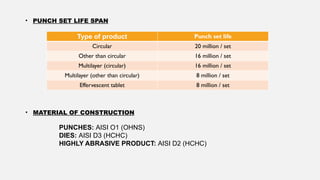
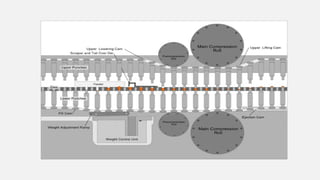
The document outlines the tablet manufacturing process, including various types of tablets such as compressed, sugar-coated, and enteric-coated tablets, as well as the steps involved in their production. It details processes like blending, granulation, and compression, specifying tooling types and their lifespan. Additionally, it discusses evaluation tests for tablets and the purposes and methods of coating.