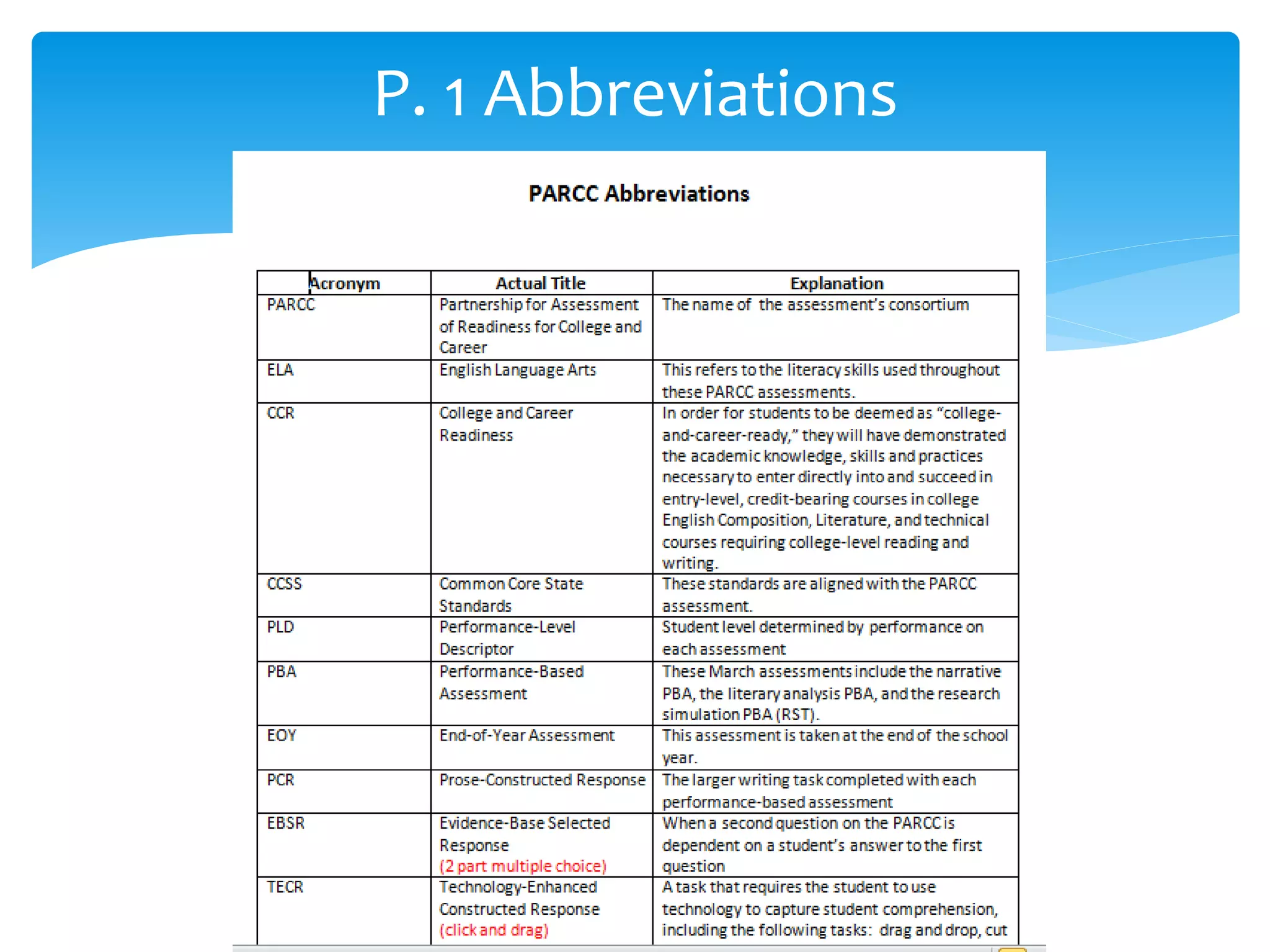
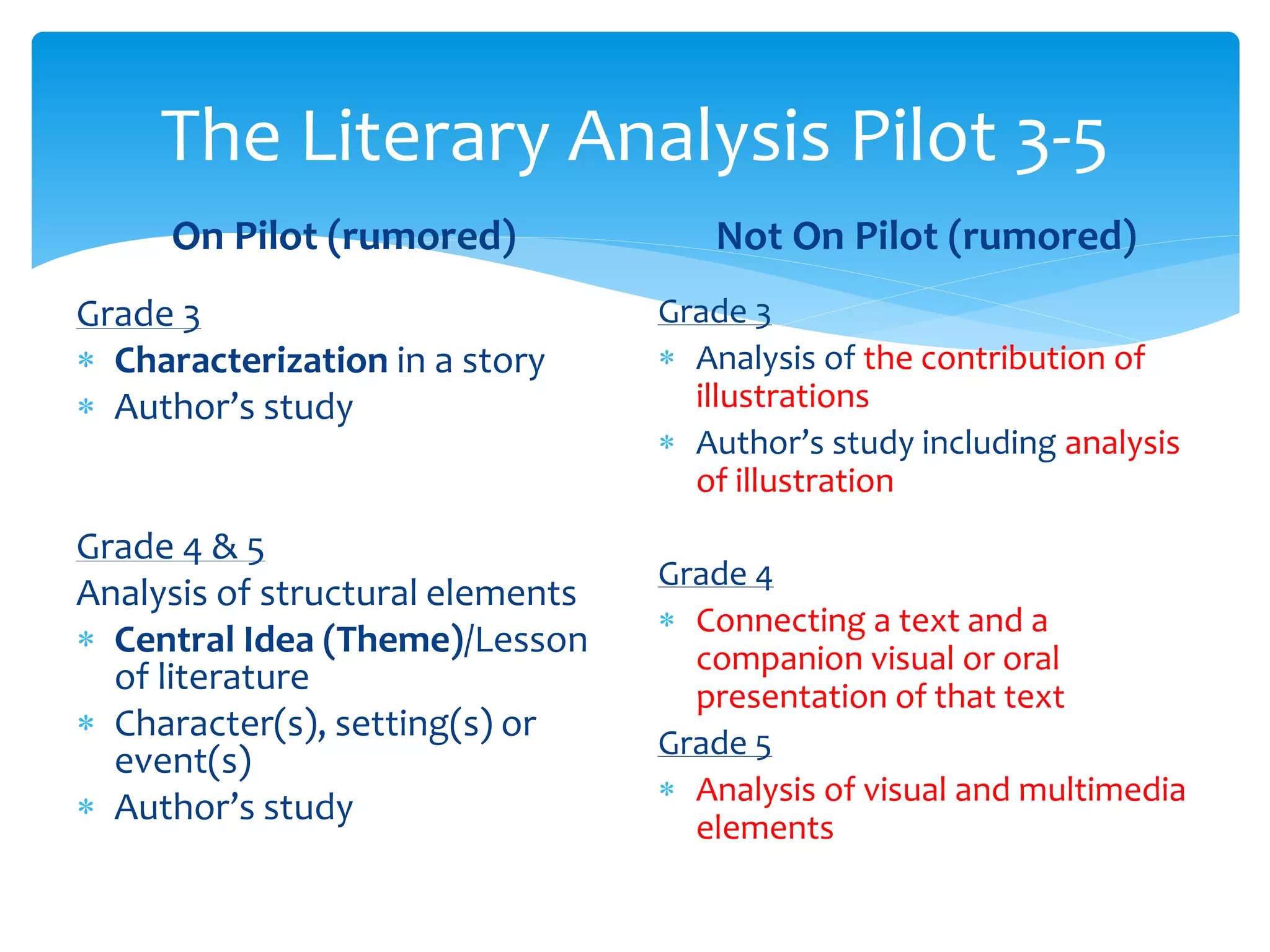
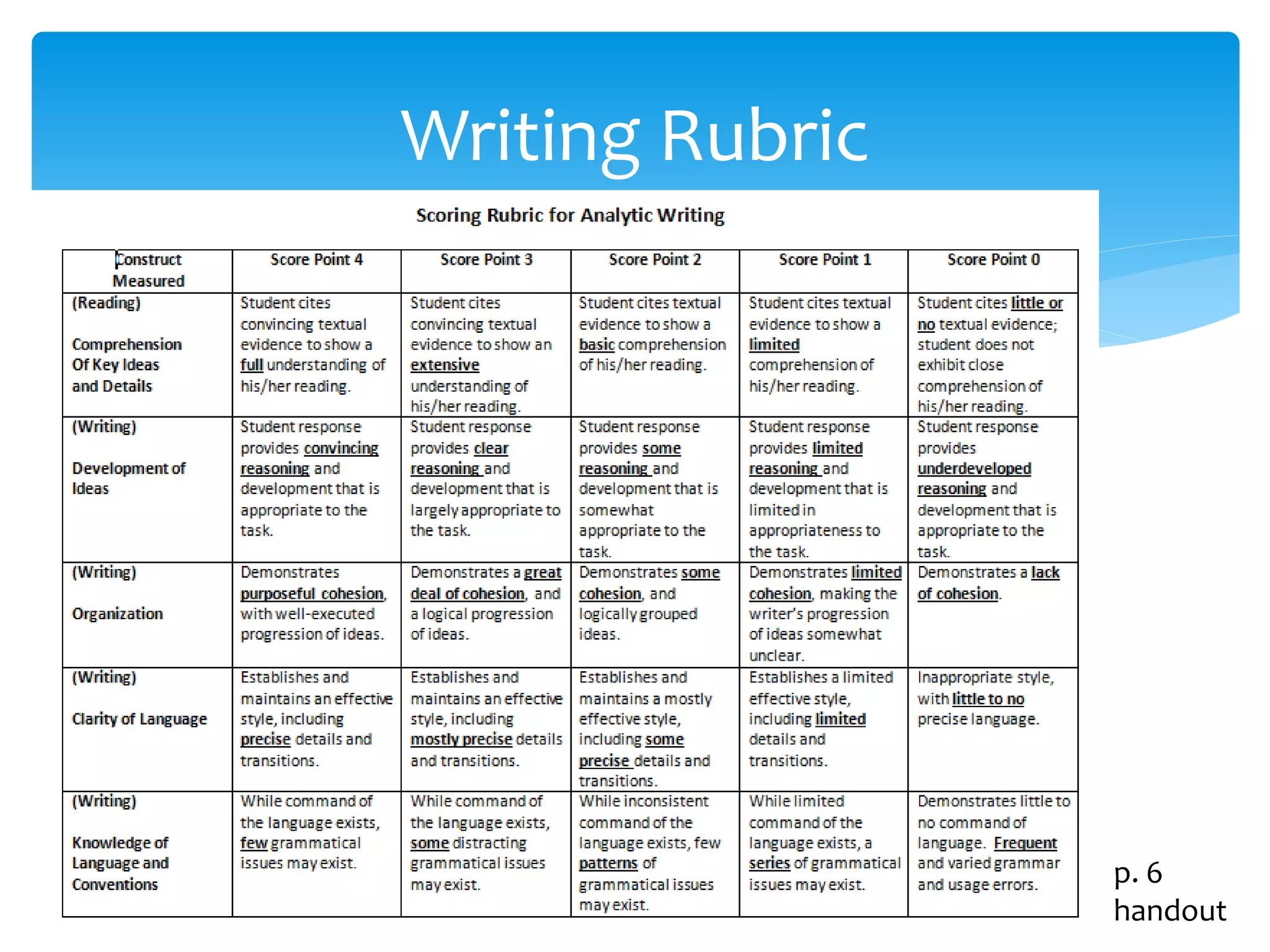
