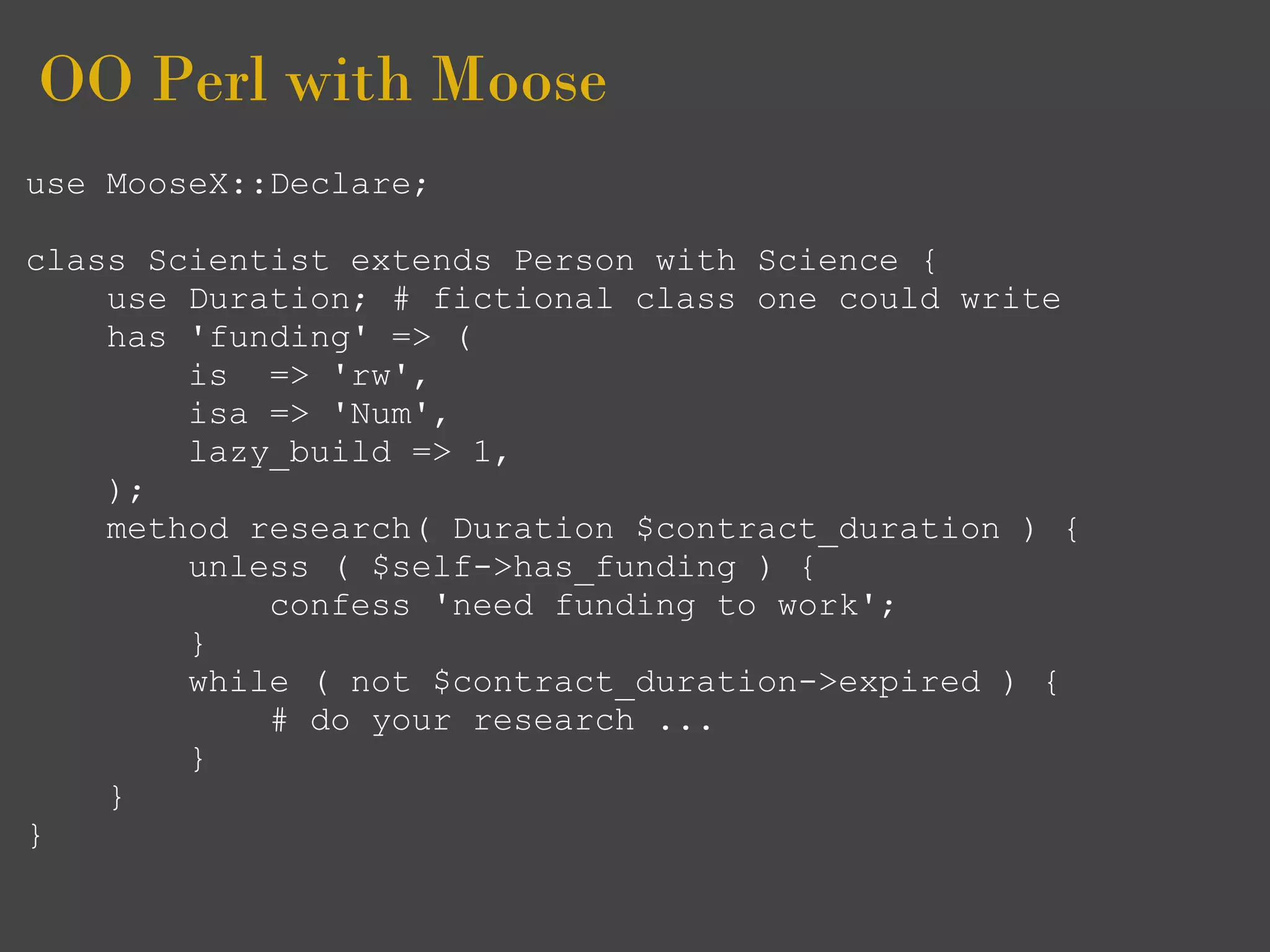
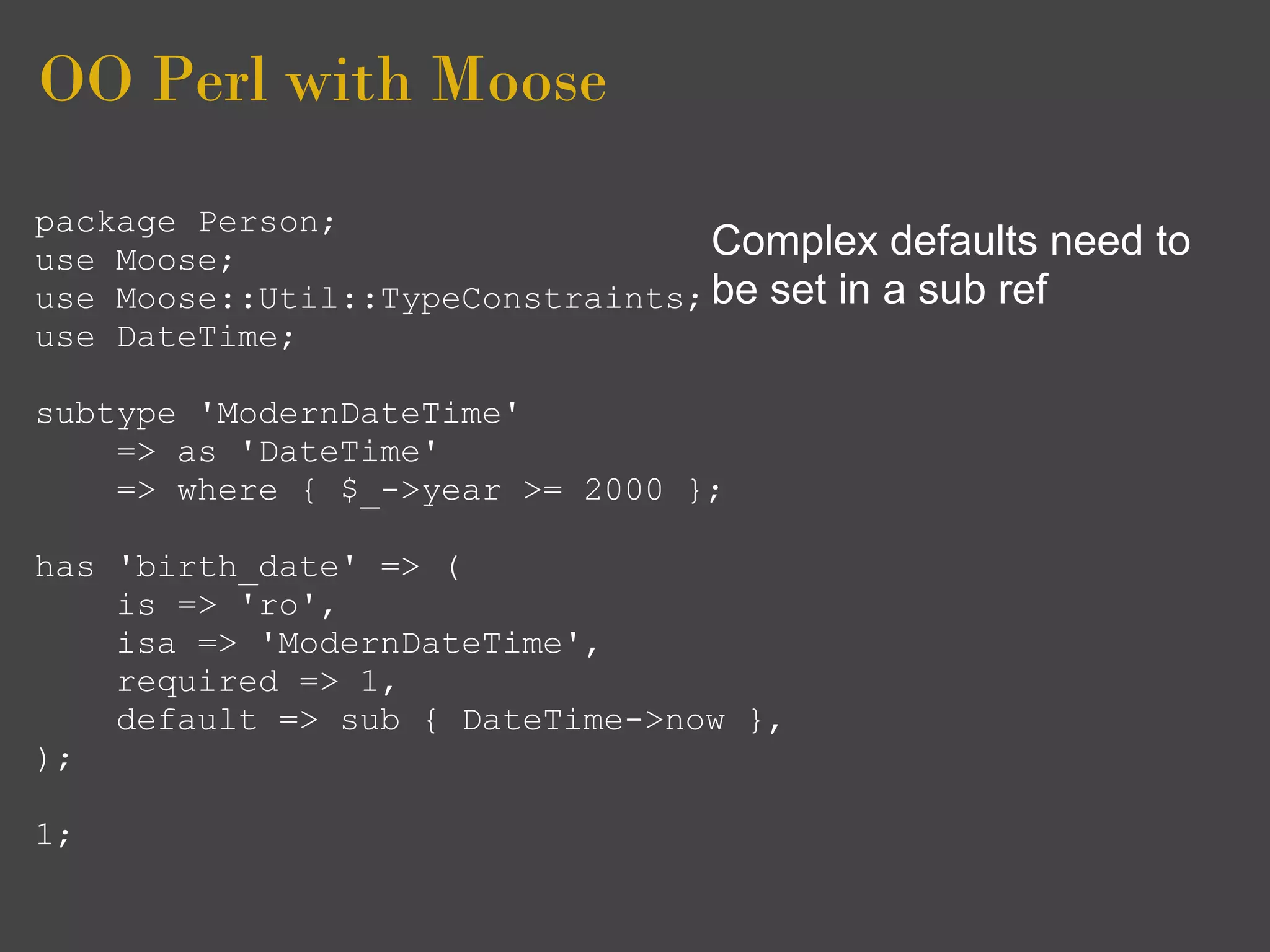
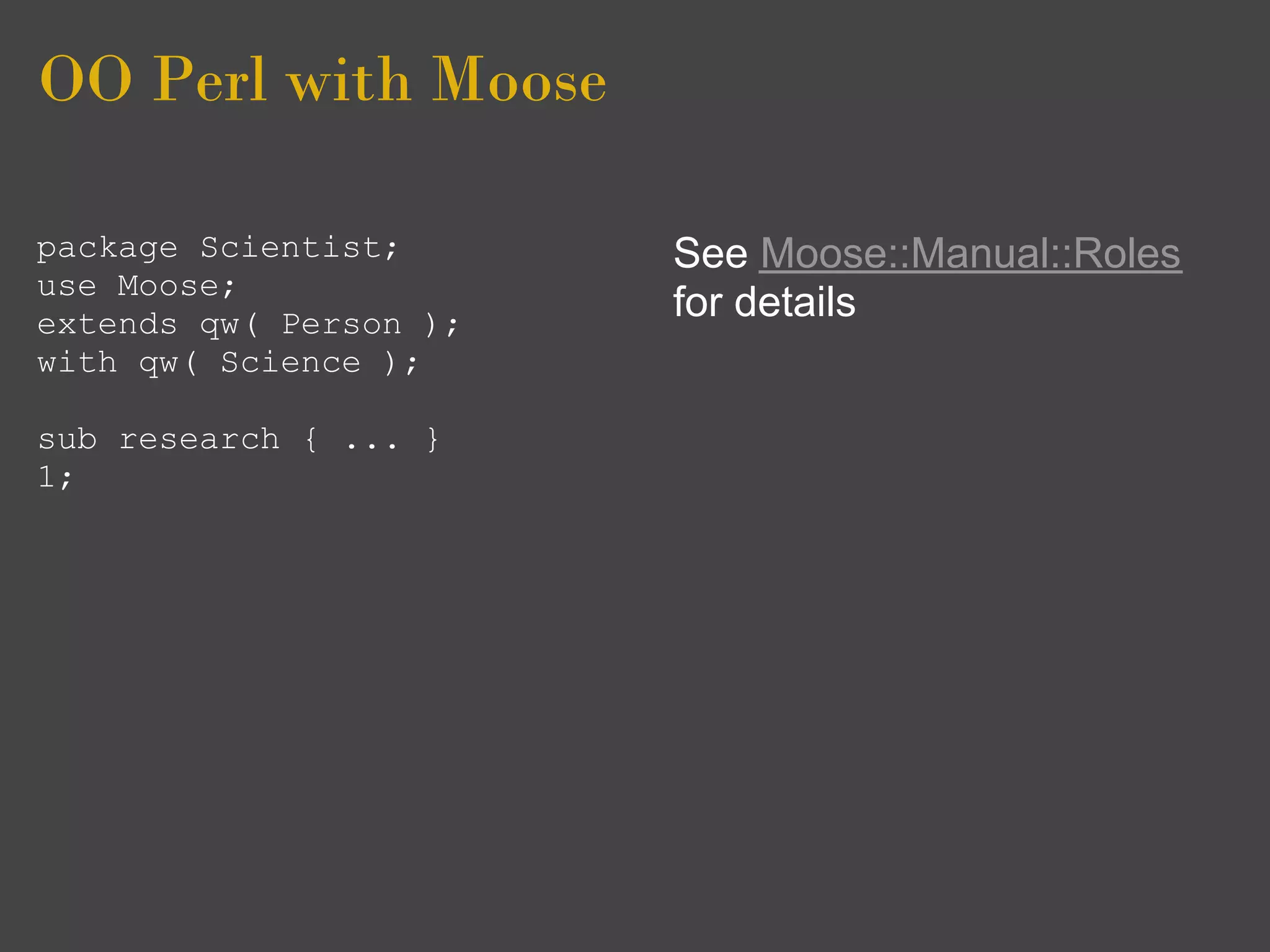
Moose is an object framework for Perl 5 that simplifies object-oriented programming. It allows classes to be defined declaratively using attributes like 'has' and inheritance is implemented