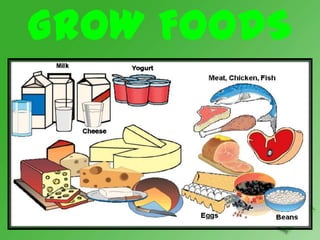
Nutrition is the process of consuming foods and using their nutrients for growth, energy, and overall health and functioning. Nutrients include macronutrients like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats which are needed in large quantities, as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals which are needed in smaller amounts. The major nutrients that provide nourishment are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, fiber, soy, and fruits and vegetables. Carbohydrates provide glucose for energy, proteins provide amino acids to build and repair the body, and fats surround and insulate cells and are needed for brain and hormone functions. Vitamins and minerals also help chemical reactions in the body and should be obtained through a balanced