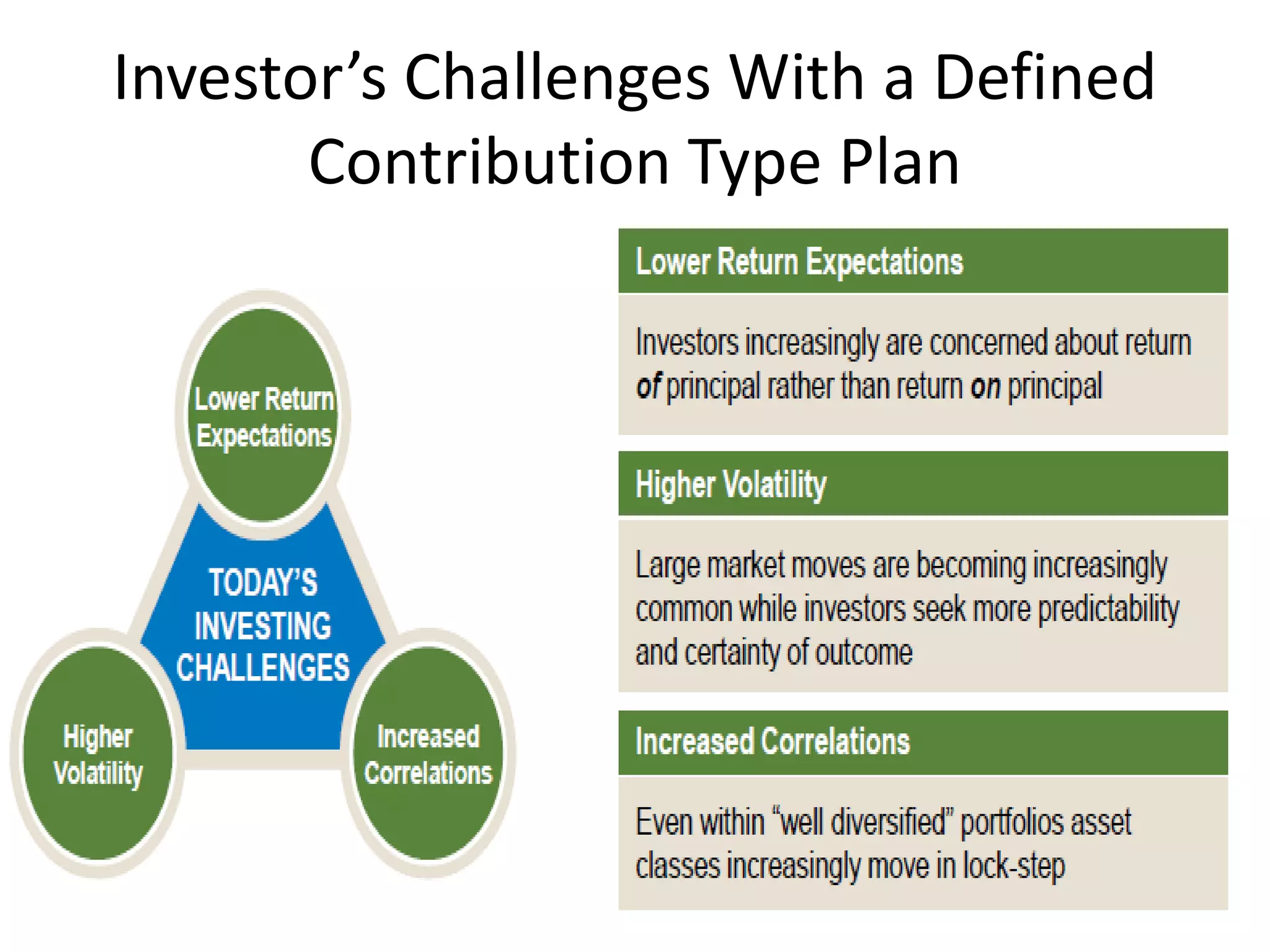
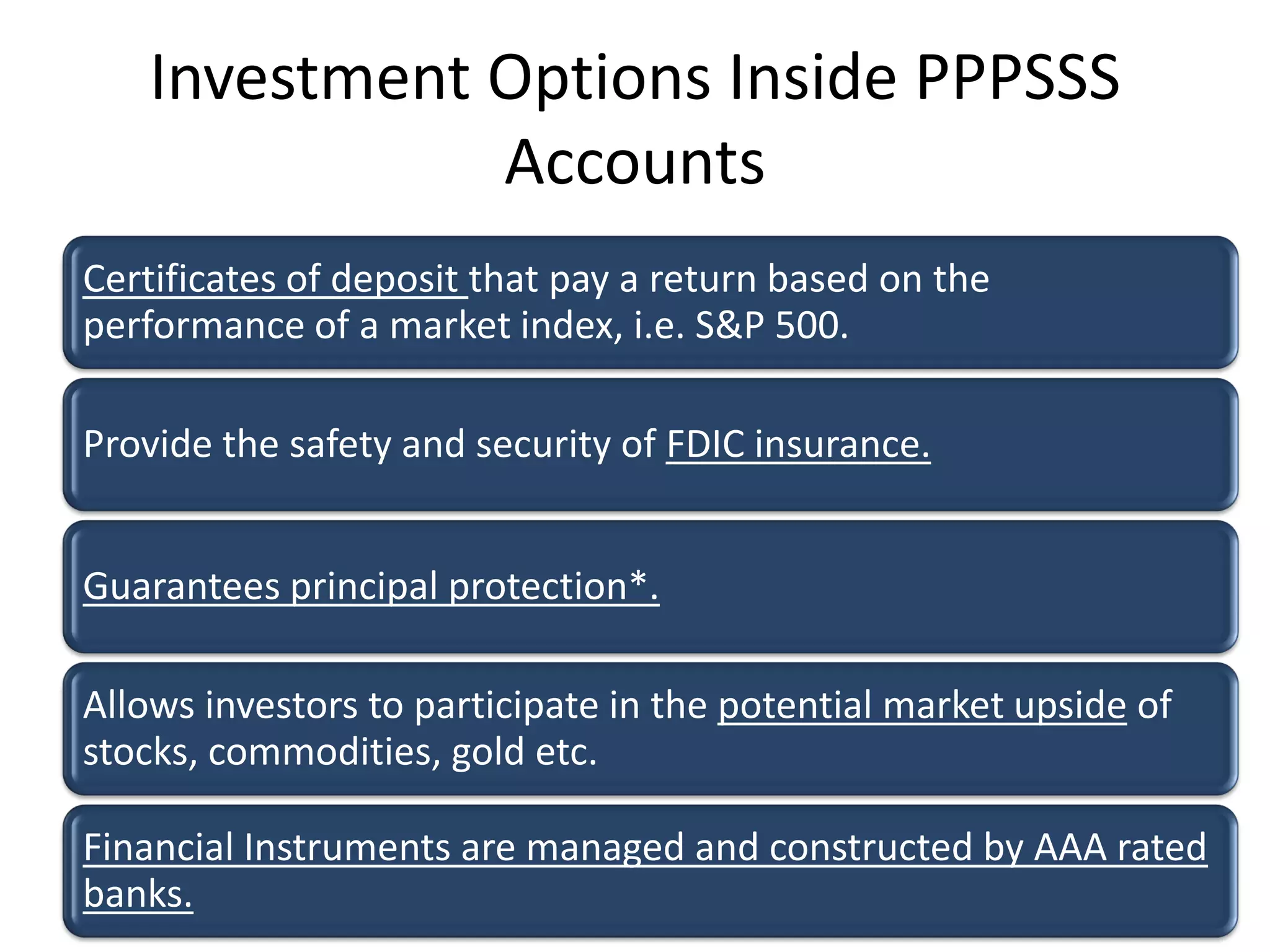
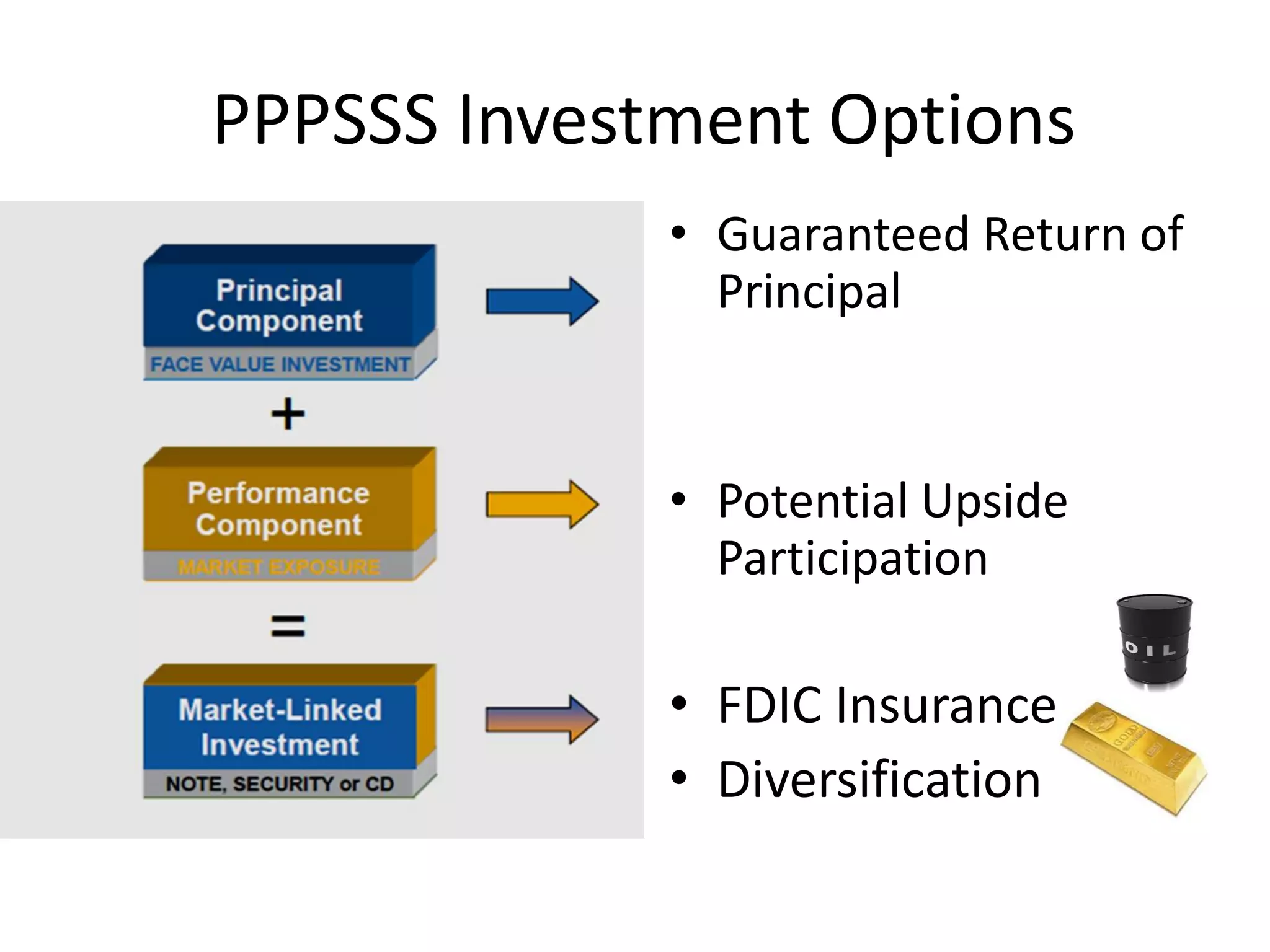
