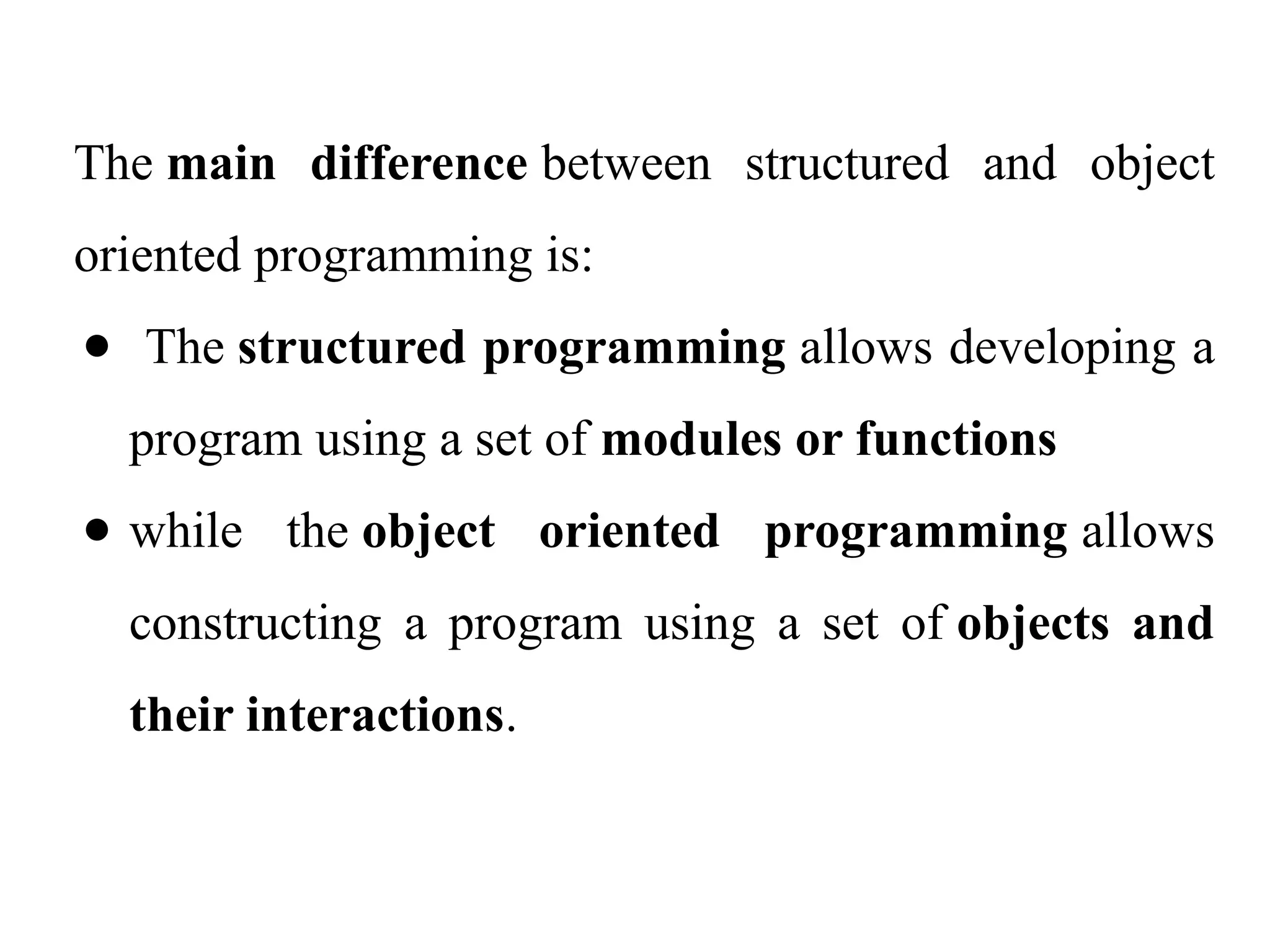
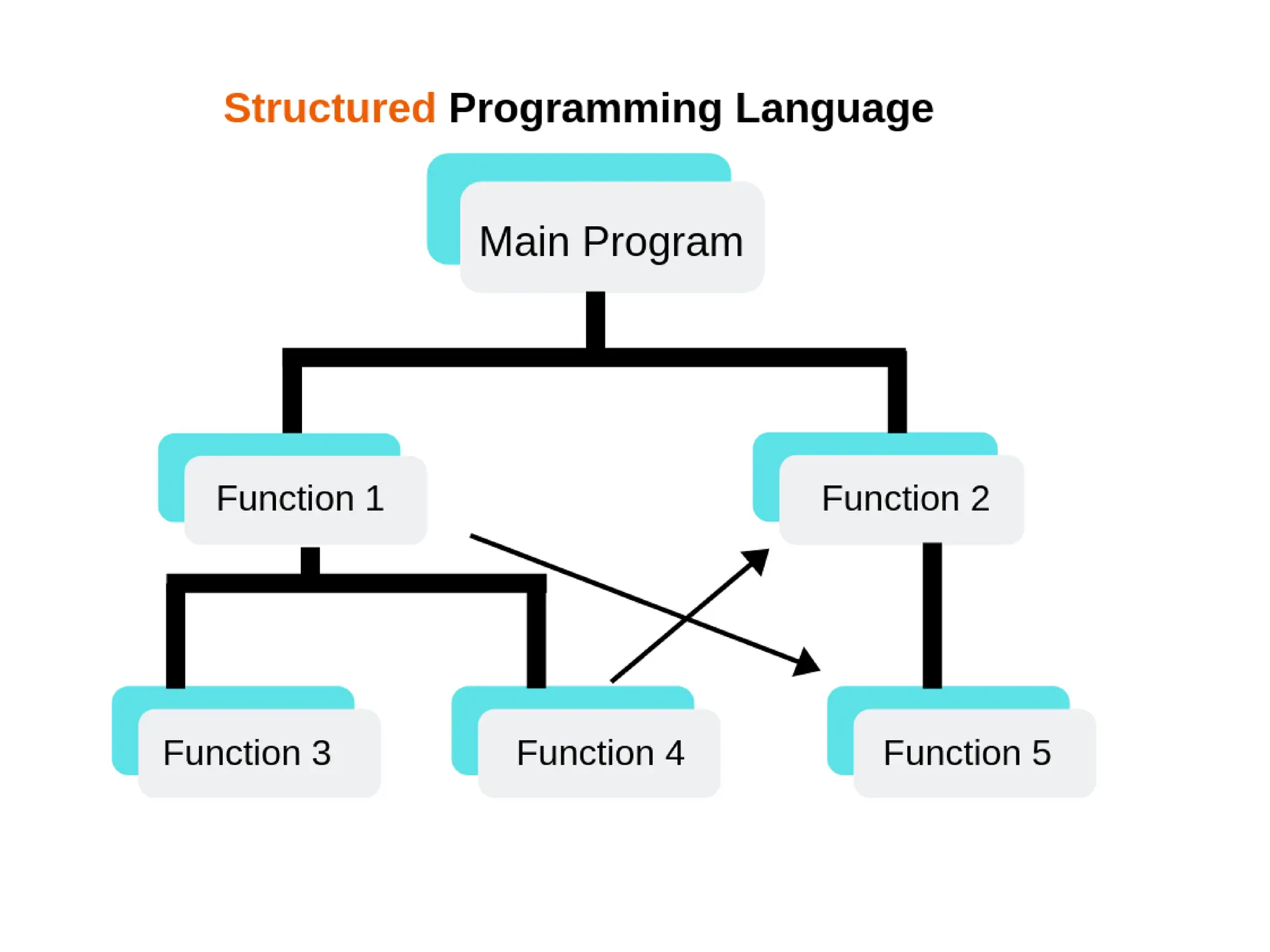
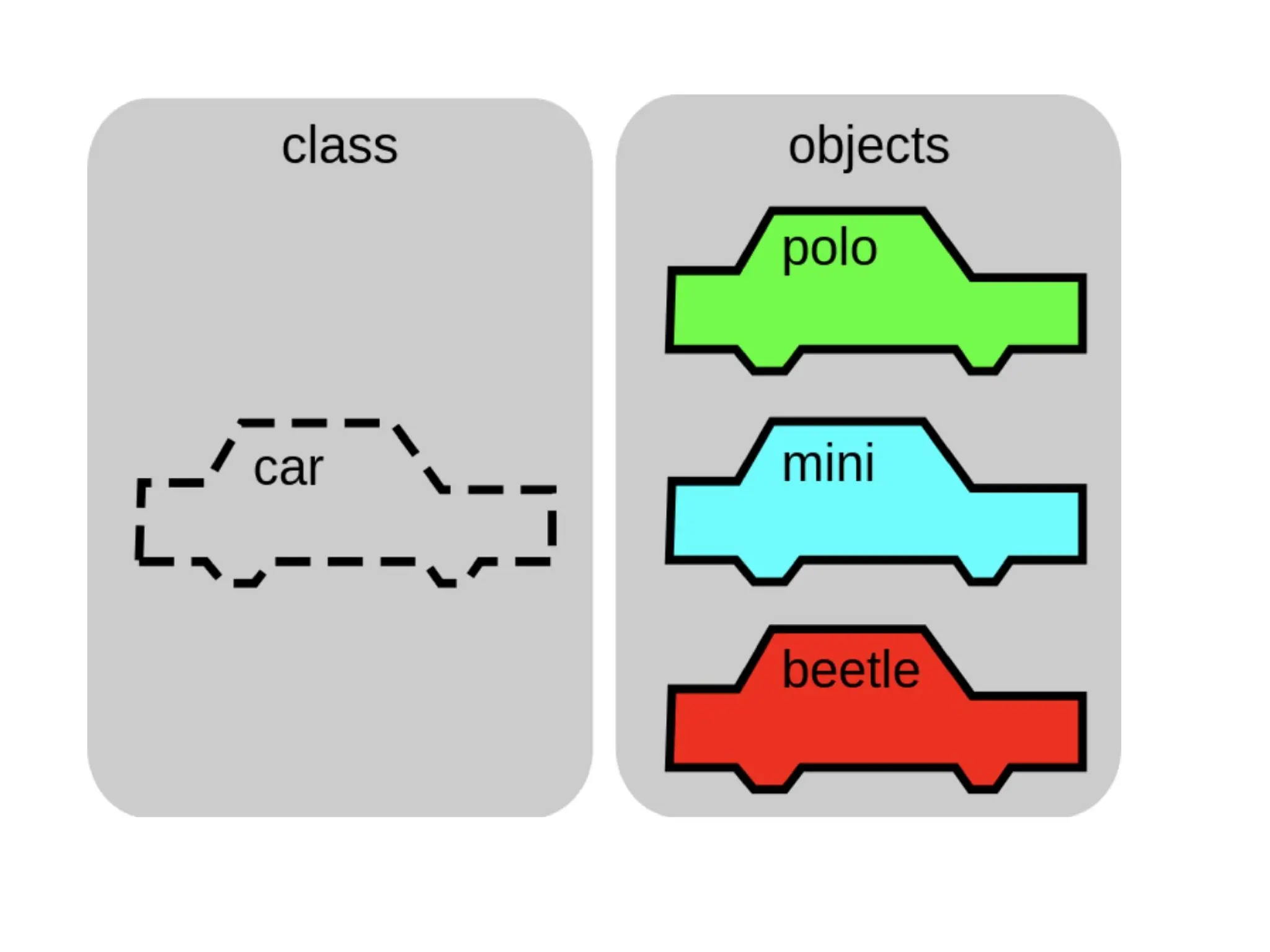
