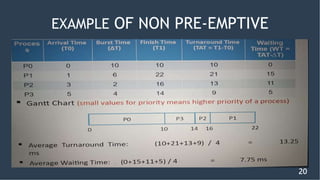
This document discusses non-preemptive scheduling algorithms. It outlines different types of non-preemptive scheduling including first come first serve (FCFS), shortest job first (SJF), and non-preemptive priority scheduling. For each algorithm, it describes the selection area, decision mode, implementation, examples, and advantages/disadvantages. It also compares preemptive versus non-preemptive scheduling and concludes that non-preemptive scheduling offers lower overhead and simplicity making it suitable for environments with timing requirements or resource limitations.