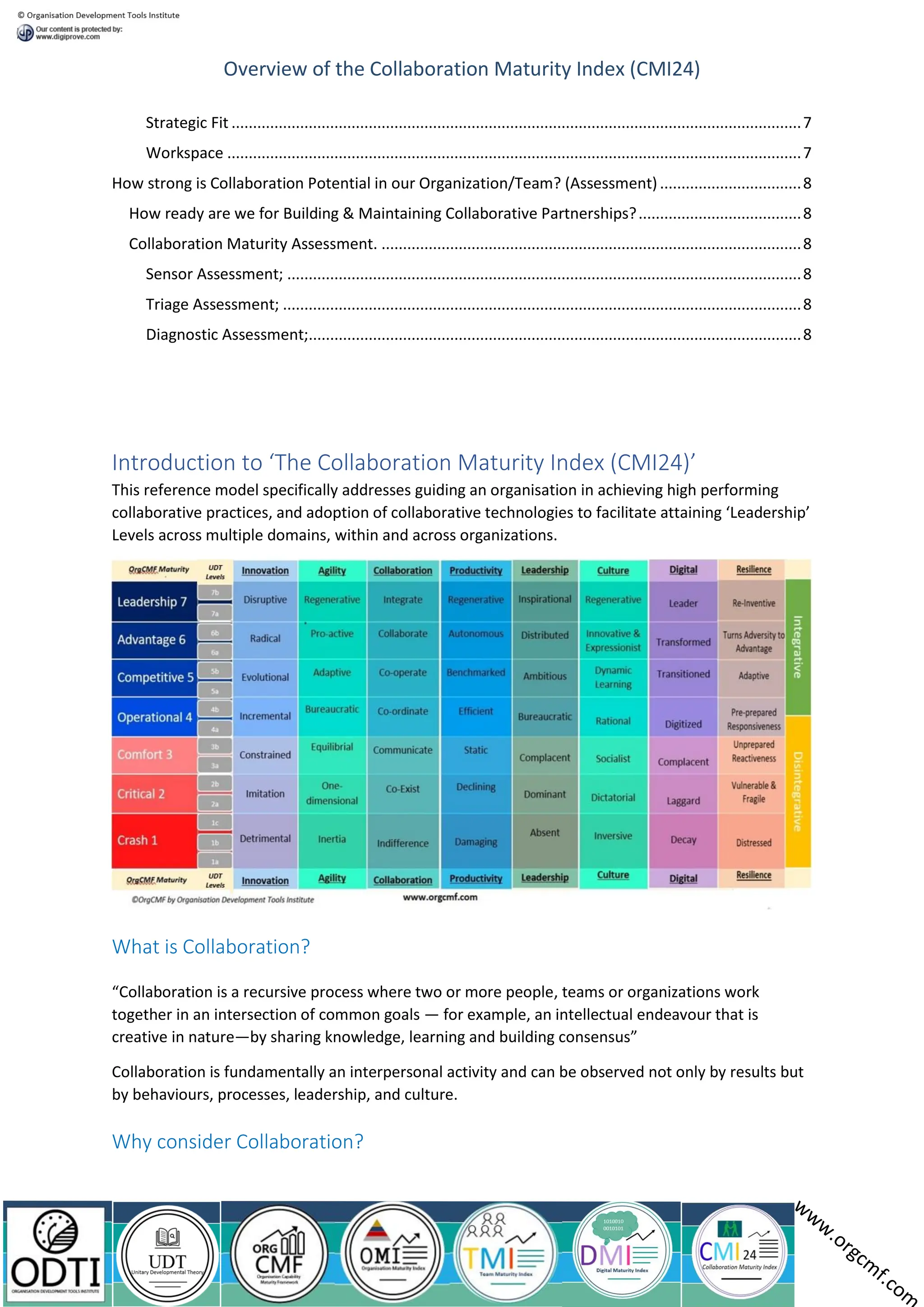
The document outlines the Collaboration Maturity Index (CMI24), a framework designed to assess and improve collaborative practices and technologies within organizations. It emphasizes the importance of interpersonal dynamics, trust, and effective communication in facilitating successful collaboration while addressing common challenges faced by organizations in this domain. The CMI24 provides various assessments to evaluate collaboration potential and readiness, highlighting the necessity of achieving certain maturity levels for effective partnerships.