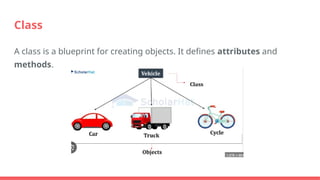
The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) and procedural-oriented programming (POP) in C++, highlighting the differences between these paradigms. It explains key concepts of OOP such as classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, data abstraction, and encapsulation, while also contrasting them with procedural programming characteristics. The text outlines the advantages of OOP, including security, code reusability, and ease of adding new data and functions.