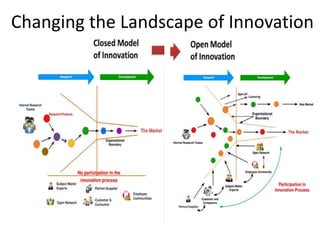
1) The document discusses open innovation and its potential benefits for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Egypt.
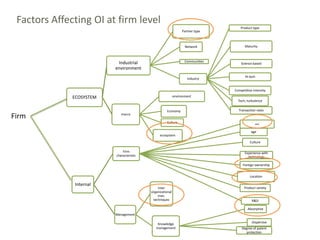
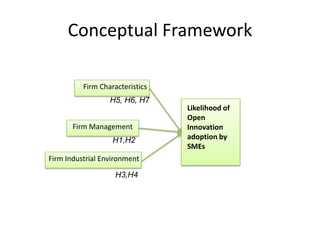
2) It proposes a conceptual framework and survey to analyze how firm characteristics and the industrial environment influence SMEs' likelihood of adopting open innovation.
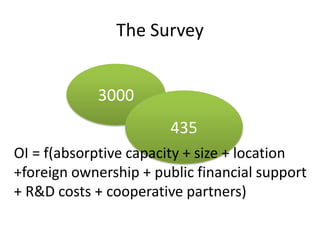
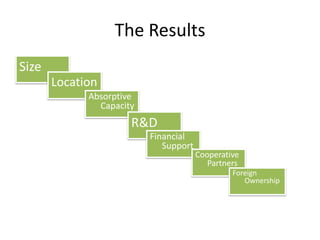
3) The results of the survey of 435 Egyptian SMEs found that a firm's absorptive capacity, size, location, foreign ownership, public financial support, R&D costs, and cooperative partners were significant factors affecting their use of open innovation.