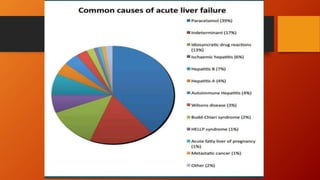
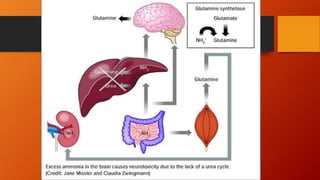
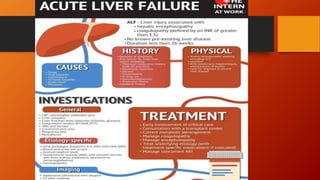
- Acute liver failure (ALF) is characterized by rapid loss of liver function and development of hepatic encephalopathy, coagulopathy, and multi-organ failure within 26 weeks. Common causes include drug overdoses, viruses, and inherited metabolic disorders.
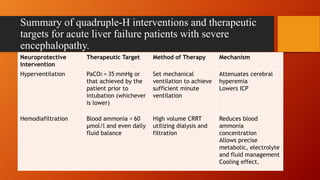
- Management involves global organ support, with a focus on circulatory resuscitation, renal replacement therapy, respiratory support, infection prophylaxis, and gastrointestinal protection. Cerebral protection measures aim to prevent intracranial hypertension through temperature control, normocapnia, mannitol, hypernatremia, and hypothermia if needed.
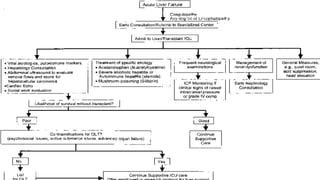
- Patients meeting criteria for liver transplantation should be transferred urgently to a specialized liver unit for assessment