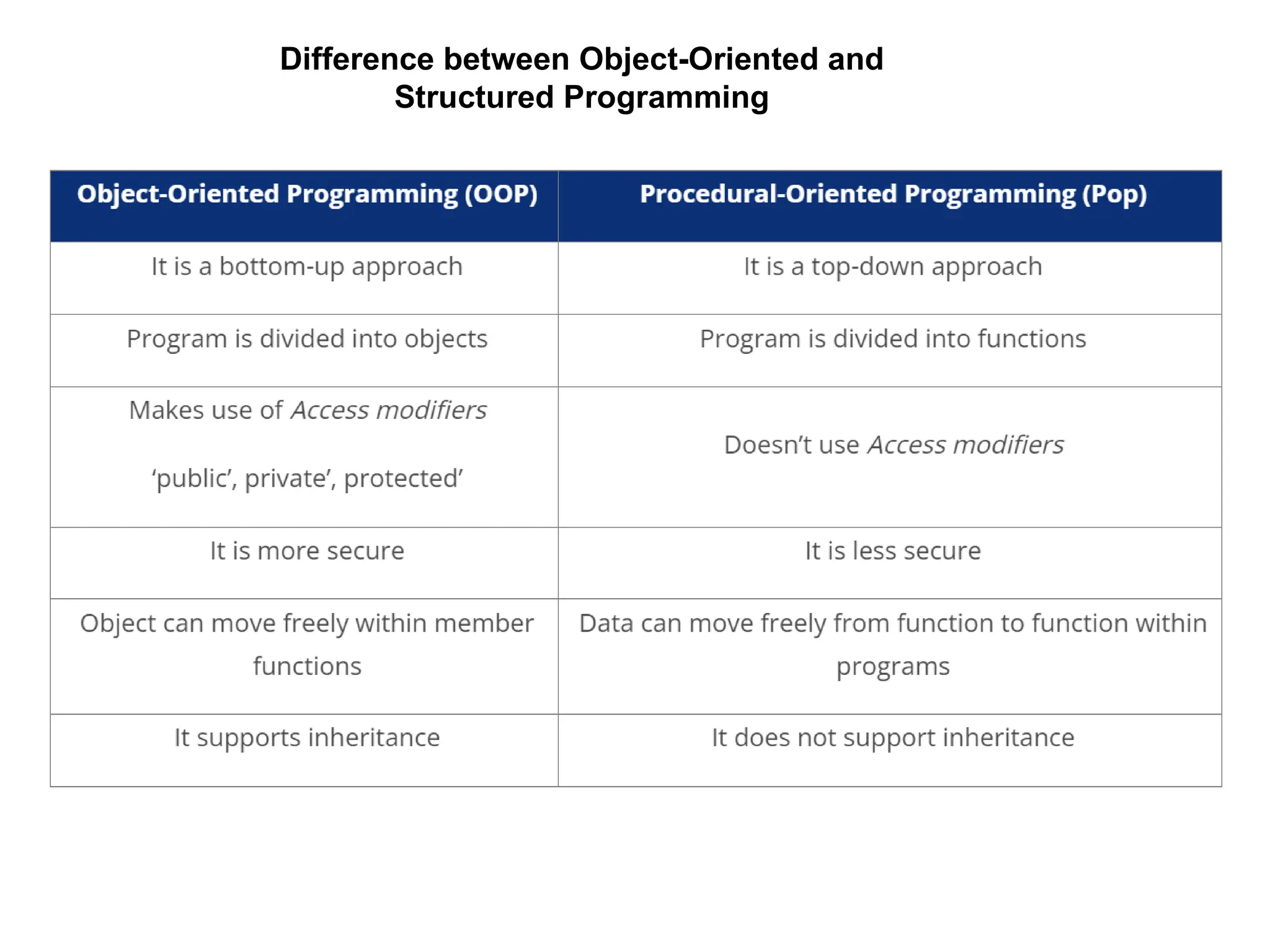
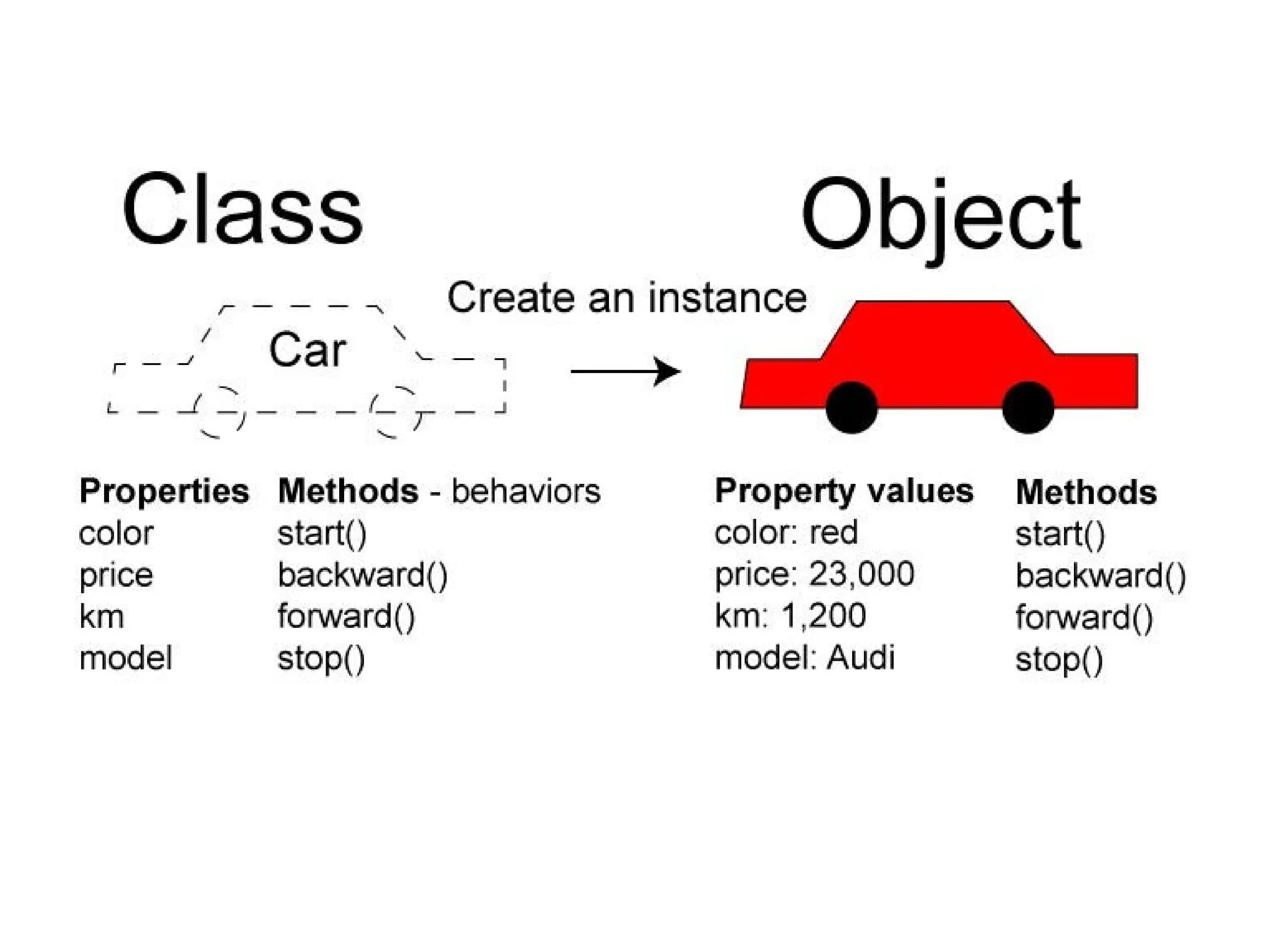
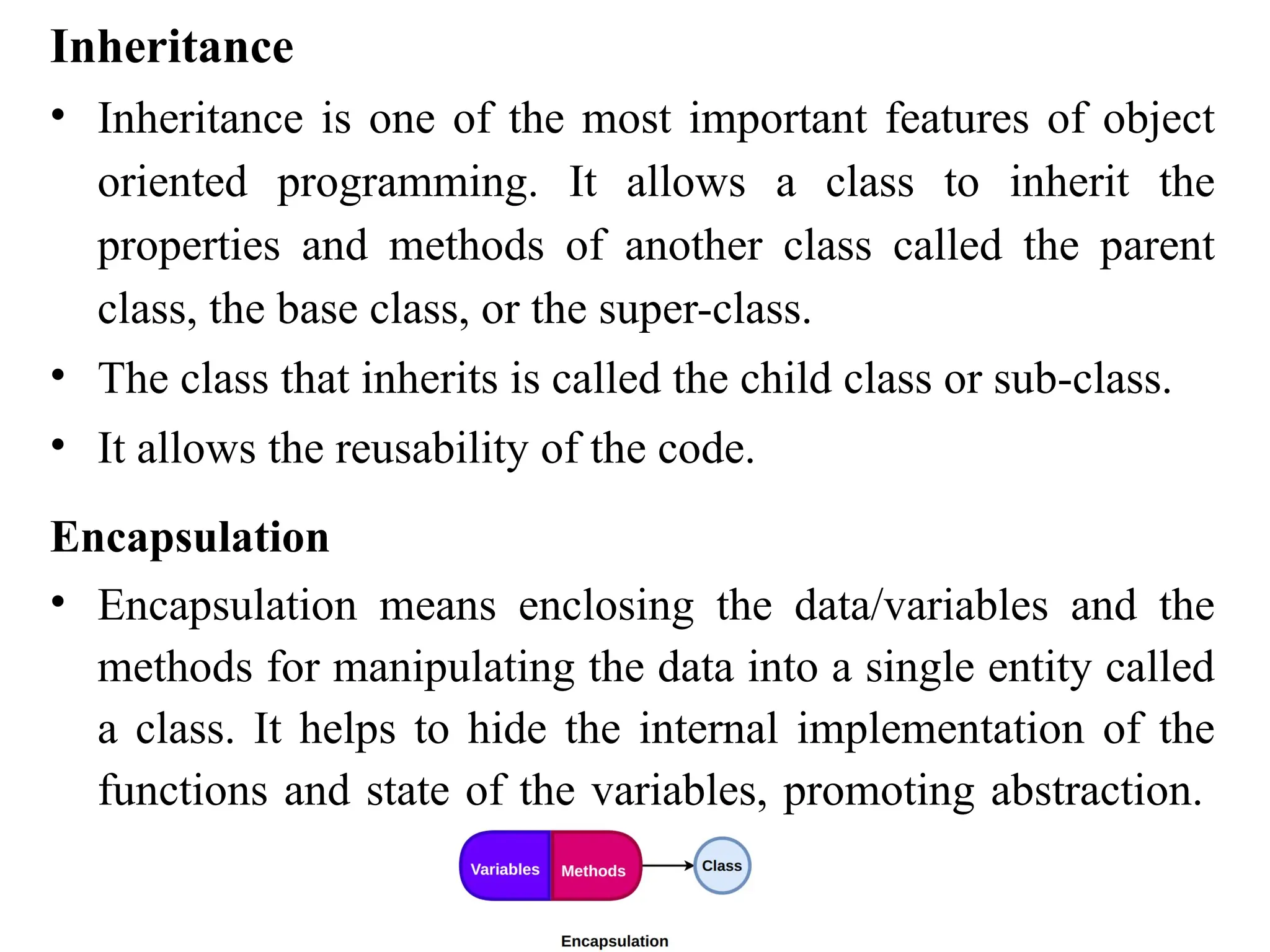
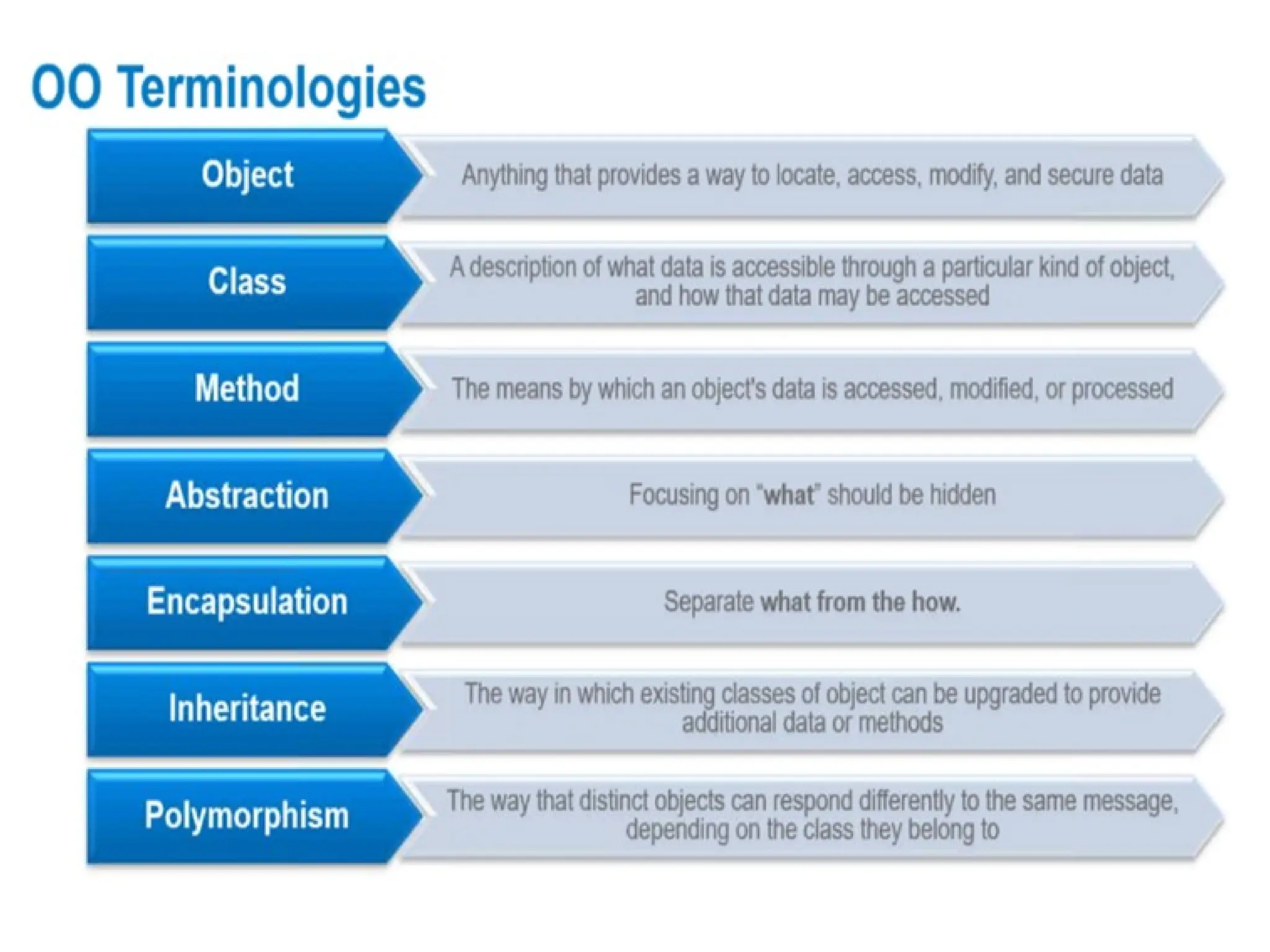
