Embed presentation
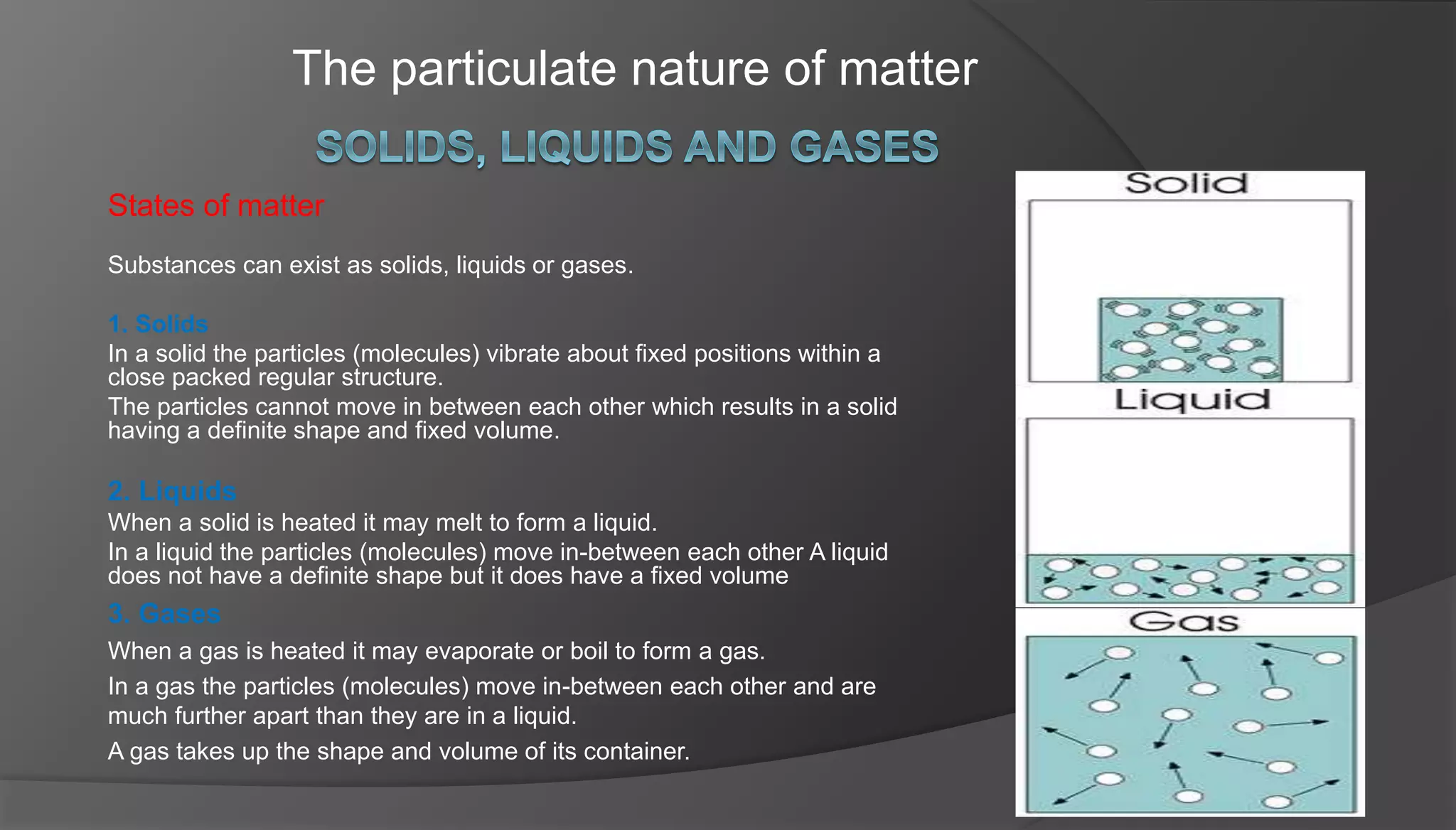
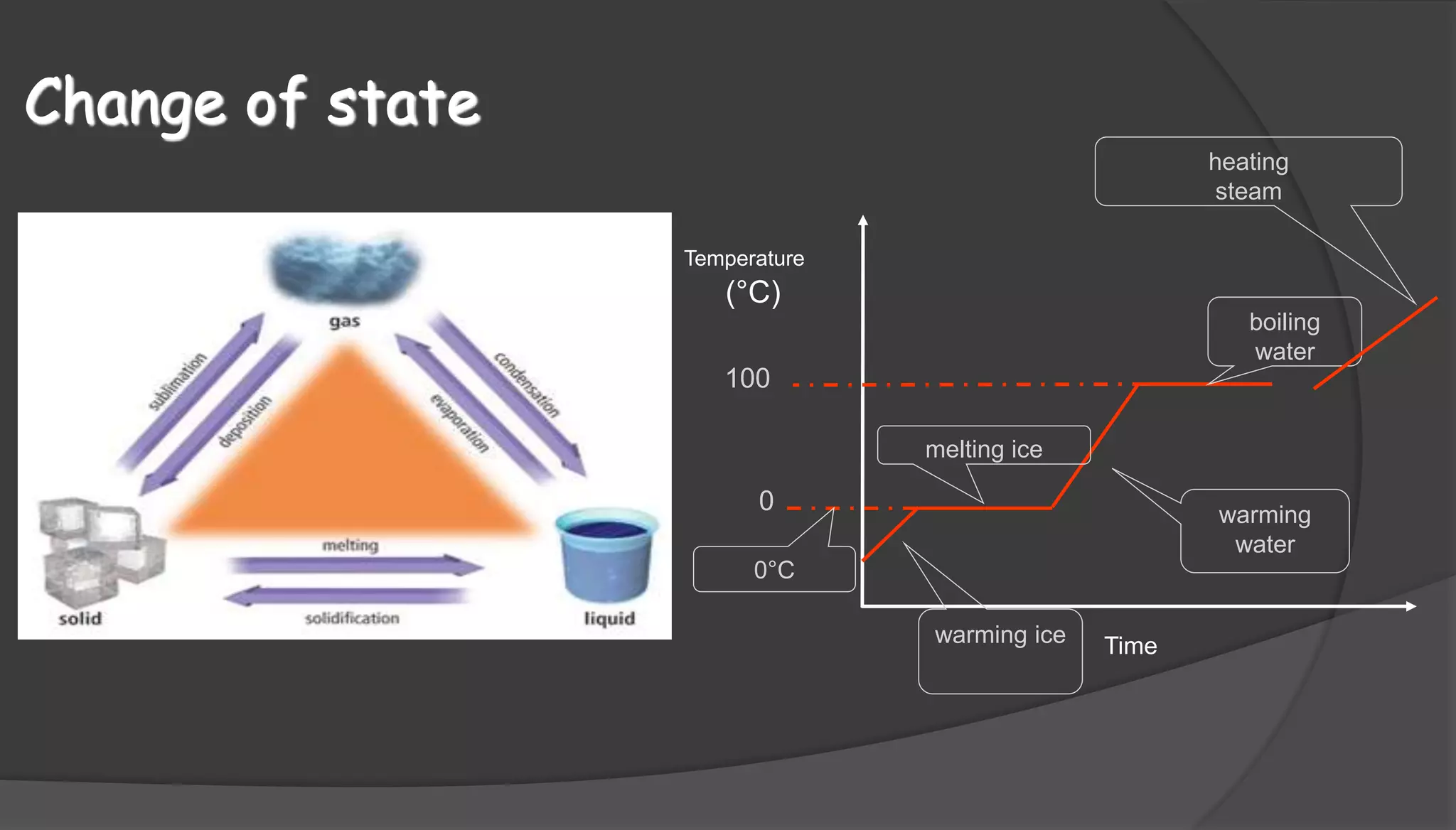
The document discusses the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that in solids, particles vibrate in fixed positions and have a definite shape and volume. In liquids, particles move between each other but the liquid has a fixed volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and fill the shape and volume of their container. The document also includes a diagram showing the changes in state from solid to liquid to gas that occur with increasing temperature over time.

