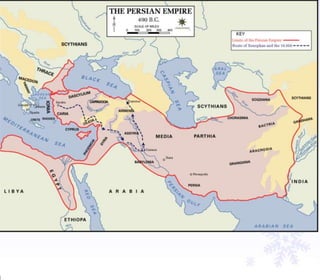
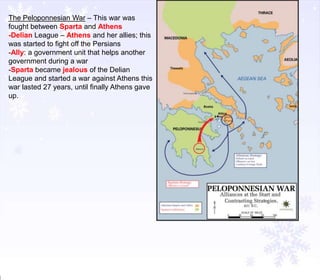
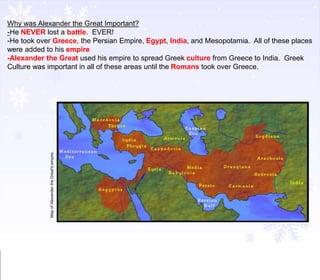
The document provides instructions for students to take notes on a lesson about Alexander the Great, including defining key terms, answering thought questions, writing objectives in their agenda, and completing a mapping activity of Alexander the Great's empire as homework. It also includes background information on empires, the Persian Wars, and leaders like Darius I and key battles between Greece and Persia.