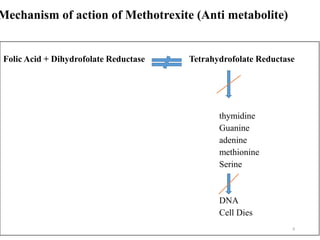
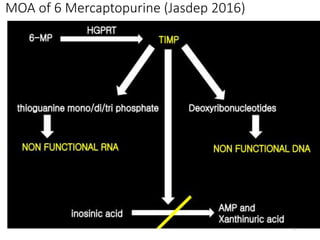
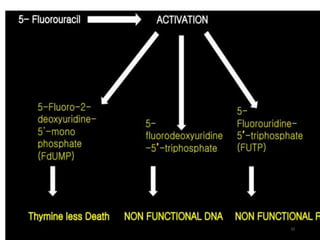
Chemotherapeutic enzymes target the nucleotide biosynthetic pathway by inhibiting enzymes involved in DNA and RNA synthesis. Nucleotides are essential for cell survival and proliferation, and tumor cells have high concentrations of nucleotide metabolites. Chemotherapeutic drugs work by blocking DNA synthesis, causing lethal events in rapidly dividing cancer cells and arresting tumor progression. Specifically, antimetabolites like methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine interfere with folate and purine metabolism, halting cancer cell division. By targeting nucleotide biosynthesis, chemotherapy aims to stop uncontrolled tumor cell growth.