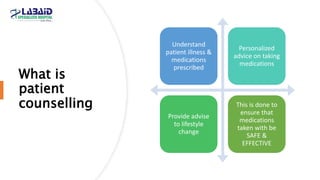
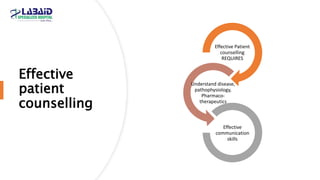
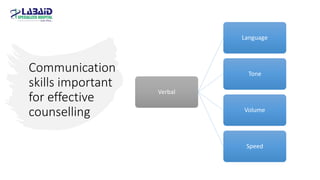
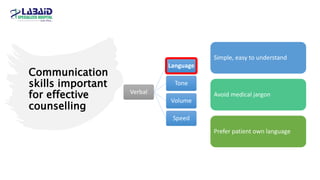
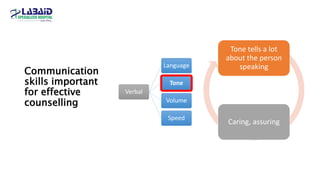
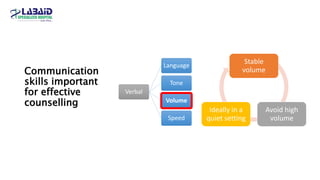
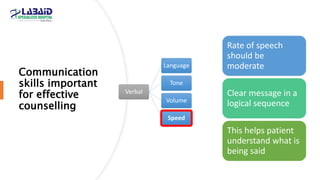
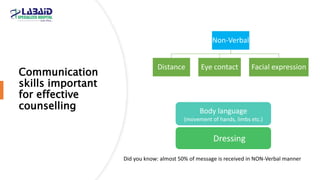
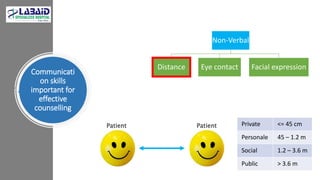
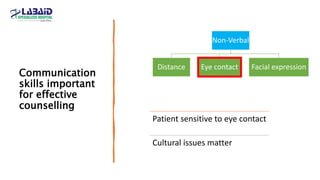
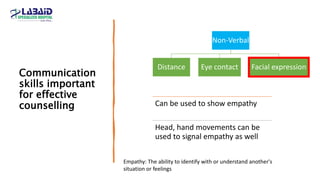
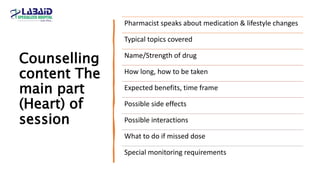
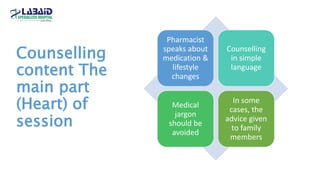
The document discusses the importance of effective patient counselling, emphasizing communication skills and the need for pharmacists to provide clear information and support regarding medications. It outlines steps in the counselling process, including preparing and conducting sessions, and highlights the implications of inadequate counselling on patient health. The text also suggests prioritizing specific patient groups for counselling and utilizing educational aids for better understanding.