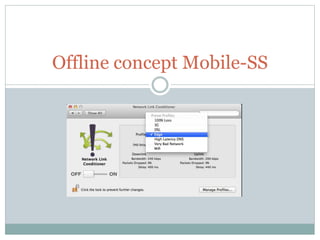
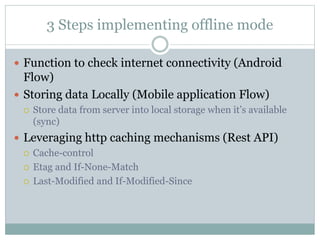
The document discusses implementing offline mode in mobile apps. It recommends providing offline functionality so users can still access content without an internet connection. It outlines three steps: 1) checking internet connectivity, 2) storing data locally on the device, and 3) leveraging HTTP caching mechanisms in REST APIs like ETags to handle caching. It also addresses detecting and resolving data conflicts that may occur when a user edits data offline versus changes made online.