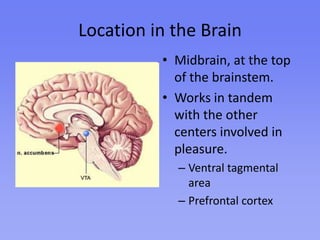
The nucleus accumbens is located in the midbrain and is part of the brain's reward circuit. It releases dopamine and serotonin and helps control rewarding, motivational, and addiction behaviors. One study found that rats became addicted to electrically stimulating their nucleus accumbens. The rats preferred the stimulation over eating and drinking, and some starved themselves to continue pressing the lever. Another study found that surprising events activated the nucleus accumbens and hippocampus in humans, showing the nucleus accumbens's role in processing novel information and memory formation. Attempts to treat depression by stimulating the nucleus accumbens only provided short-term relief and did not effectively treat depression long-term.











![Drug addiction – unusually high levels of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens.Works CitedCrane, J., & Hannibal, J. (2009). Psychology: Course Companion. Oxford: Oxford University Press.Dubuc, B. (2002, September). The Pleasure Centres Affected by Drugs. In The Brain from Top to Bottom. Retrieved from http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/Fernandez-Espejo, E. (2000, May). How does the Nucleus Accumbens Function? In Pub Med [biomedical data base]. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedHarmon, K. (2010, February 24). Surprised? How the Brain Records Memories of the Unexpected. In The Scientific American. Retrieved from http://www.scientificamerican.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleusaccumbens-100406125853-phpapp01/85/Nucleus-Accumbens-14-320.jpg)