with 'extends'. Attributes can have types, defaults, and delegated accessors. Roles provide reusable traits and are composed into classes using 'with'. Moose supports features like multiple inheritance, method overriding, and required interface methods.






































































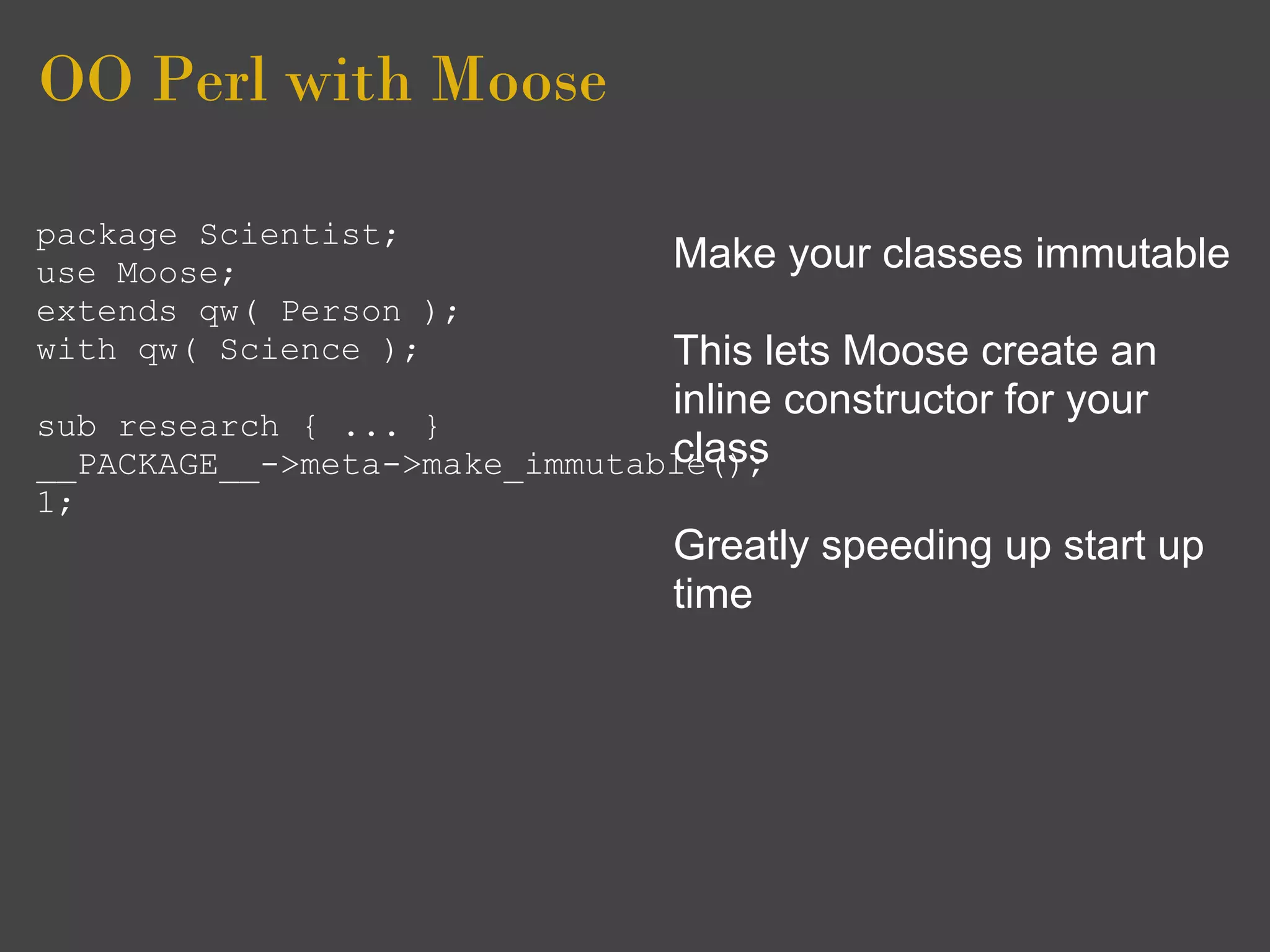


![OO Perl with Moose
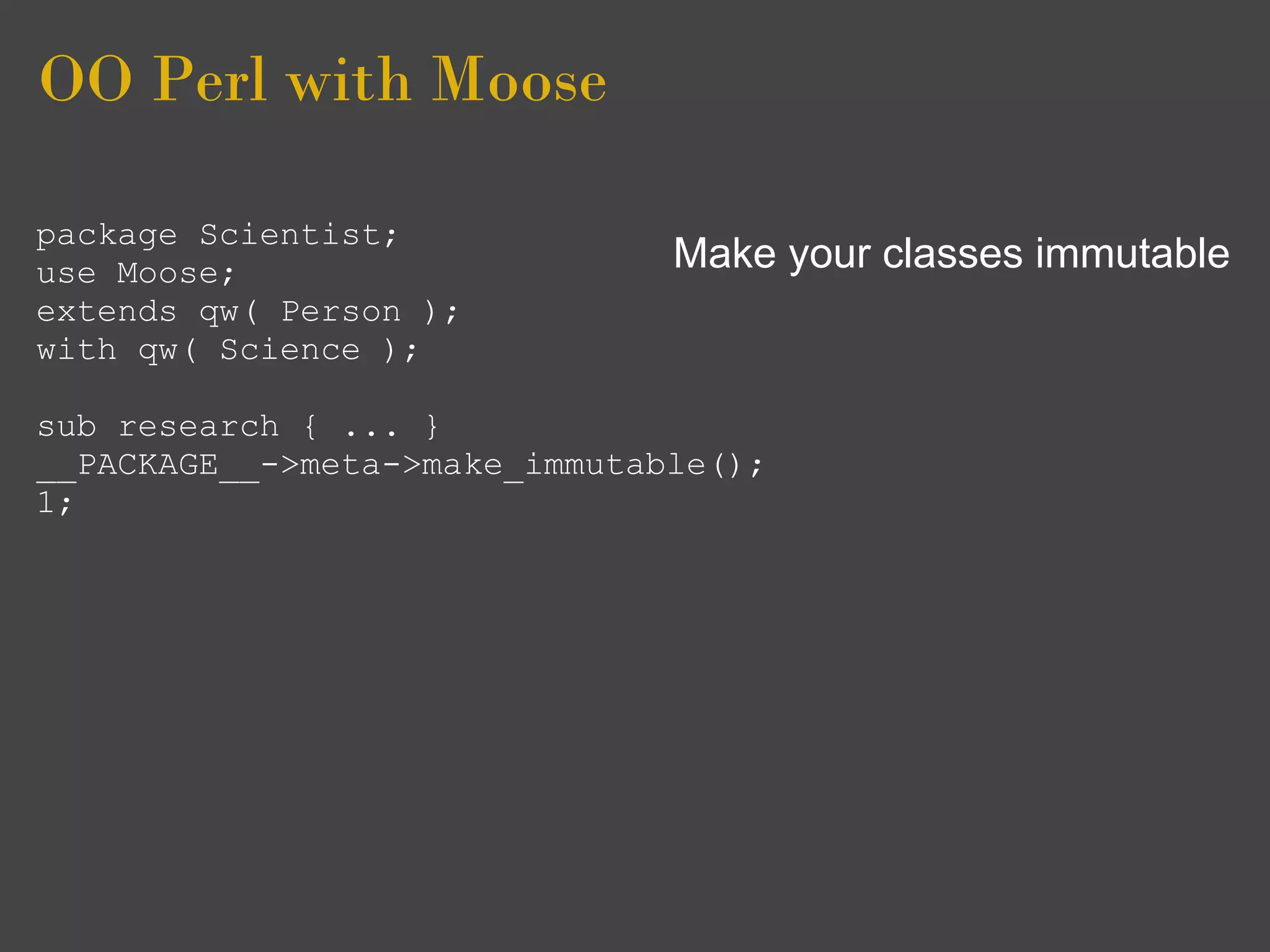
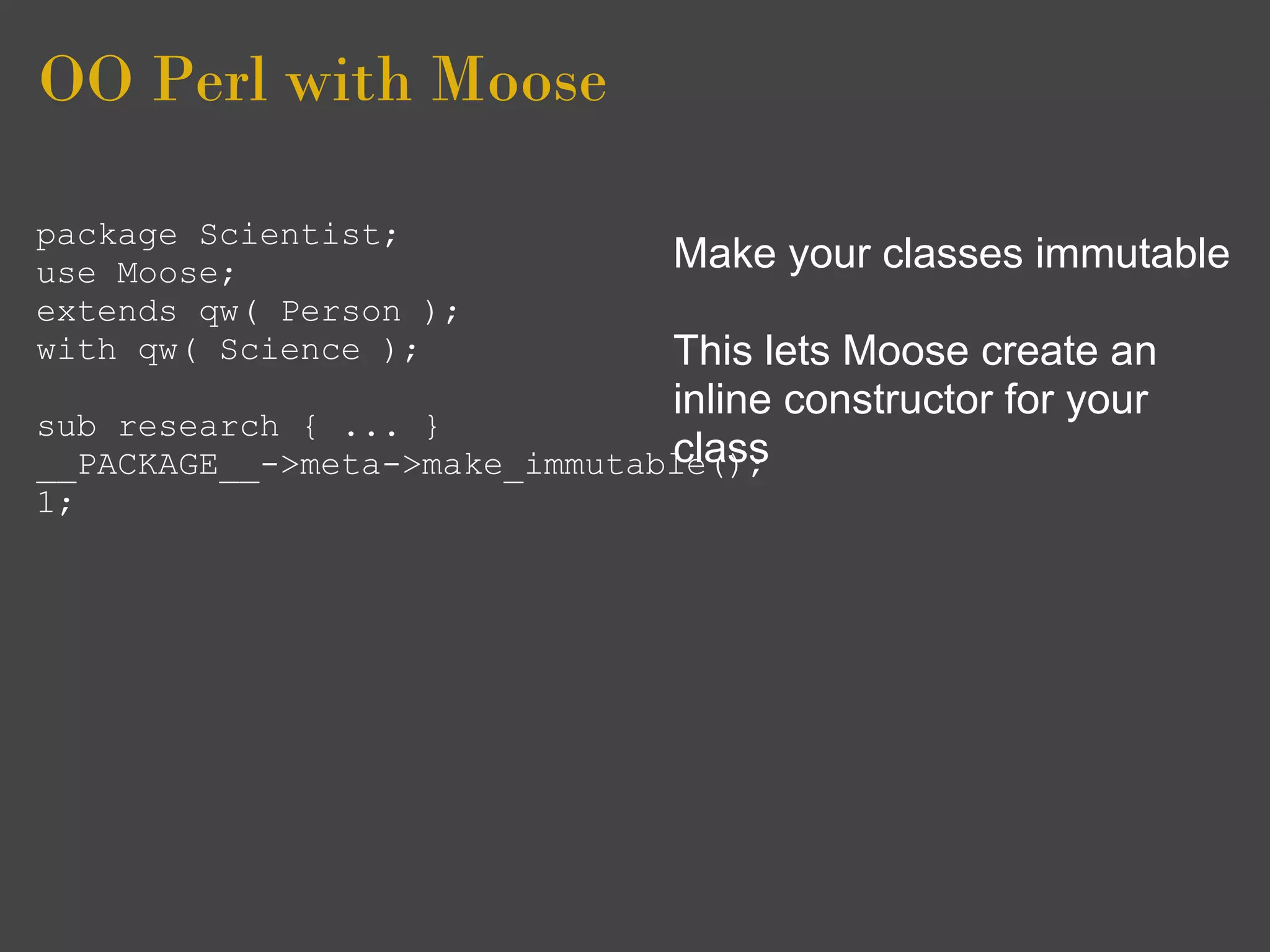
package Scientist;
use Moose; Also you are adviced to clean
use namespace::clean up after your class
-except => [qw( meta )];
extends qw( Person ); i.e remove all Moose sugar