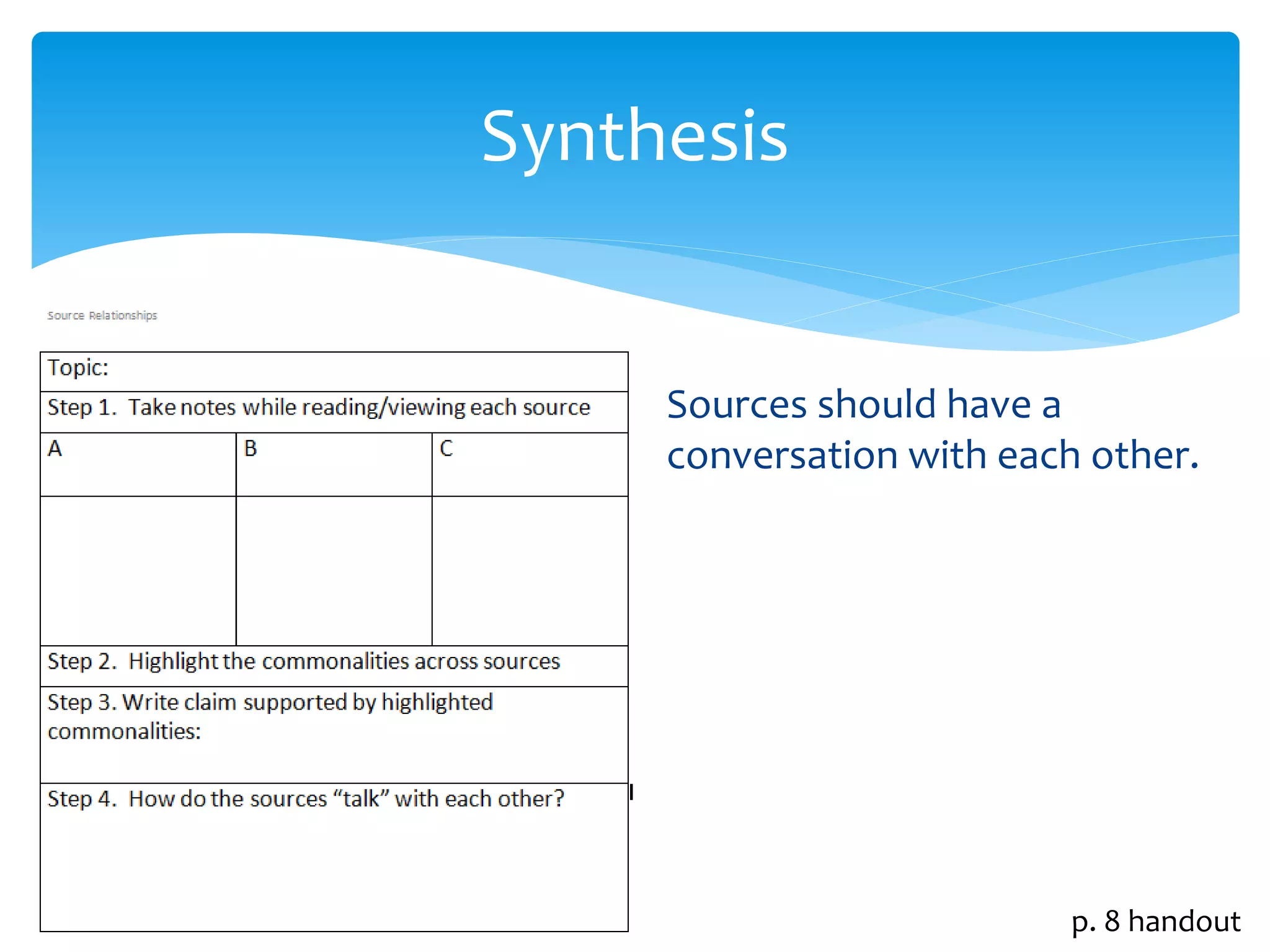
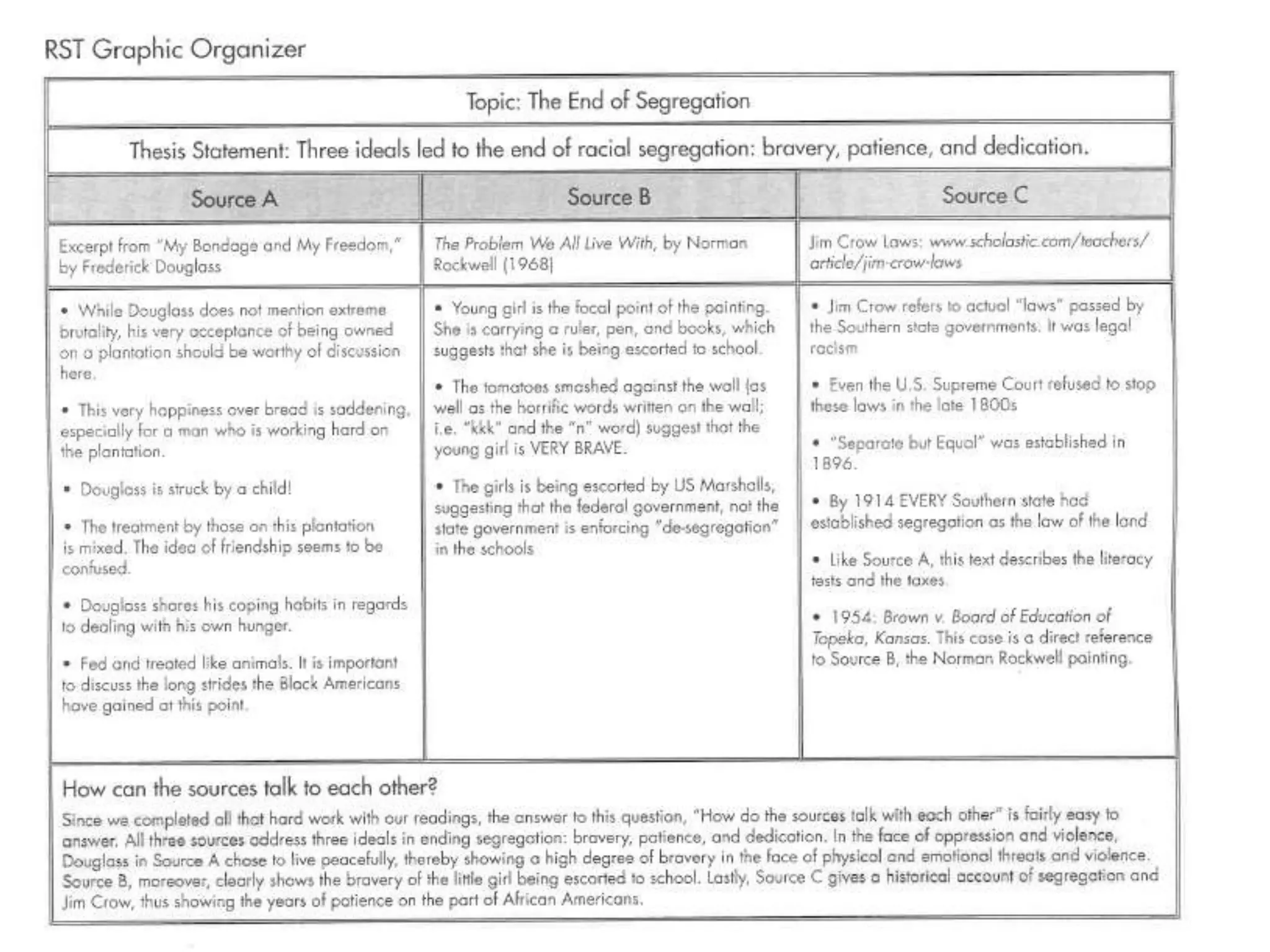
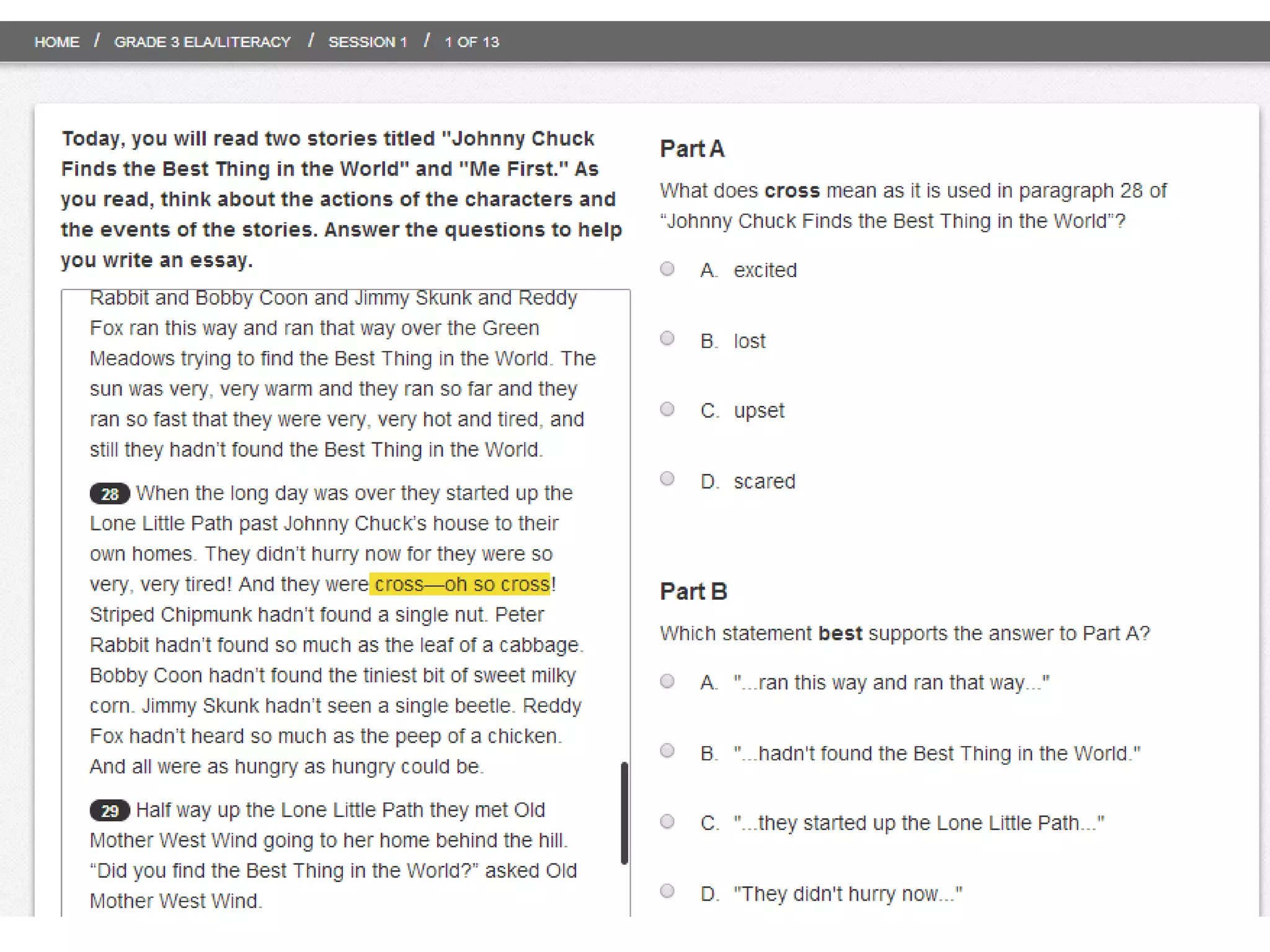