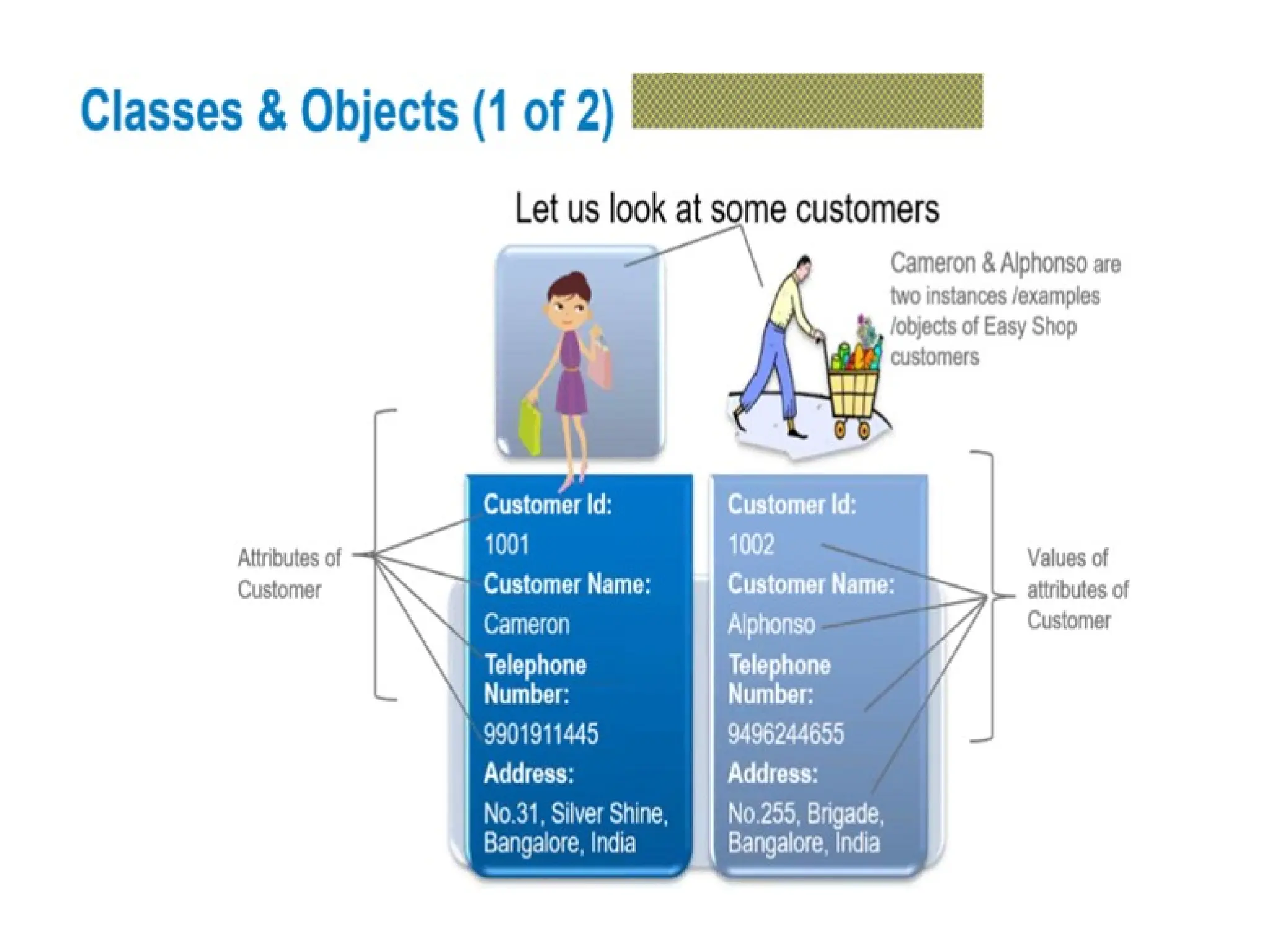
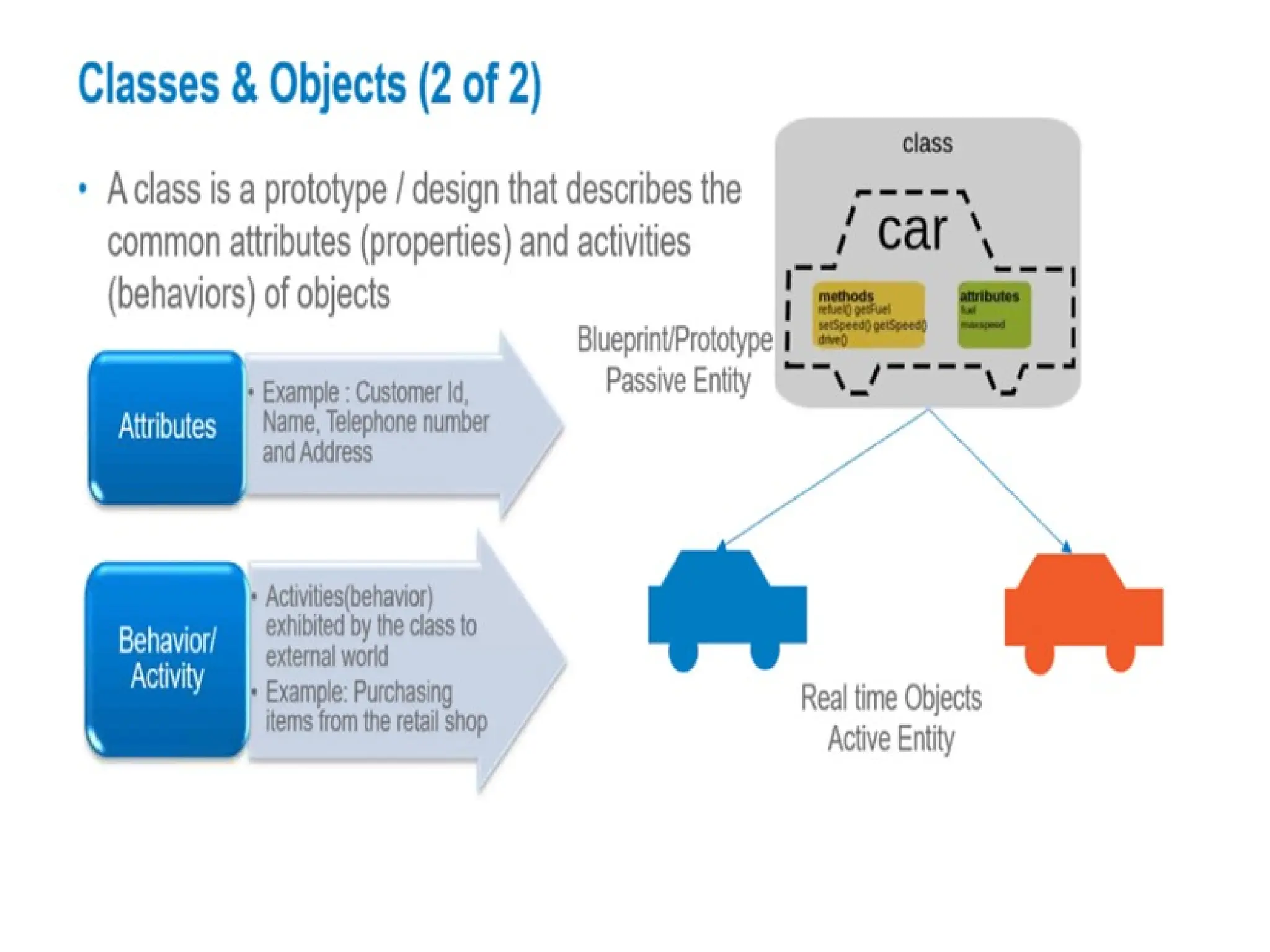
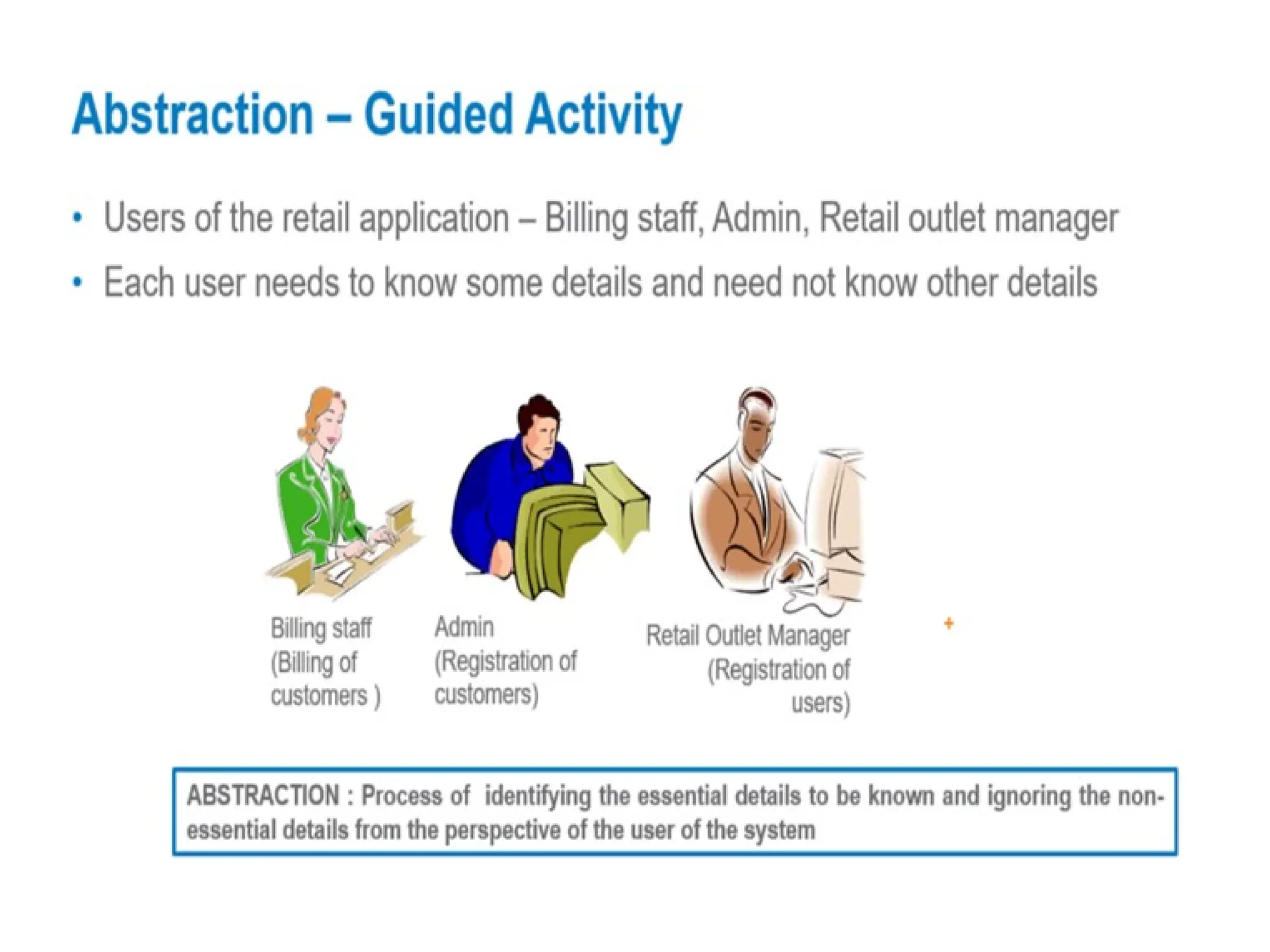