with qw( Science );
from packages using your
sub research { ... } classes
__PACKAGE__
->meta->make_immutable();
1;
Alternatively](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooperlwithmoose3-100722072606-phpapp01/75/OO-Perl-with-Moose-85-2048.jpg)








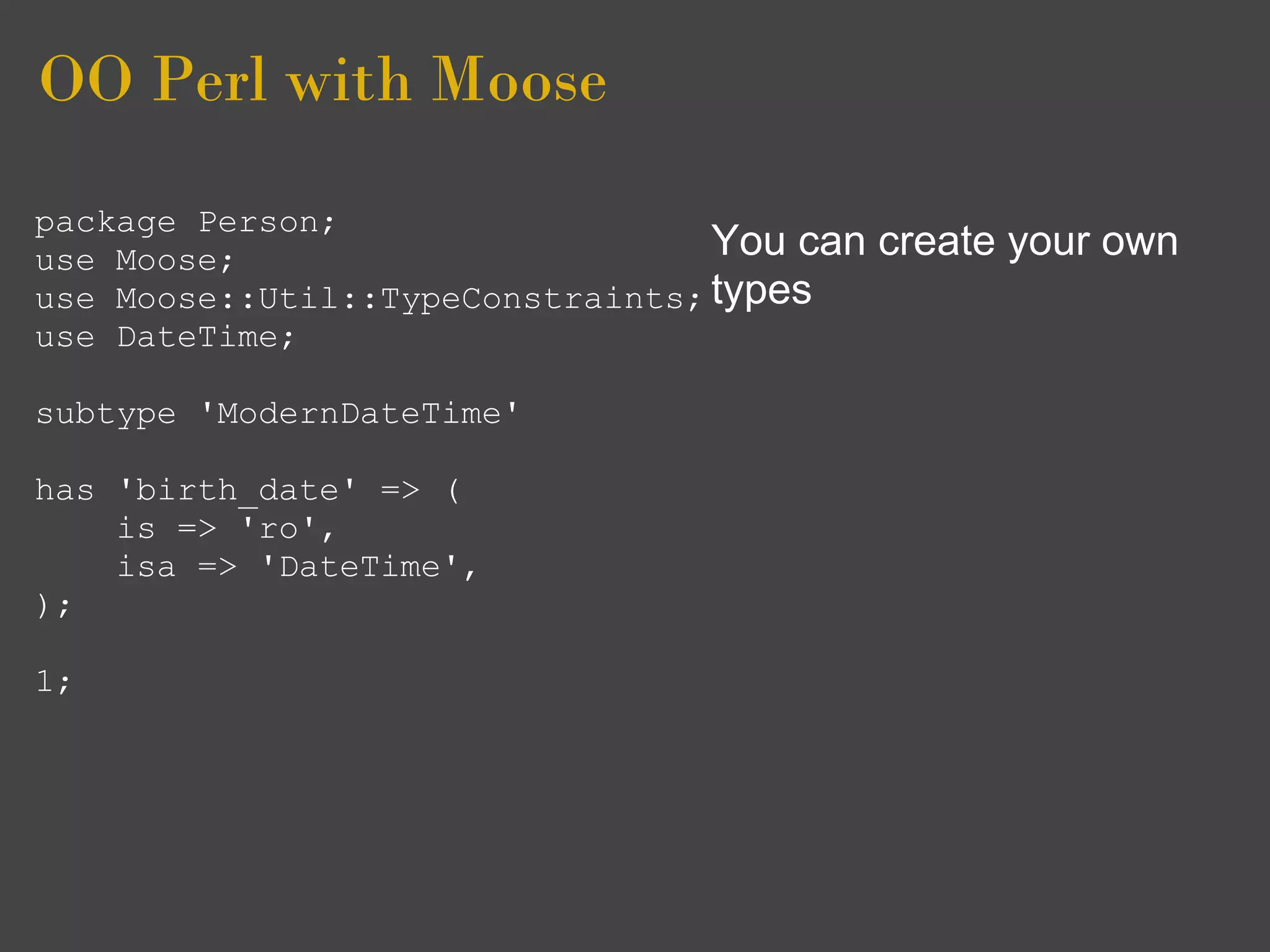
