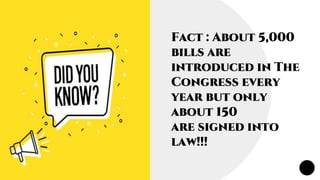
This document provides information about the process of introducing and passing bills in the Indian Parliament. It discusses the different types of bills - money bills, ordinary bills, and constitutional amendment bills. A bill is first introduced in the Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha and goes through several readings where it is discussed and can be amended. It then needs to pass both houses of Parliament and receive presidential assent to become a law. The document outlines each stage of this process from introduction of a bill to it becoming an act or law.