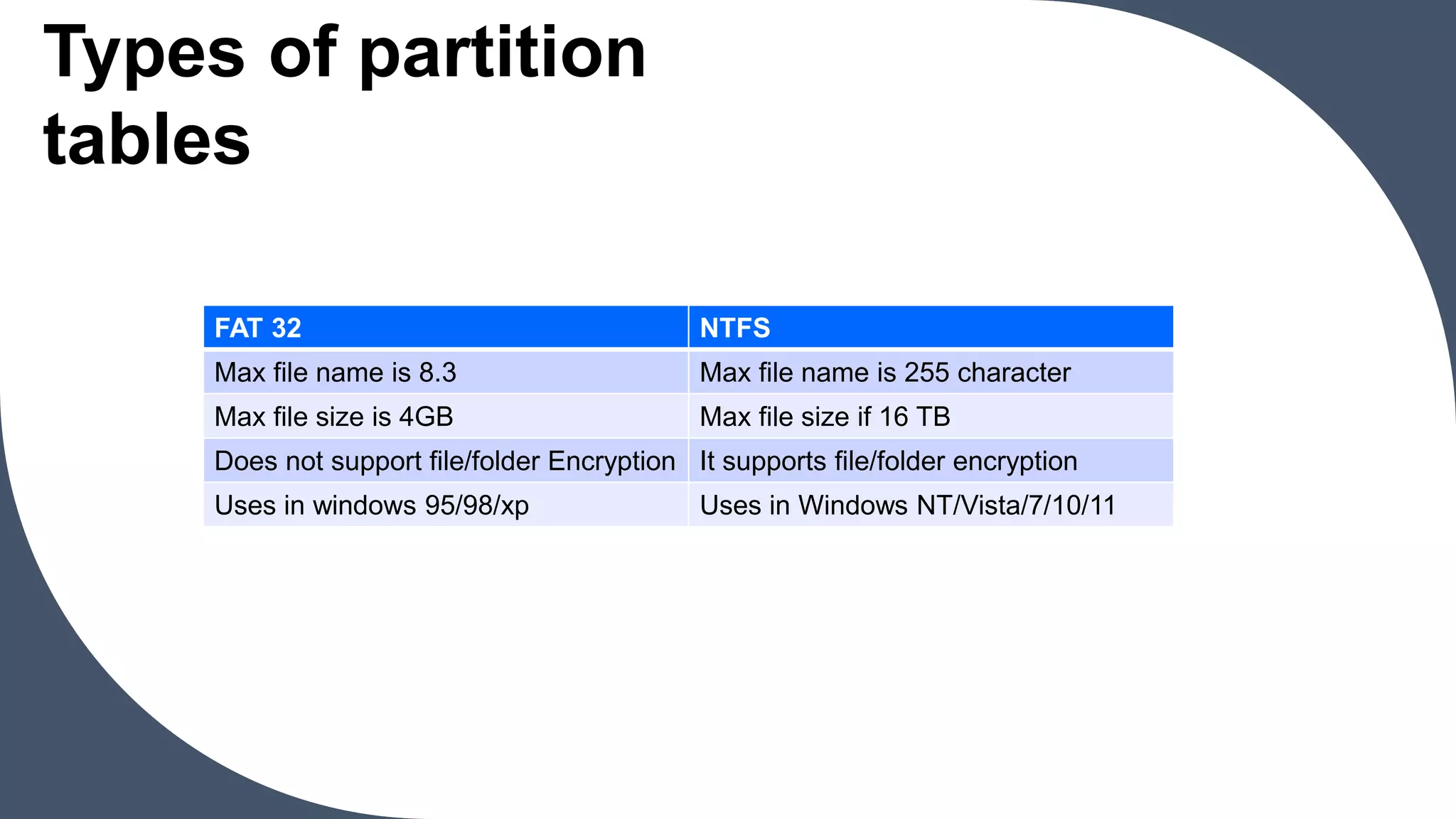
Formatting creates a file system on disk partitions by defining tracks and sectors. A track is a physical division of data on a disk, a sector subdivides tracks, and clusters group sectors to organize files. Disk partitioning logically divides a hard disk's storage space into separate partition or drive areas. Partition table types include FAT32 and NTFS, which support different maximum file names, sizes, and features. MBR partition types are primary, extended, and logical. Partitioning provides benefits like organizing data, improving performance, and facilitating backup and restore.