![OO Perl with Moose
package Person;
use Moose; Lastly you will note that
use namespace::clean Moose introduces its own
-except => [qw( meta )]; boiler plate code
# attributes and methods
__PACKAGE__->meta->make_immutable();
1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooperlwithmoose3-100722072606-phpapp01/75/OO-Perl-with-Moose-94-2048.jpg)
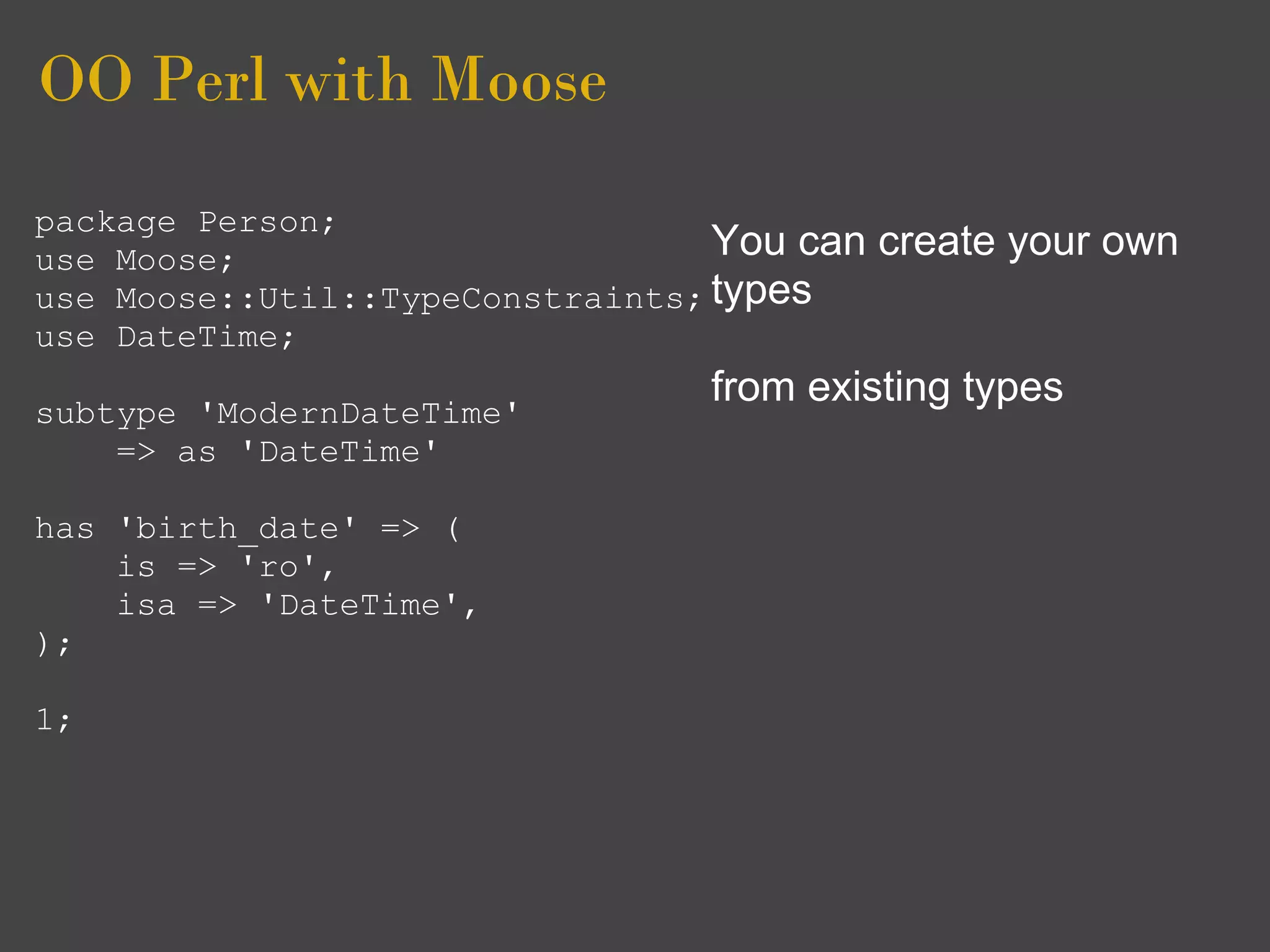
![OO Perl with Moose
package Person;
use Moose; Lastly you will note that
use namespace::clean Moose introduces its own
-except => [qw( meta )]; boiler plate code
# attributes and methods
__PACKAGE__->meta->make_immutable(); is an extension
There that
