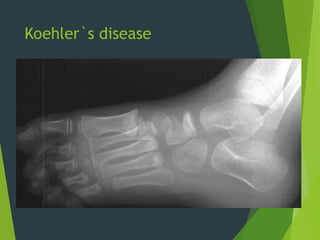
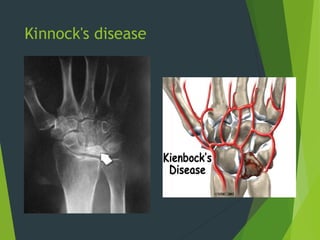
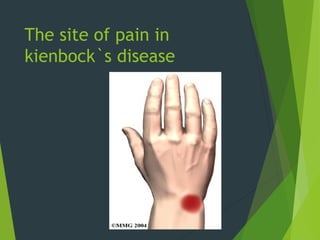
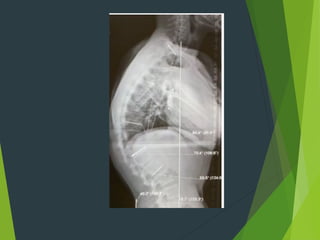
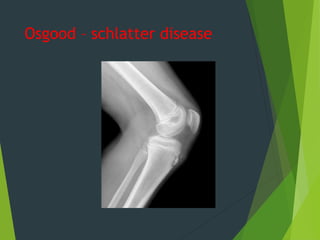
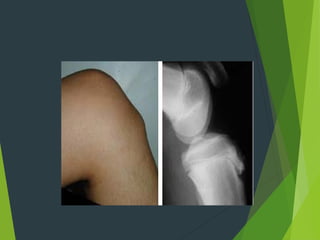
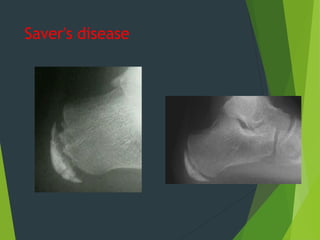
Osteochondrosis refers to bone damage and necrosis caused by trauma or repetitive stress, primarily affecting children and adolescents. It includes various types, such as crushing, pulling, and splitting osteochondritis, each with different clinical presentations and treatments. Management typically involves rest, activity modification, and in some cases, surgical intervention.