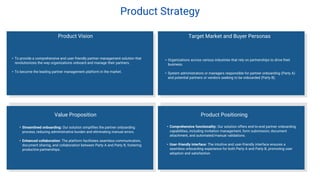
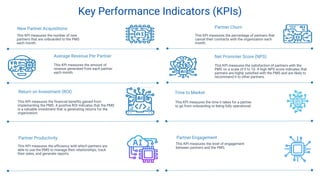
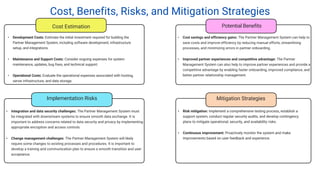
The document proposes a Partner Management System to automate and streamline the partner onboarding process. It discusses problems with manual onboarding including inefficiency and errors. The proposed system would reduce costs, improve accuracy and security by automating tasks like form submission and validation. It provides an overview of the solution, including features like collaboration tools and integration with other systems. Market opportunities and competitors are also analyzed.