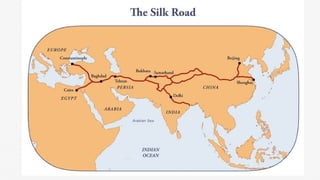
The document discusses economic globalization, outlining its definition, drivers, and impact on local and international trade, with a focus on the role of transnational and multinational corporations. It highlights historical trade developments, the complexity of the global economy, and the challenges countries face in benefiting from globalization, citing poverty issues in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa. Perspectives on the success of globalization vary, with some arguing it reduces poverty while others point out the unequal benefits it brings.