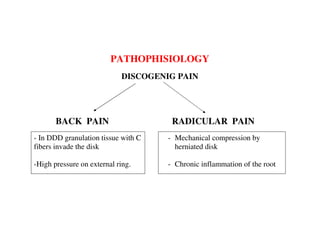
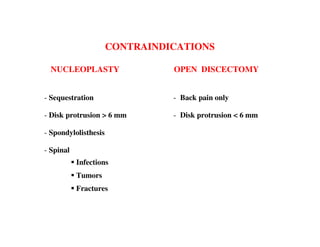
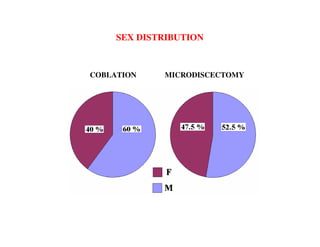
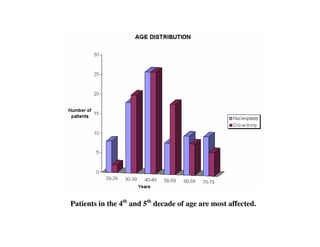
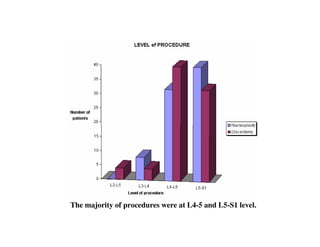
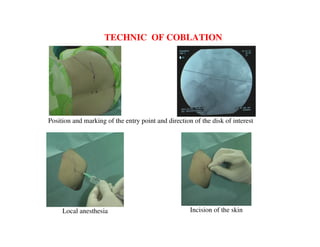
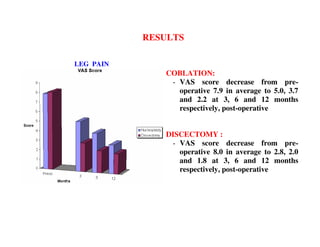
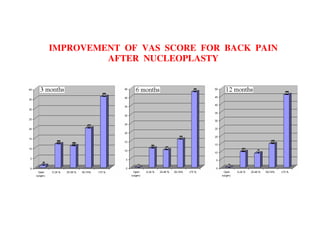
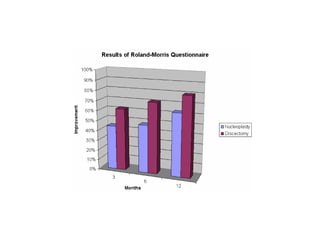
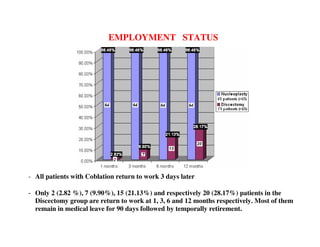
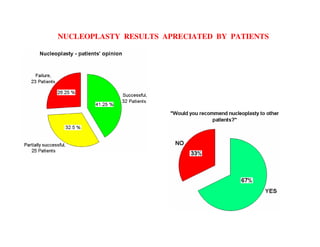
Coblation nucleoplasty and open microdiscectomy are compared in treating lumbar disc protrusions. 80 patients underwent each procedure. Leg pain, as measured by VAS scores, improved more for microdiscectomy patients initially but steadily improved for nucleoplasty patients as well over 12 months. Nucleoplasty allowed nearly all patients to return to work within 3 days while most microdiscectomy patients remained on medical leave for over 3 months. Both procedures provided significant pain relief, but nucleoplasty had advantages of less invasiveness and quicker return to work.