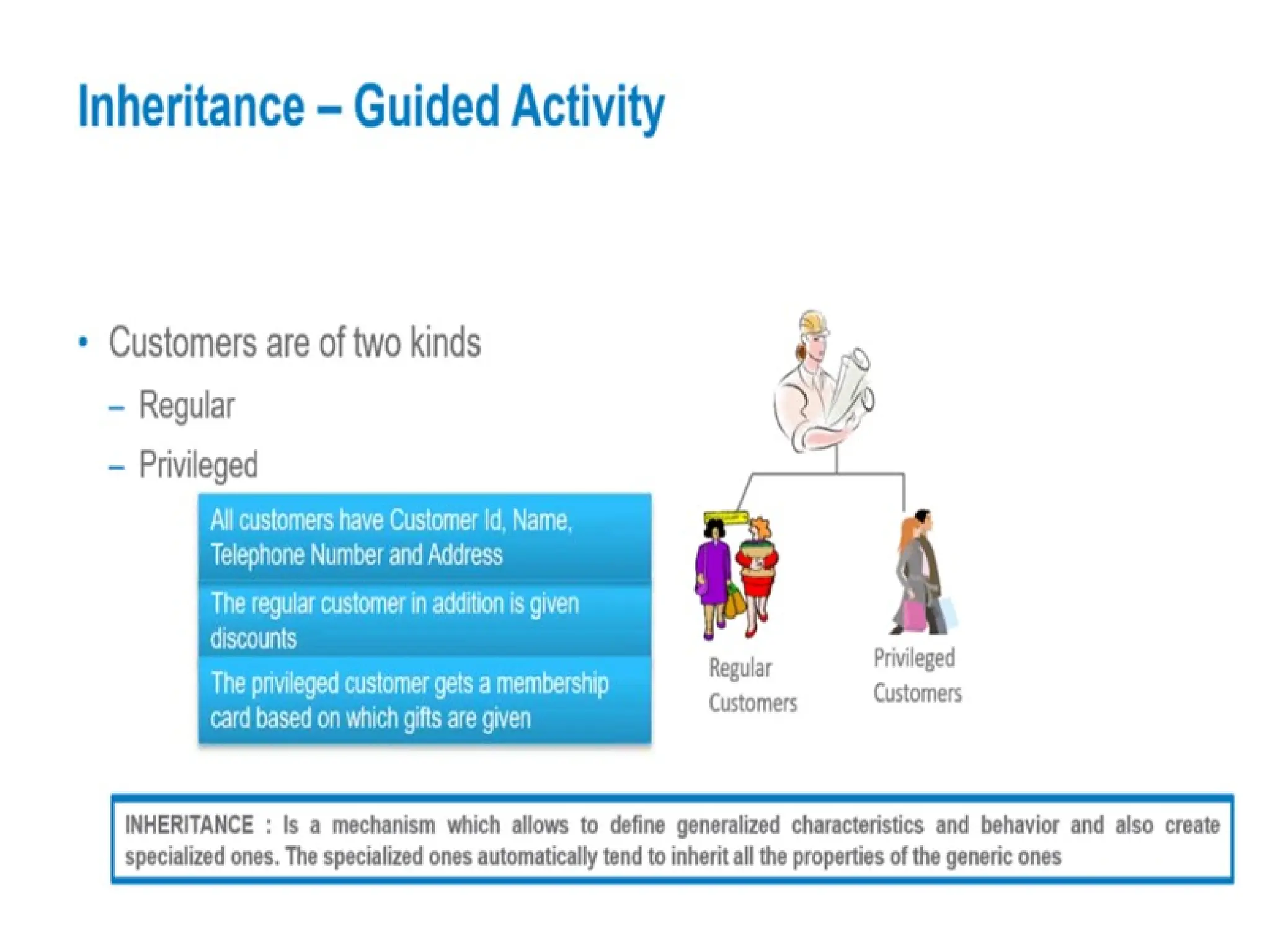
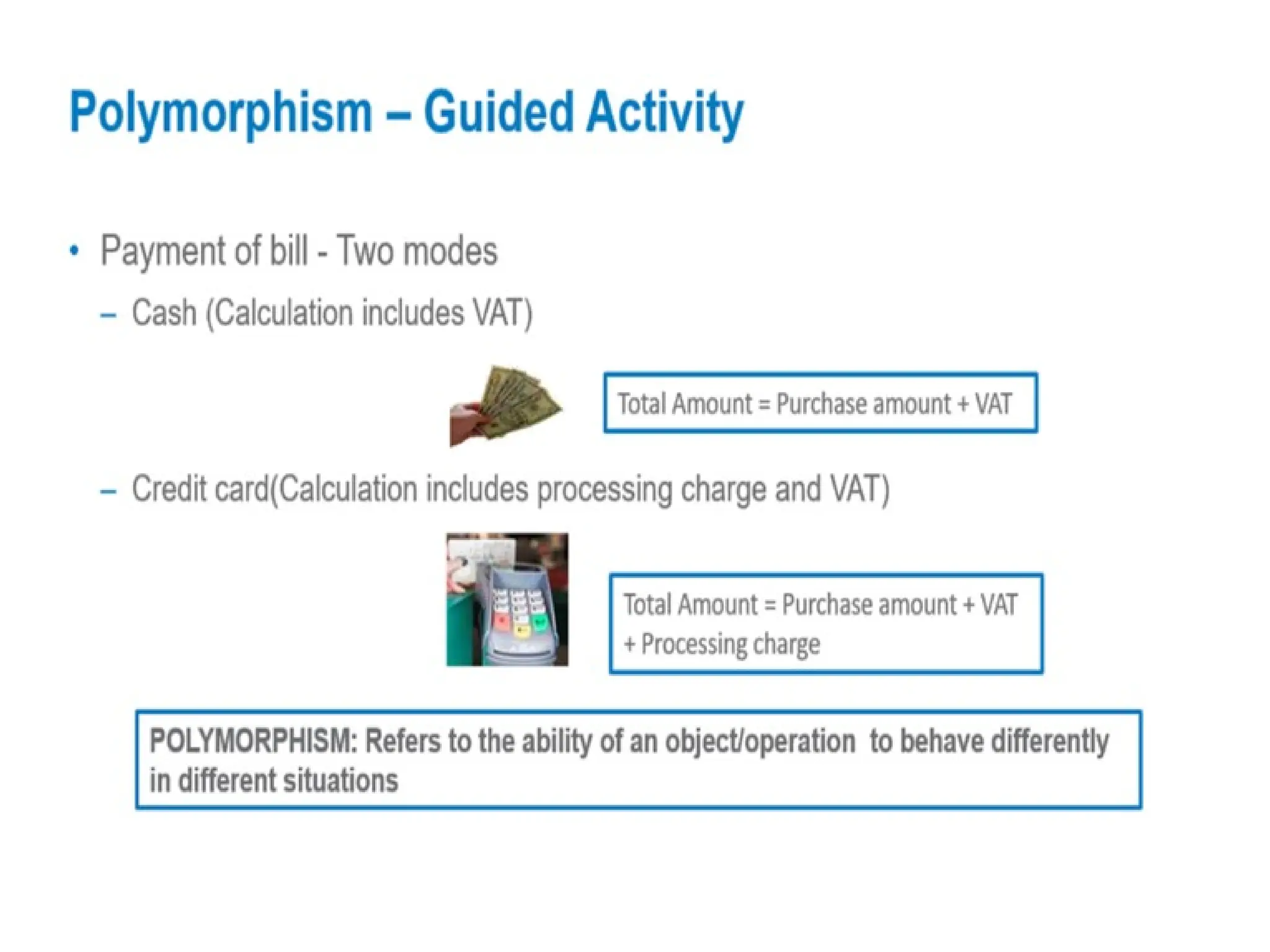
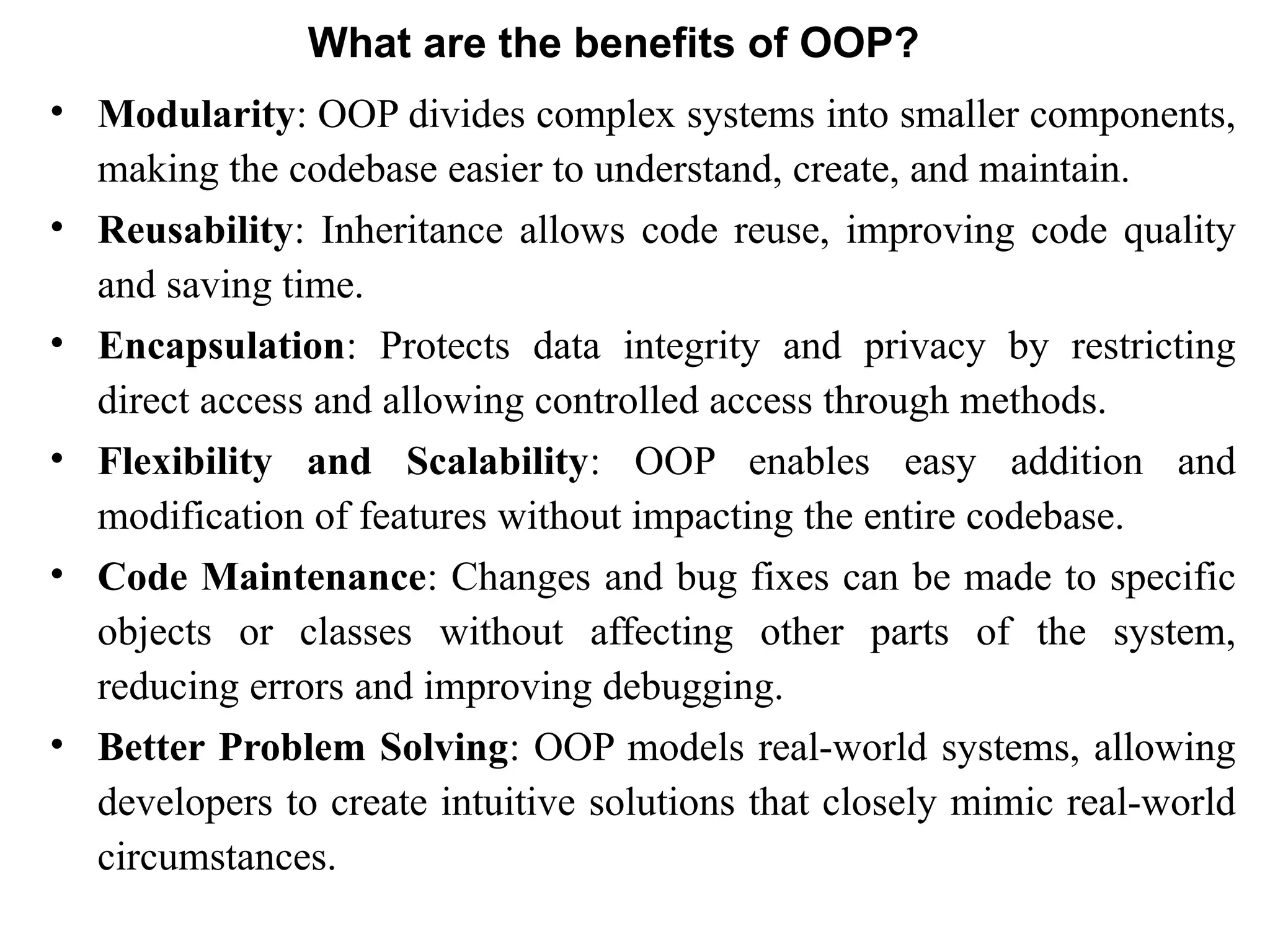
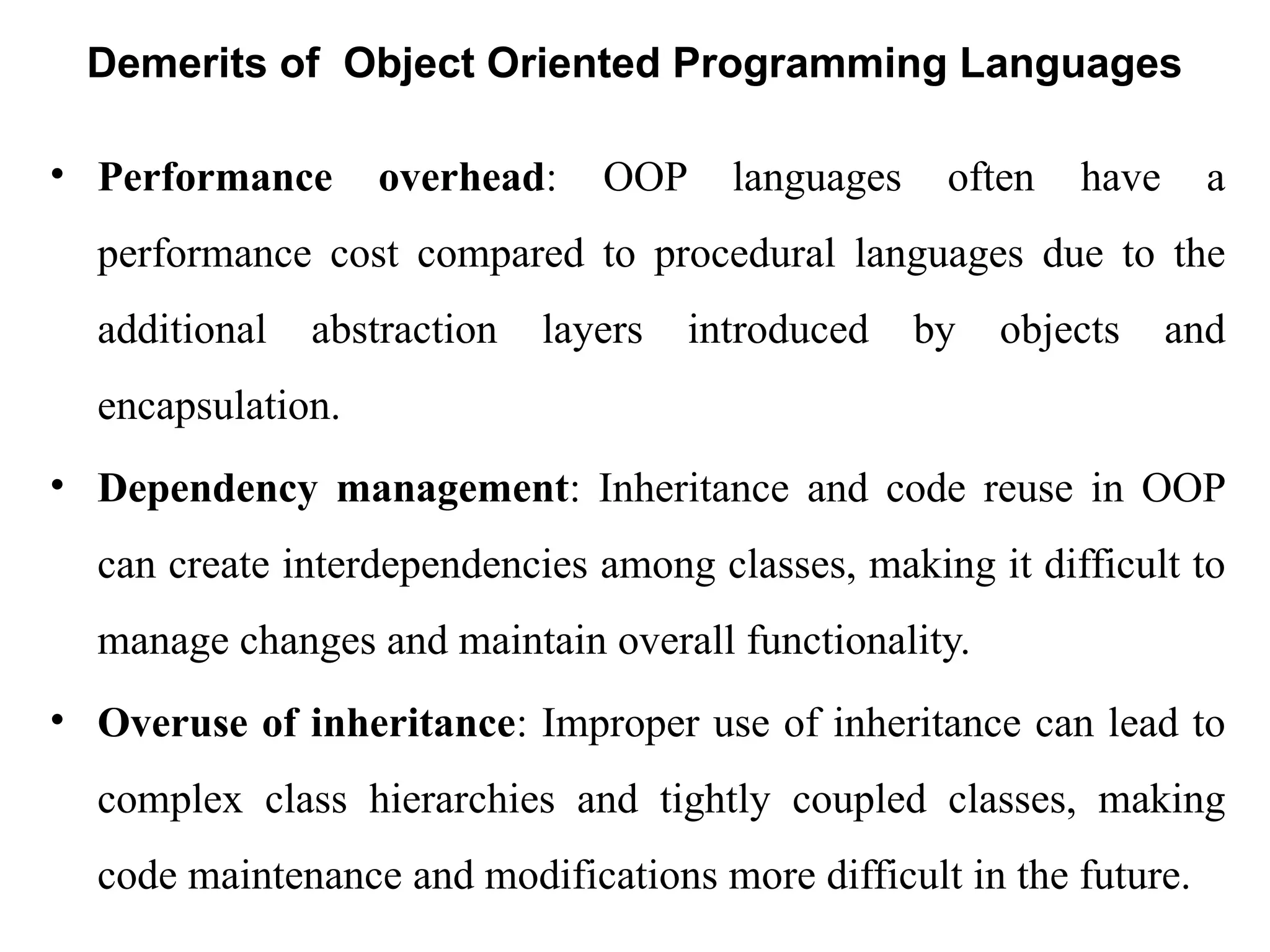
