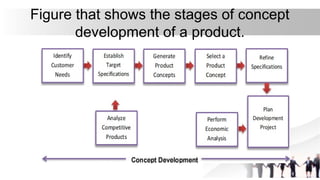
This document outlines the personal entrepreneurial competencies (PECs) essential for effective entrepreneurship, emphasizing the importance of skills such as creativity, discipline, decision-making, and good planning. It provides learning objectives and activities designed to help students identify and assess these competencies, particularly in the context of food processing businesses. Additionally, it covers product development and marketing strategies, including the significance of branding and conducting SWOT analysis to evaluate business opportunities.