1; reduces this](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooperlwithmoose3-100722072606-phpapp01/75/OO-Perl-with-Moose-95-2048.jpg)
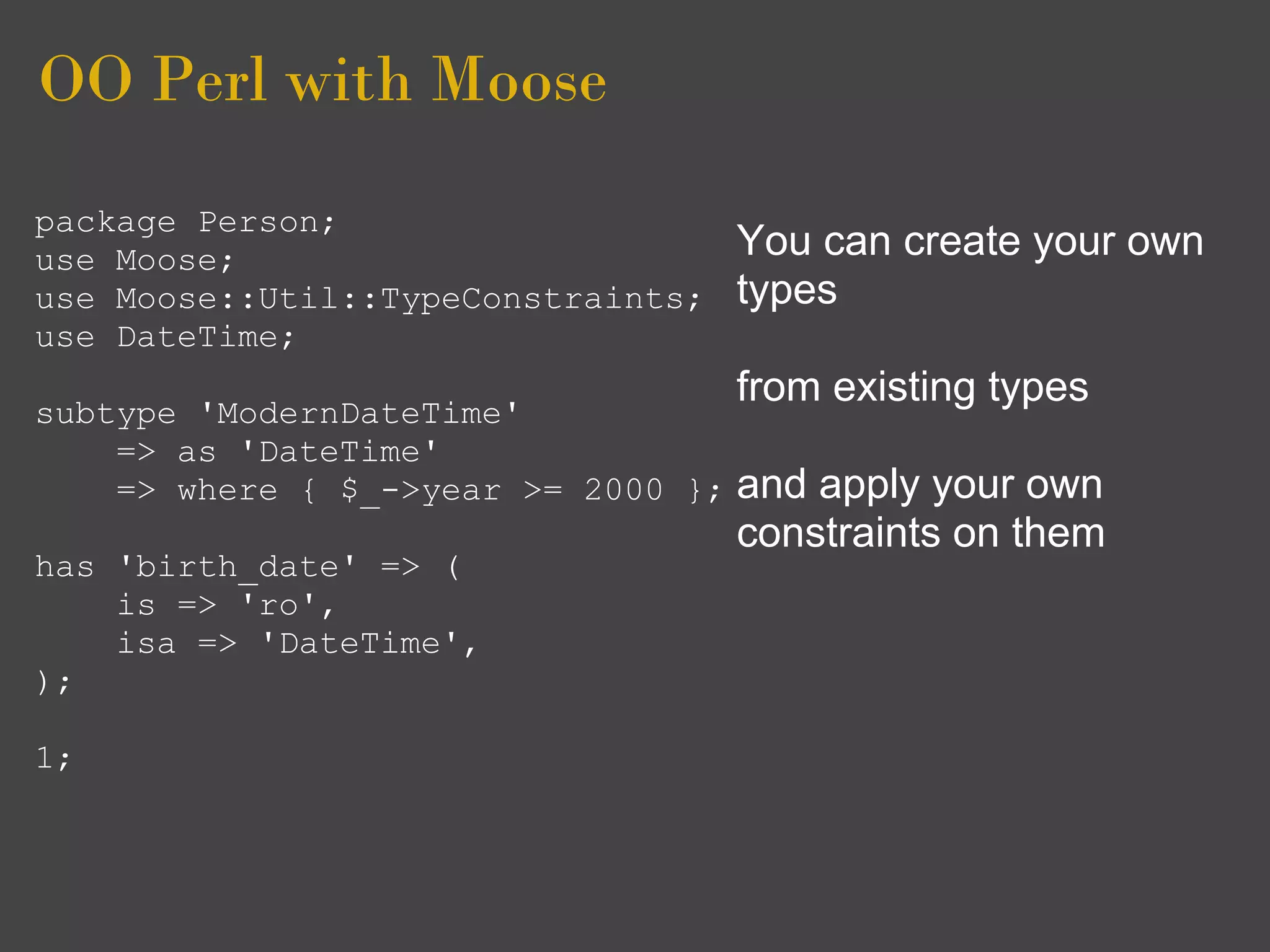
![OO Perl with Moose
package Person;
use Moose; Lastly you will note that
use namespace::clean Moose introduces its own
-except => [qw( meta )]; boiler plate code
# attributes and methods
__PACKAGE__->meta->make_immutable(); is an extension
There that
1; reduces this
MooseX::Declare](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooperlwithmoose3-100722072606-phpapp01/75/OO-Perl-with-Moose-96-2048.jpg)