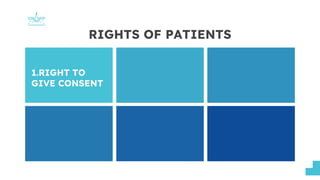
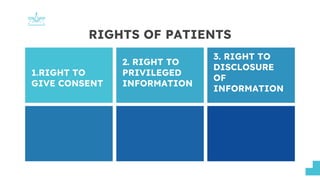
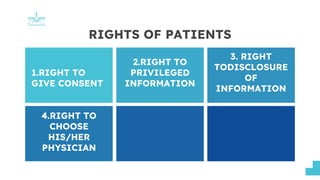
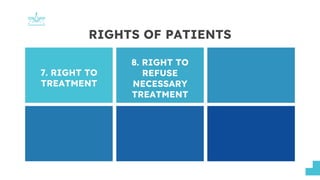
This document discusses patients' rights. It outlines several key rights that patients have, including the right to give consent for treatment, the right to privileged medical information, and the right to disclosure of information from their medical records. The document also discusses patients' rights to choose their own physician, to privacy, to their religious beliefs, and to refuse treatment. It provides sources for these rights, such as the Bill of Rights, Hippocratic Oath, and medical ethics codes. The presentation aims to review patients' rights and address dilemmas in upholding them in clinical settings.