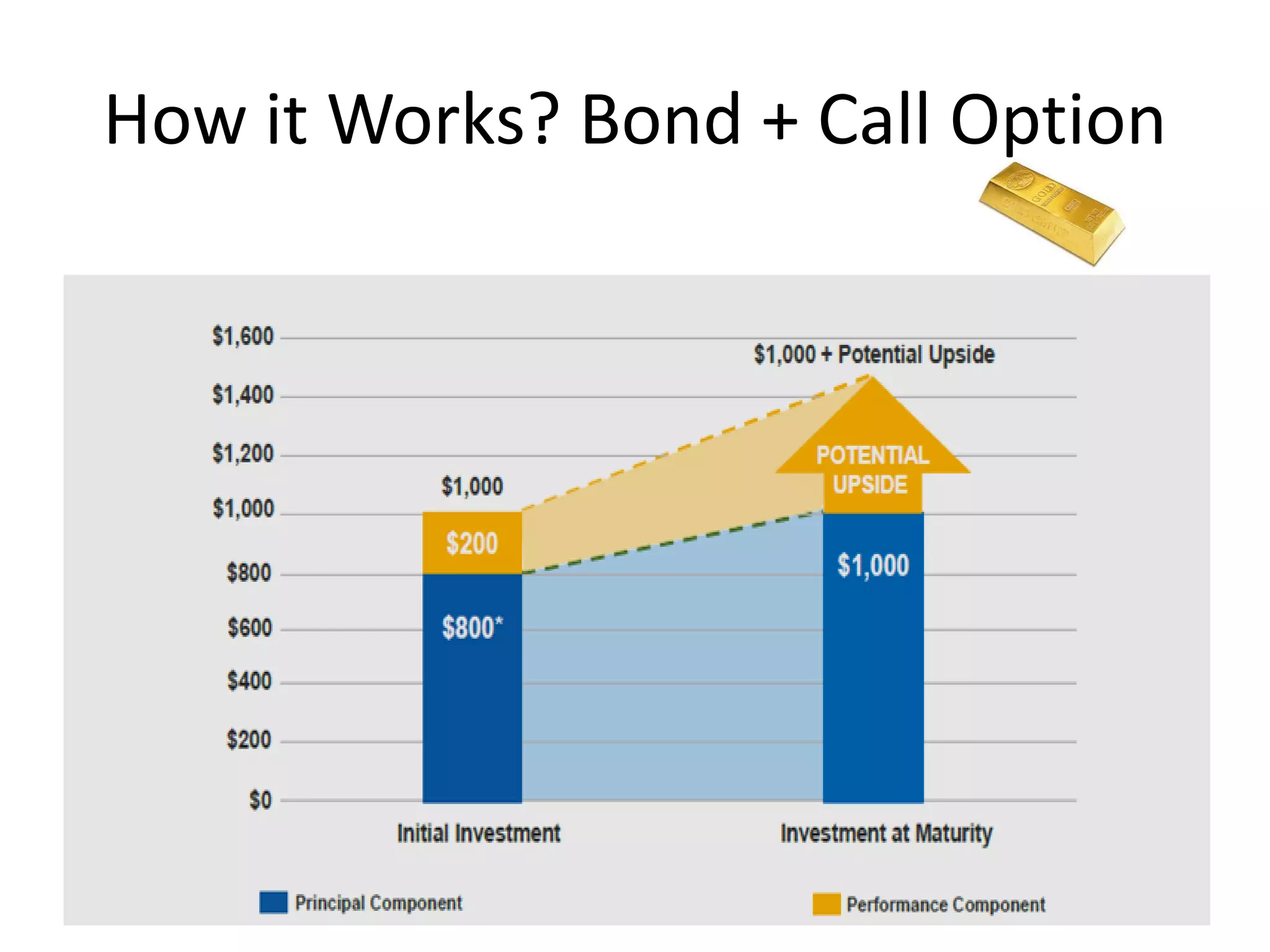
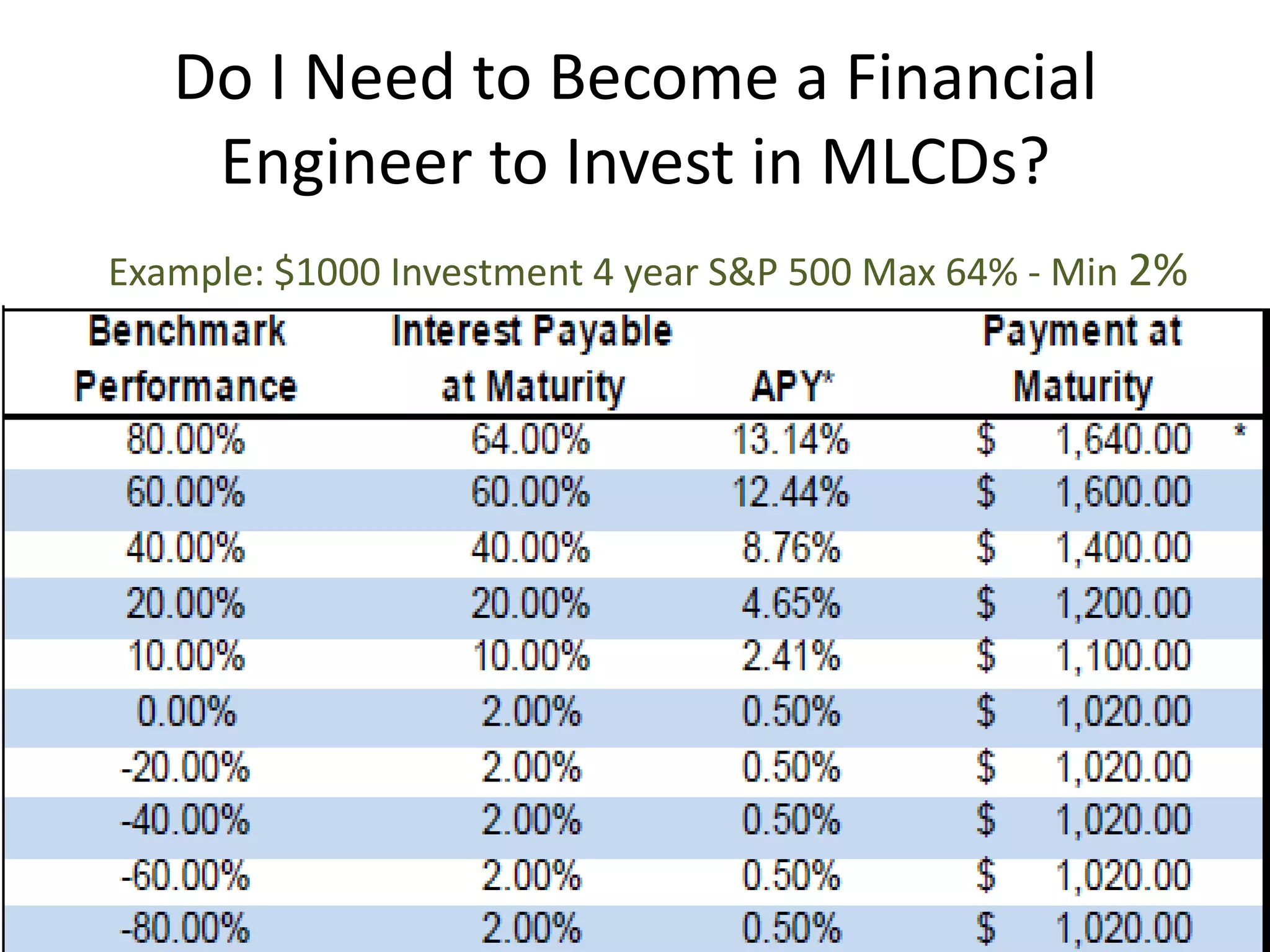
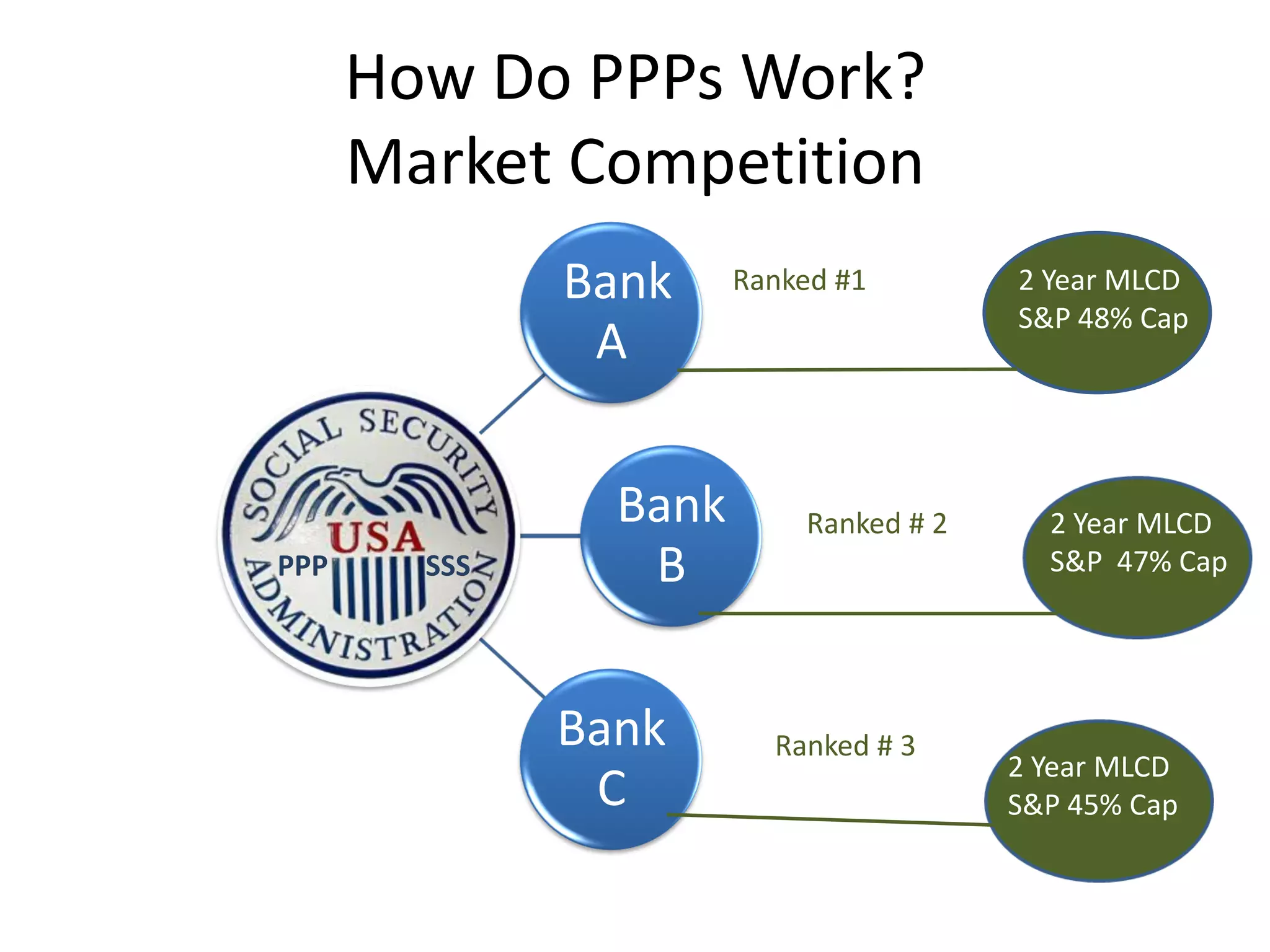
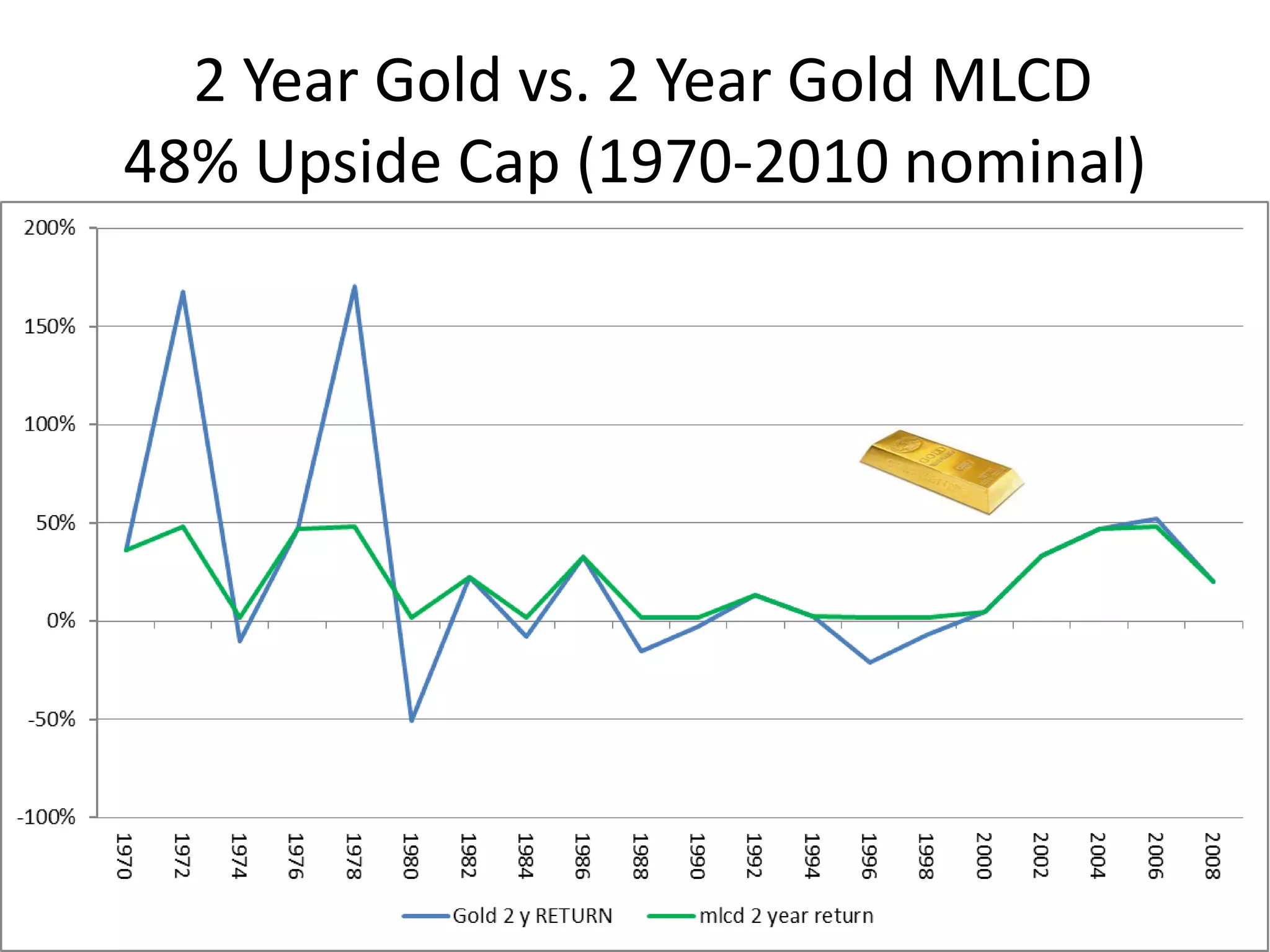
