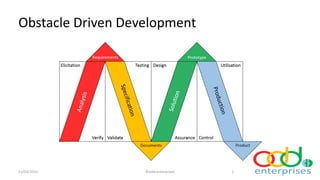
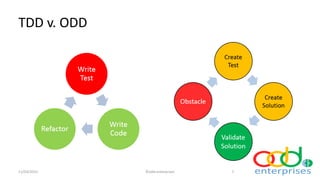
Obstacle Driven Development (ODD) is a development process that integrates concepts from various methodologies like test-driven development and agile principles, focusing on feedback and verification. ODD emphasizes the importance of specifications, testing procedures, and the linkage of tests with product elements to enhance quality assurance and the overall development process. The document outlines the structure, flowcharts, and timeline of ODD's evolution while detailing how it aims to streamline product development by addressing obstacles systematically.