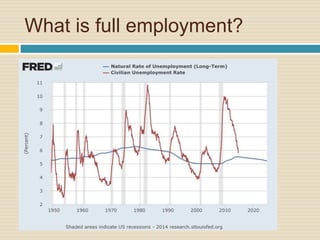
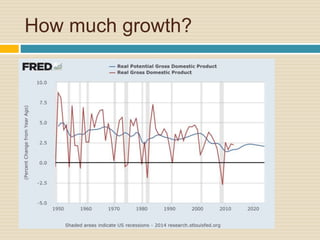
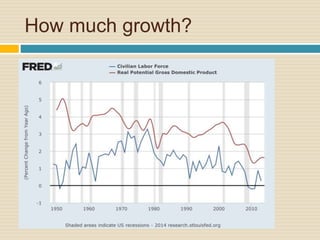
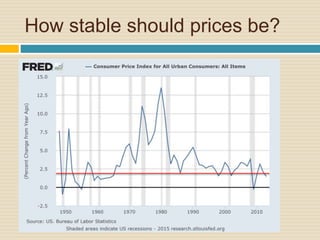
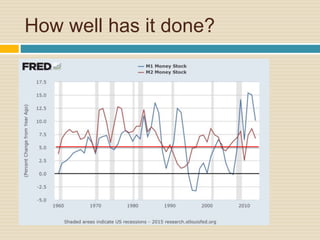
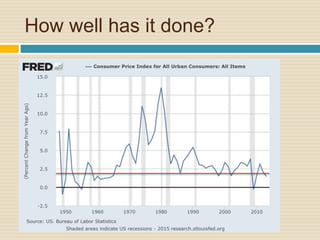
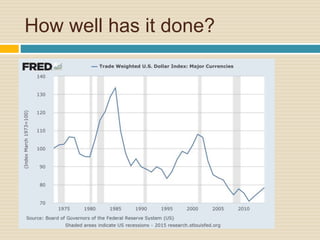
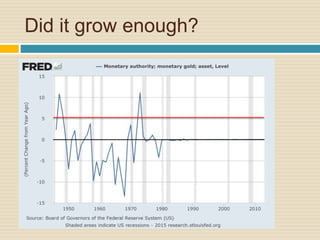
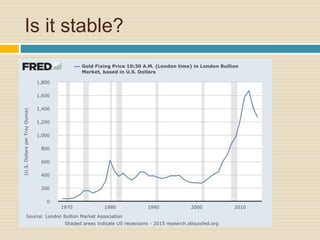
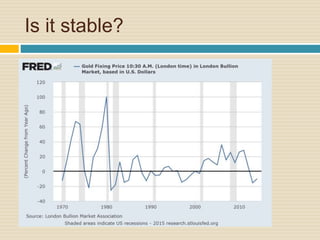
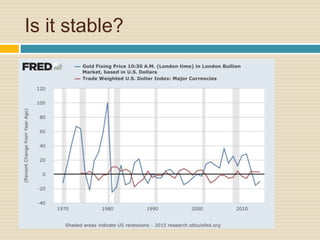
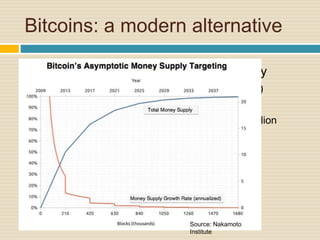
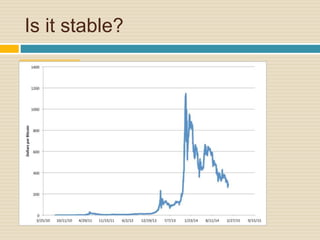
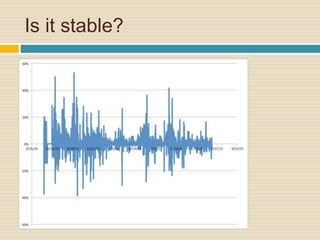
This document discusses different types of money and inflation. It compares fiat money, gold, and bitcoins. For fiat money, the pros are that it is easy to achieve stable growth by increasing the money supply, but the con is it is easy to grow the money supply too quickly and lose trust. For gold, the pros include easier maintenance of trust, but the cons are that it is difficult to increase the supply at a fast enough rate and costly to use as money. For bitcoins, the pros are that it is decentralized with no central authority and a limited supply set by an algorithm, but the cons include not growing supply enough and not being well established. The document raises questions about defining full employment, the appropriate