Hypernatremia is defined as a plasma sodium level greater than 145 meq/L and is associated with high mortality rates, particularly in hospitalized and ICU patients. The condition can arise from water deficits or excessive sodium, with various risk factors including age and impaired thirst mechanisms. Treatment involves careful management of the sodium levels to avoid rapid shifts, with oral or intravenous administration of water and monitoring of underlying causes.





![• Hypernatremia due to water loss
The loss of water must occur in excess of electrolyte losses in order to
raise [Na].
Nonrenal water loss may be due to evaporation from the skin and
respiratory tract (insensible losses) or loss from the GI tract.
Diarrhea is the most common GI cause of hypernatremia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-6-320.jpg)


![• Hypernatremia secondary to nonosmotic urinary water loss is usually
caused by
(a) impaired vasopressin secretion (central diabetes insipidus [CDI]) or
(b) resistance to the actions of vasopressin (nephrogenic diabetes
insipidus [NDI]).
Partial defects occur more commonly than complete defects in both
types.
Patients with DI generally do not develop hypernatremia if they are able
to maintain fluid intake adequate to compensate for the water loss.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-9-320.jpg)






![Clinical Presentation
• Hypernatremia results in contraction of brain cells as water shifts to
attenuate the rising ECF osmolality.
• Thus, the most severe symptoms of hypernatremia are neurologic,
including altered mental status, weakness, neuromuscular irritability,
focal neurologic deficits, and, occasionally, coma or seizures. The
presence of encephalopathy is a poor prognostic sign in hypernatremia,
and carries a mortality rate as high as 50%.
• As with hyponatremia, the severity of the clinical manifestations is
related to the acuity and magnitude of the rise in plasma [Na].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-17-320.jpg)
















![• Chronic asymptomatic hypernatremia
The risk of treatment-related complication is increased due to the
cerebral adaptation to the chronic hyperosmolar state, and the plasma
[Na] should be lowered at a more moderate rate (between 5 and 8
mEq/L/d).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-36-320.jpg)

![Traditionally, correction of hypernatremia has been accomplished by
calculating free water deficit by the equation:
Free water deficit = {([Na] - 140)/140} X (TBW)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-38-320.jpg)
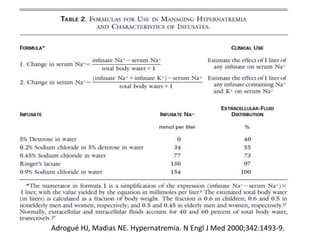
![• Alternatively,
• The change in [Na] from the administration of 1000 ml fluid can be
estimated as follows:
• Because hypernatremia suggests a contraction in water content, TBW is
estimated by multiplying lean weight (in kilograms) by 0.5 in men (rather
than 0.6) and 0.4 in women.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypernatremia-240421111345-4f9762e6/85/patient-approach-and-algorithm-in-hypernatremia-pptx-39-320.jpg)