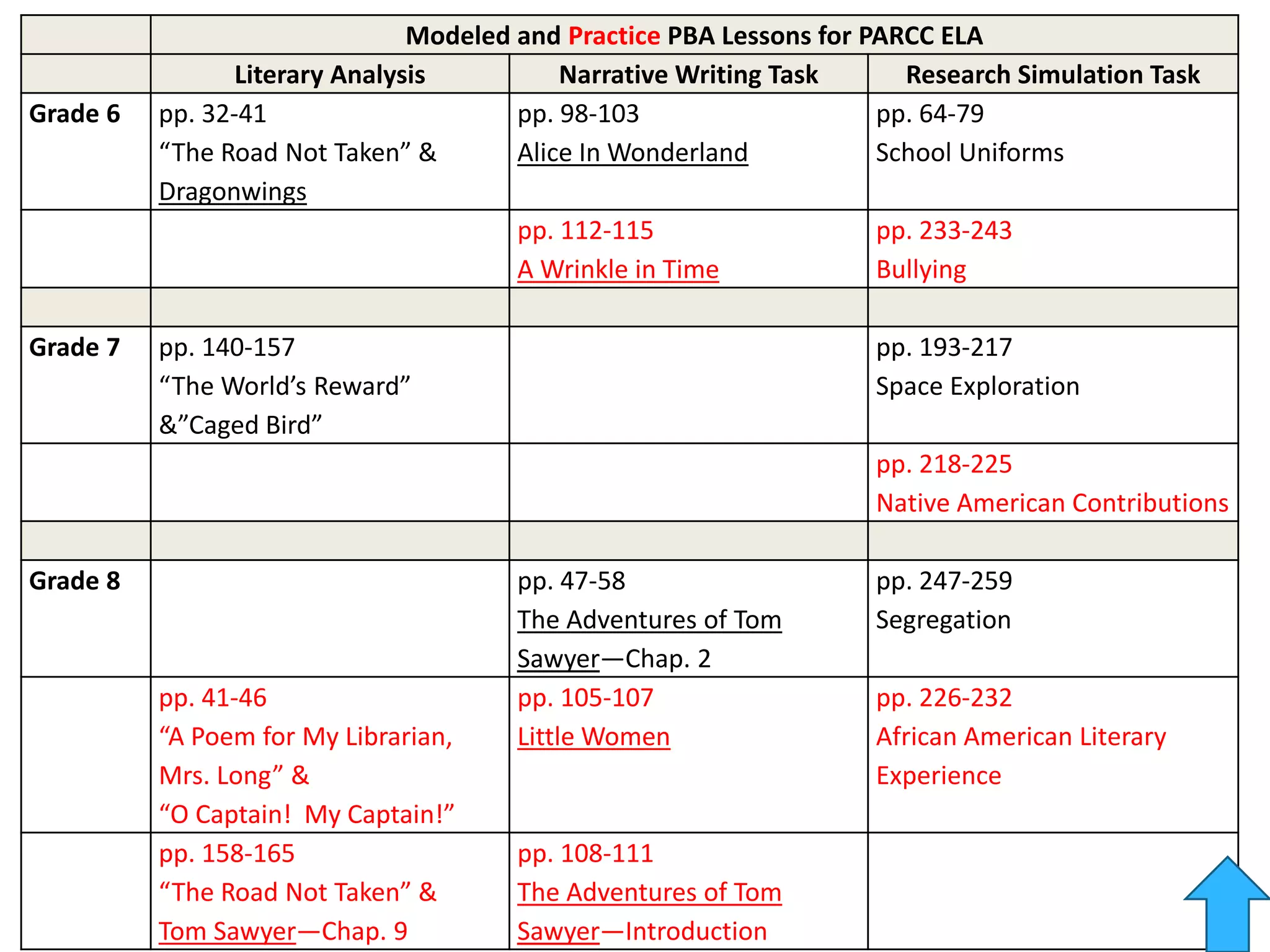
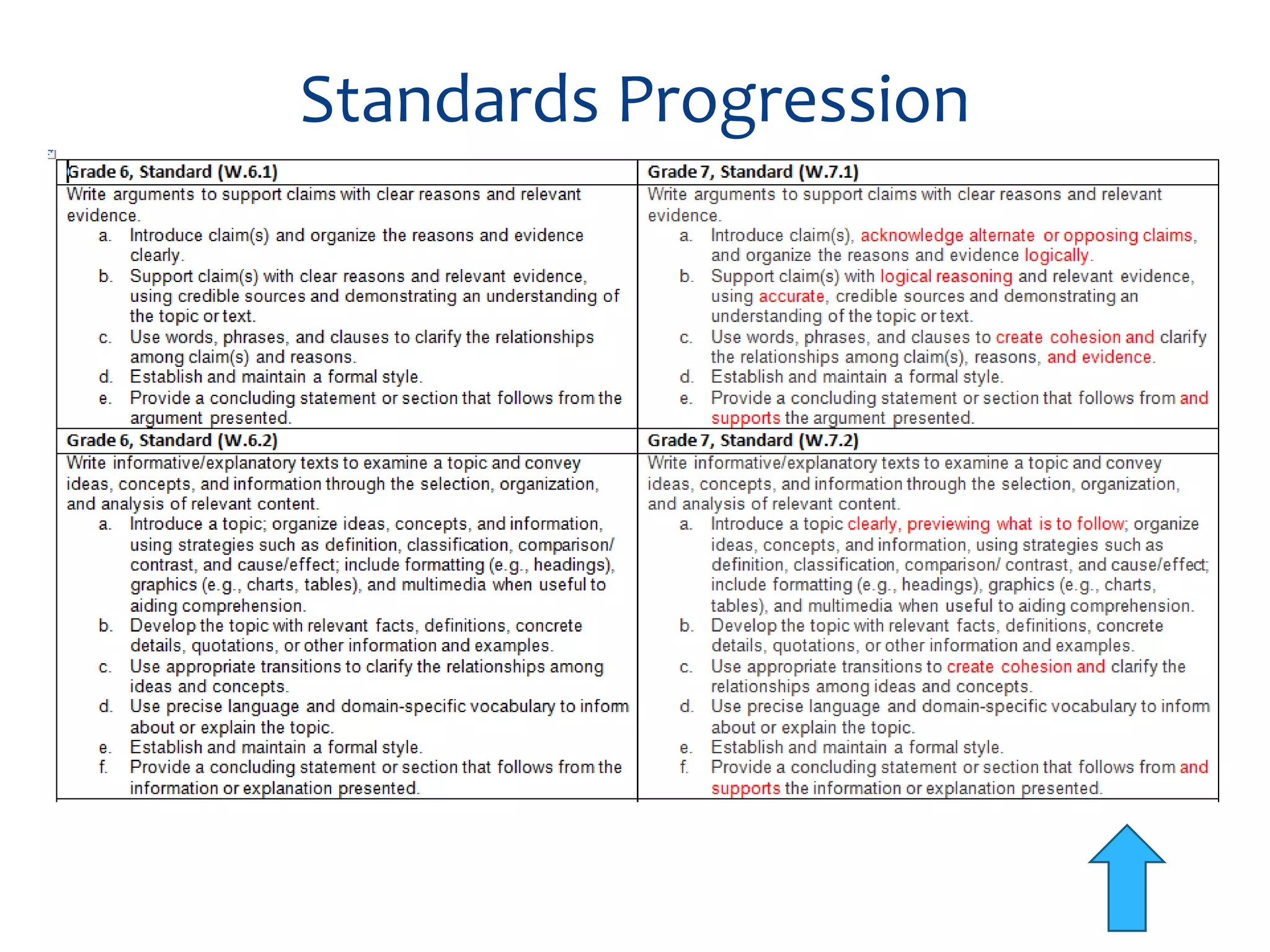
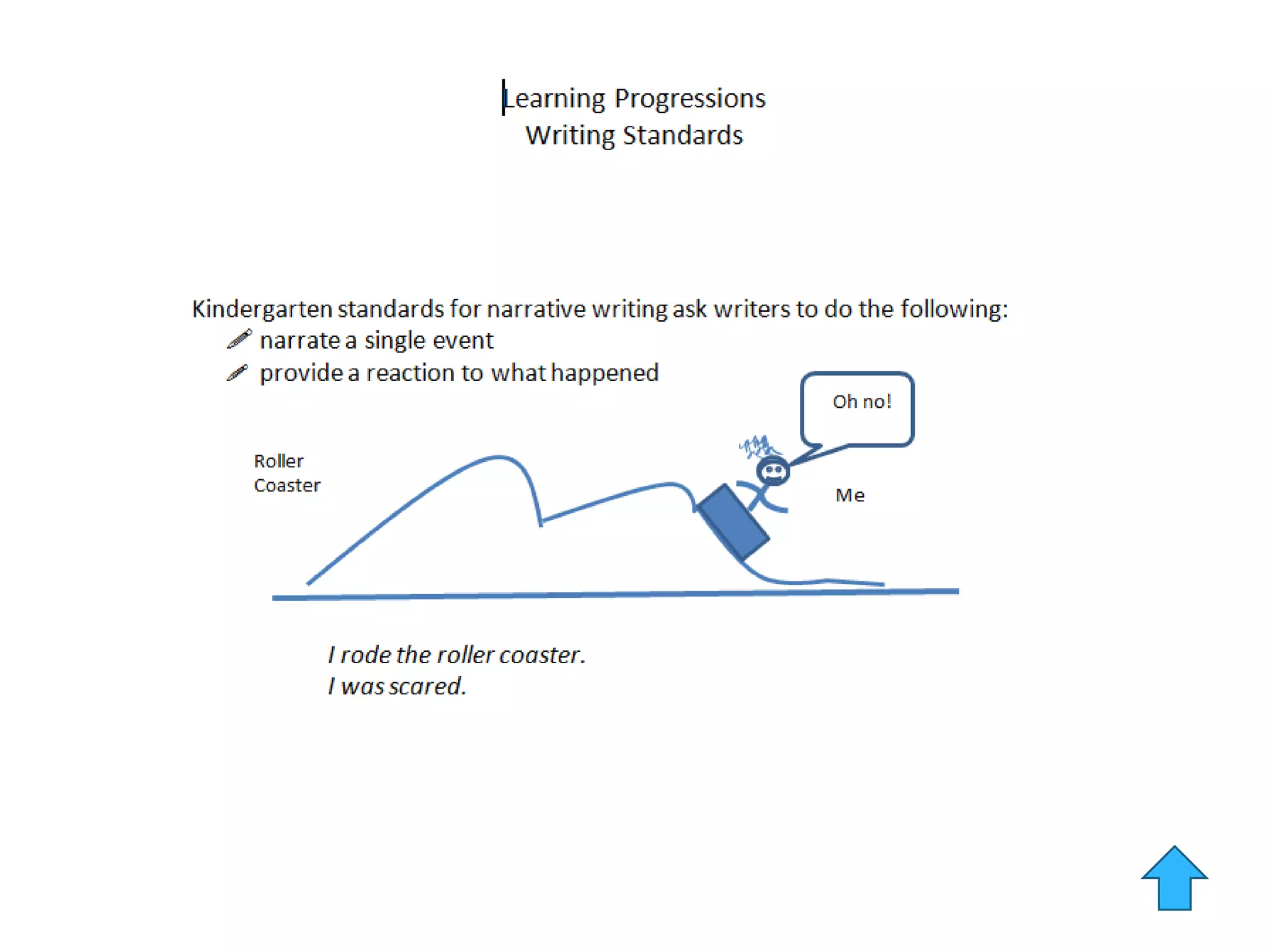
