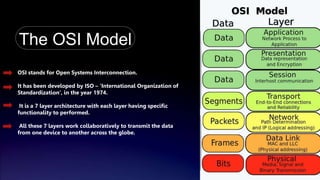
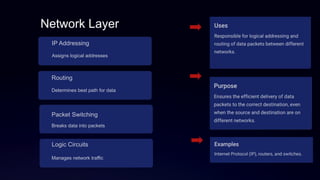
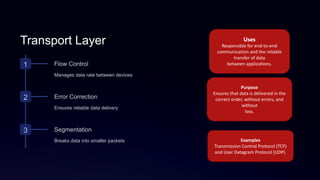
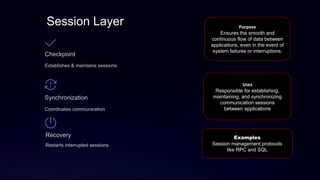
The document discusses the OSI model, developed by the International Organization for Standardization in 1974, detailing its seven-layer architecture that facilitates data transmission across networks. Each layer, including the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layers, has distinct roles such as error correction, addressing, and session management. The summary highlights the interdependence of these layers in ensuring reliable and efficient data communication.