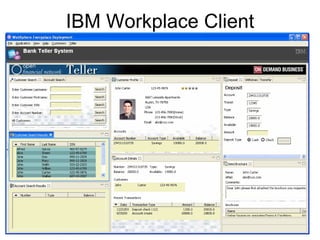
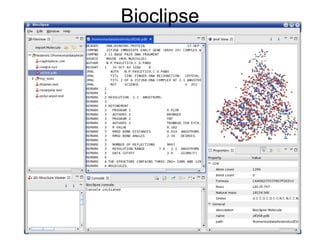
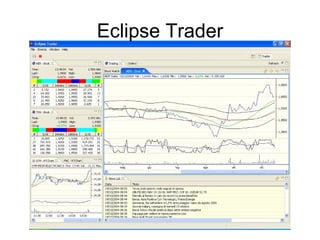
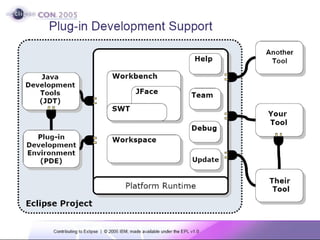
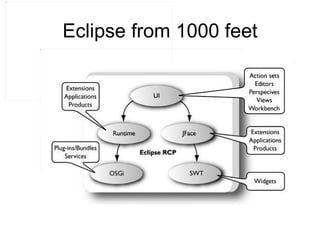
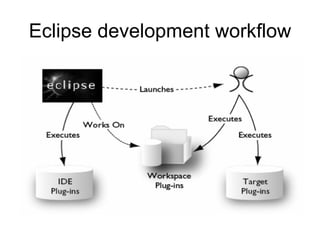
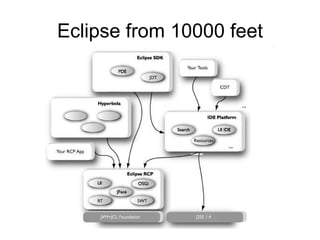
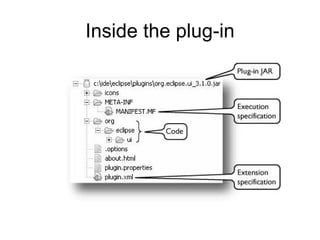
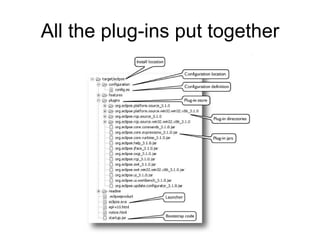
The document discusses the Eclipse Rich Client Platform (RCP) which allows developers to build desktop applications using the Eclipse framework and plug-in architecture. RCP provides reusable UI components, integration with the operating system, and tools for deployment and updating applications. It also describes how plugins extend the functionality of an RCP application and how the plugin architecture works using OSGi and lazy loading of contributions.