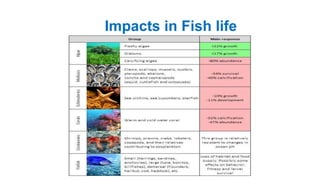
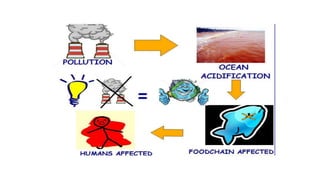
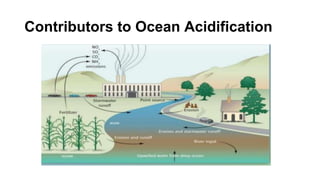
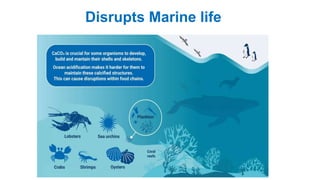
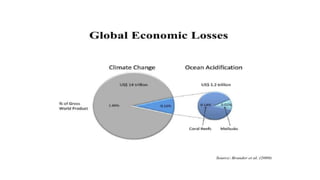
The document discusses ocean acidification, which occurs when excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is absorbed by seawater, leading to increased acidity. This process negatively impacts marine life, particularly calcifying organisms, coral reefs, and the overall marine food chain, while also affecting local economies reliant on marine resources. Solutions proposed include reducing fossil fuel usage, promoting eco-friendly alternatives, and implementing strict regulations to mitigate the effects of ocean acidification.