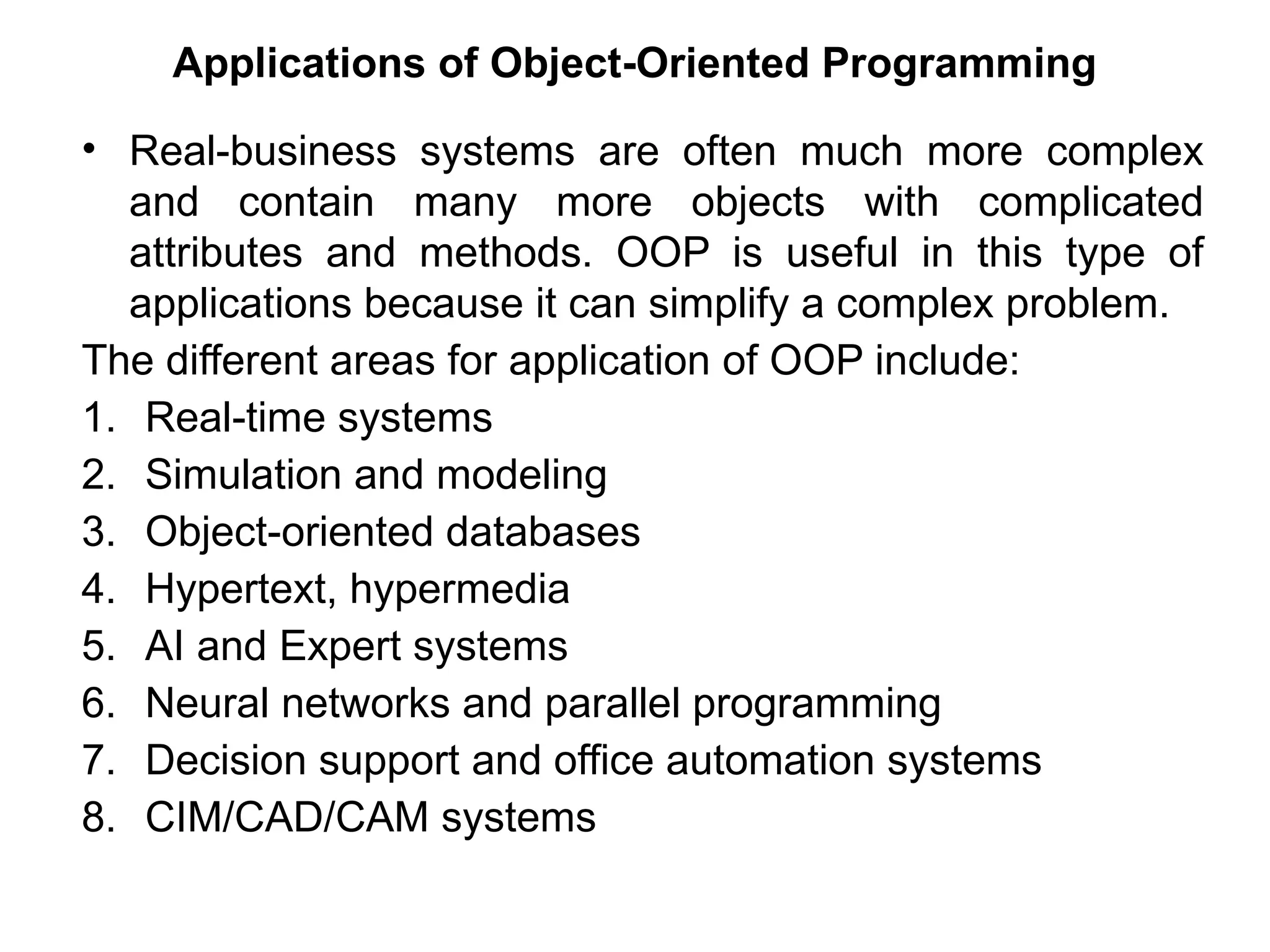
Object-oriented programming (OOP) differs from structured programming by using objects and their interactions over functions and modules. Key concepts include classes (templates for objects), abstraction (simplifying complexity), polymorphism (multiple forms), inheritance (reusability of code), and encapsulation (data protection). Benefits of OOP include modularity, reusability, and better problem-solving, while drawbacks can involve performance issues and complexity in class hierarchies.