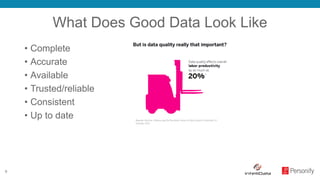
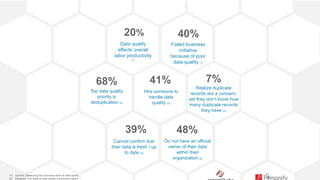
The document discusses the importance of data quality in enhancing business analytics and decision-making, highlighting that poor data costs companies significantly each year. It outlines a data maturity model, detailing stages from 'data aware' to 'data driven', where each stage reflects increasing sophistication in data integration and utilization. The goal is to achieve high-quality, trusted data that empowers organizations to enhance performance and make informed decisions.