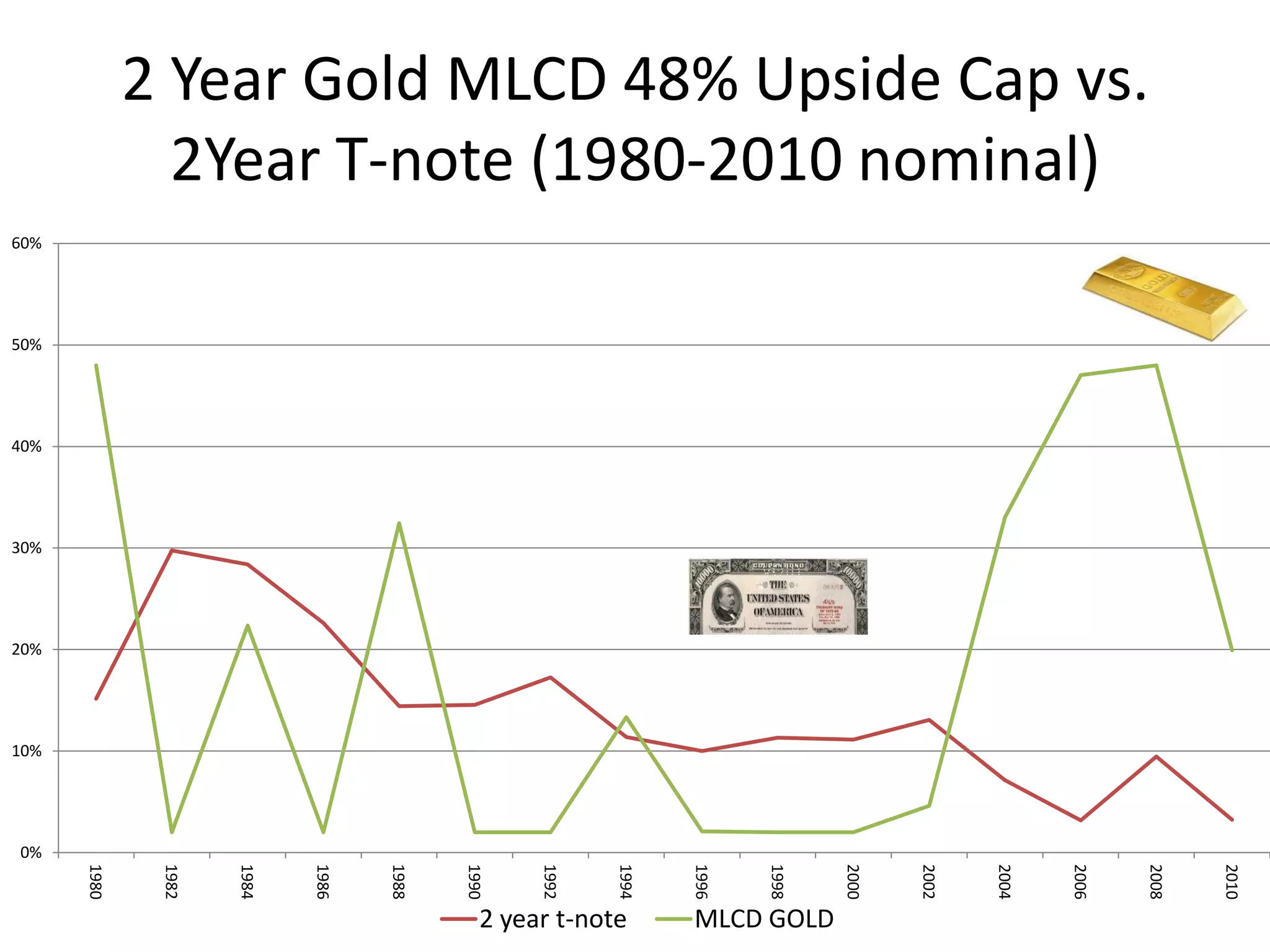
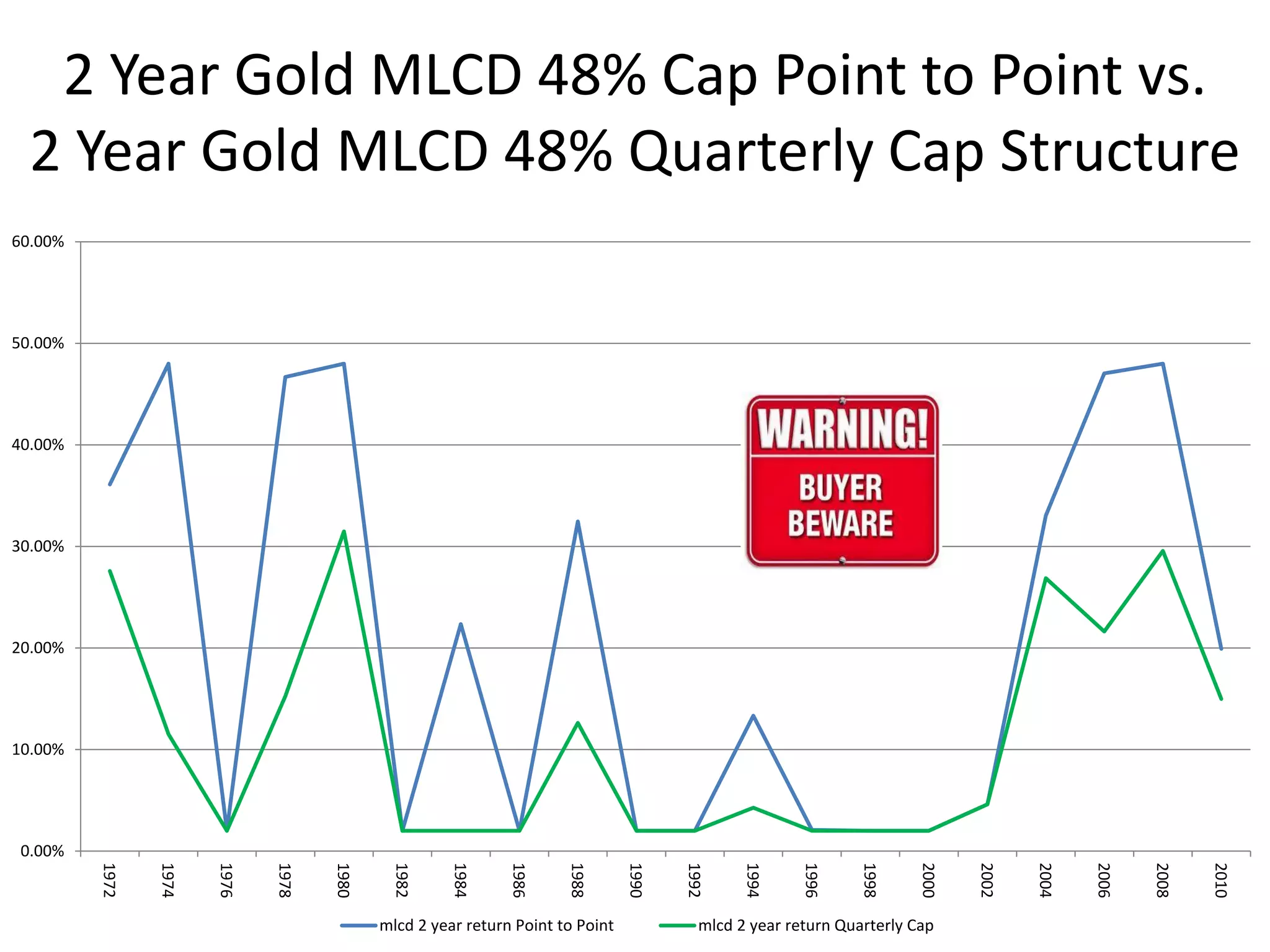
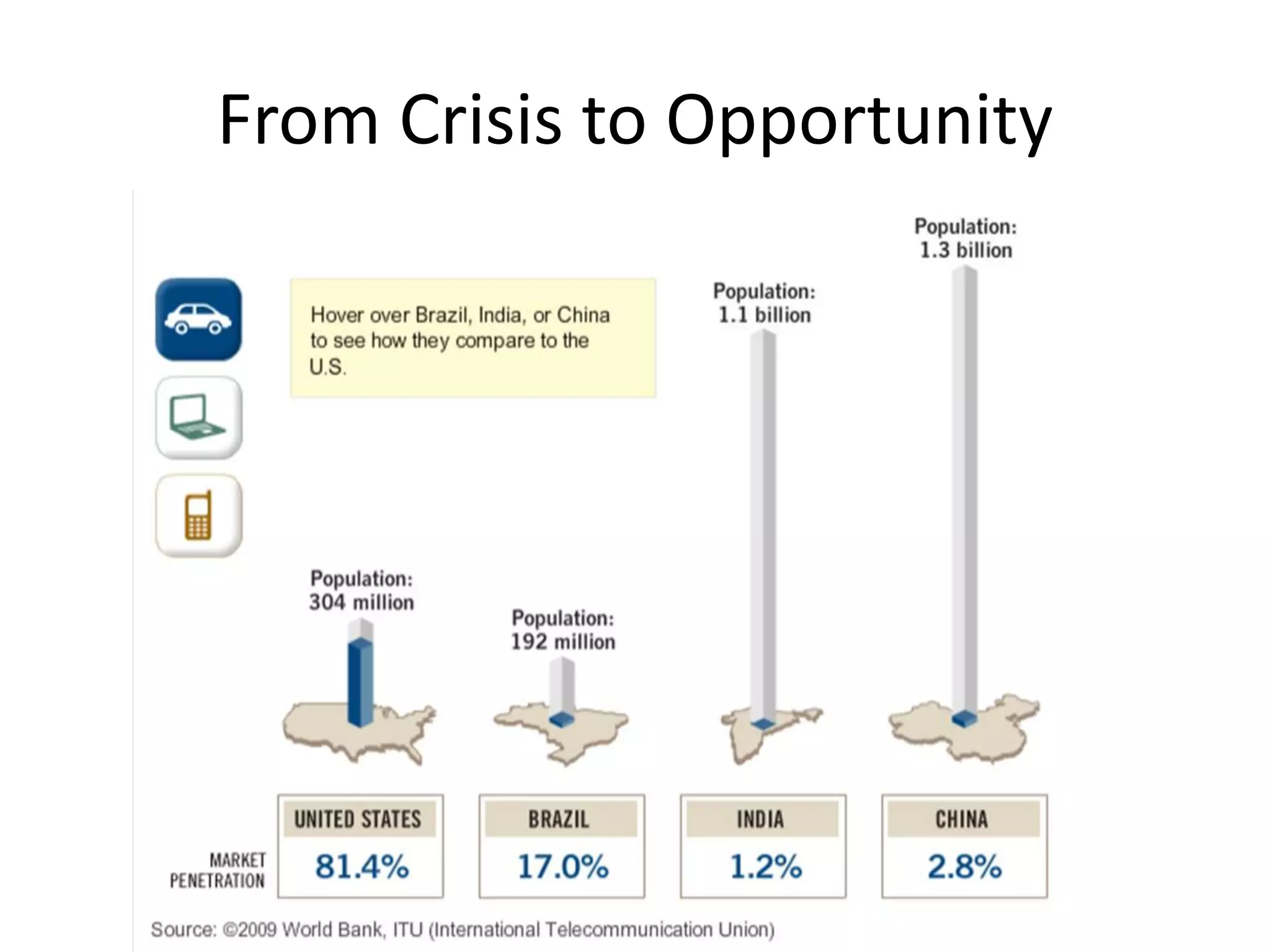
This document discusses options for transitioning the U.S. Social Security system to a model of personal public-private social security saving accounts (PPPSSS). It outlines some of the key issues with the current Social Security system, such as its unsustainability given demographic trends. It then presents two policy alternatives: maintaining the status quo by raising taxes and cutting benefits, or transitioning to a PPPSSS model where half of Social Security taxes are invested in retirement accounts that offer principal protection, upside potential from market participation, and FDIC insurance. The document provides examples of how PPPSSS accounts would work using market-linked certificate of deposits tied to market indexes.