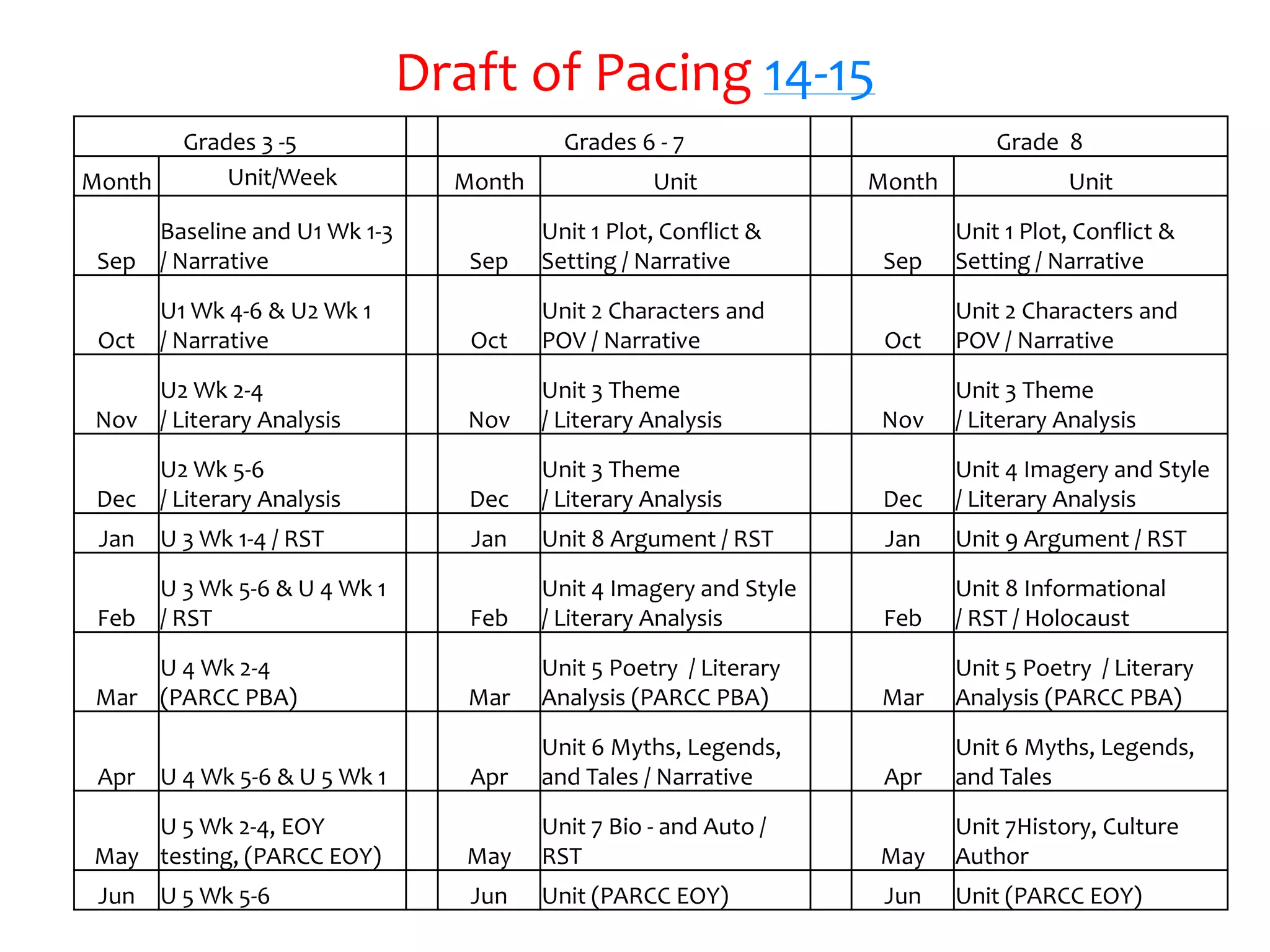
This document provides an overview of the PARCC assessment, including its three main sections - the Literary Analysis Task, Research Simulation Task, and Narrative Task.
It describes the parts of each section, such as multiple choice questions, constructed response items, and writing prompts. It also provides sample passages and prompts that could be used for practice. Suggestions are made for classroom instruction, such as using shared writing lessons and exemplar essays. Key terms like analyze, compare and contrast are emphasized.