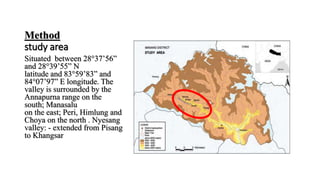
This document discusses the collection of Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Yarsagumba) in the Nyeshang valley of Manang, Nepal. It provides background on Yarsagumba, including that it grows above 3,500 meters in the Himalayas and is used to treat various diseases. The objective and methods of the study are described. Key findings include that the best areas for collection are between 3,500-5,000 meters, and that harvest has declined significantly in recent years due to overharvesting and habitat destruction. The conclusion emphasizes the need for sustainable practices like minimizing overgrazing to protect grasslands and maintain healthy Yarsagumba populations.







![References
• Chhetri P. (2014) Livelihood Strategies of People in the Himalayan Region of
Nepal: A Study in the Villages of Eastern Manang, Independent Study
Project (ISP) Collection. Paper 1831.
• Devkota S. (2006) Yarsagumba [Cordyceps sinensis (Berk.) Sacc.]; Traditional
Utilization in Dolpa District, Western Nepal .Our Nature 4:48-52.
• Devkota S. (2009) the frequency and relationship of flowering plants on
the distribution pattern of Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Banko Janakari, 19 (1)
• Thapa BB, Panthi S , Rai RK, Shrestha UB ,Aryal A, Shrestha S,Shrestha B
(2014) An Assessment of Yarsagumba (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) Collection
in Dhorpatan Hunting Reserve, Nepal. Journal of Mountain Science: 11(2):
555-562.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yarsa-171119153146/85/Ophiocordyceps-sinesis-9-320.jpg)
